B - 1 + 6 = 7 Editorial by evima
Solution 1Without loss of generality, we assume \(A_{1} \leq A_{2}\).
The answer to this problem is the same as the number of pairs of positive integers \((X_{1}, X_{2})\) that satisfy the following conditions:
- \(10 ^ {A_{1} - 1} \leq X_{1} < 10 ^ {A_{1}}\)
- \(10 ^ {A_{2} - 1} \leq X_{2} < 10 ^ {A_{2}}\)
- \(10 ^ {A_{3} - 1} \leq X_{1} + X_{2} < 10 ^ {A_{3}}\)
The sum of a positive number \(X_{1}\) with \(A_{1}\) digits and a positive number \(X_{2}\) with \(A_{2}\) digits will be a positive number with either \(A_{2}\) digits or \(A_{2} + 1\) digits, so if \(A_{3}\) is neither \(A_{2}\) nor \(A_{2} + 1\), the answer is \(0\).
Thus, we only need to consider the two cases where \(A_{3} = A_{2}\) or \(A_{3} = A_{2} + 1\).
If \(A_{3} = A_{2}\)
Since \(X_{1}\) is positive, the conditions can be rewritten as follows:
- \(10 ^ {A_{1} - 1} \leq X_{1} < 10 ^ {A_{1}}\)
- \(10 ^ {A_{2} - 1} \leq X_{2} < 10 ^ {A_{2}} - X_{1}\)
By fixing \(X_{1}\), the answer can be expressed by the following formula:
\[\sum_{X_{1} = 10^{A_{1} - 1}}^{10^{A_{1}} - 1} \max(0, 9 \times 10^{A_{2} - 1} - X_{1})\]
If \(A_{1} = A_{2}\)

The idea is to find the area of the lower left part of the above figure.
\[\sum_{X_{1} = 10^{A_{1} - 1}}^{10^{A_{1}} - 1} \max(0, 9 \times 10^{A_{2} - 1} - X_{1}) = \sum_{X_{1} = 10^{A_{2} - 1}}^{9 \times 10^{A_{2} - 1}} (9 \times 10^{A_{2} - 1} - X_{1}) = \dfrac{(8 \times 10^{A_{1} - 1})(8 \times 10^{A_{1} - 1} + 1)}{2}\]
If \(A_{1} < A_{2}\)
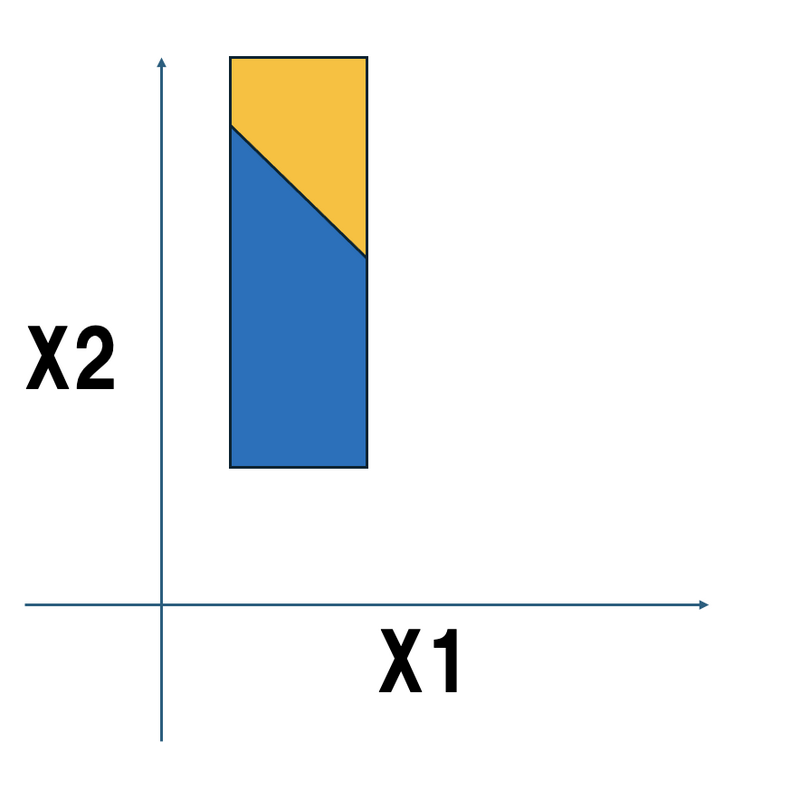
The idea is to find the area of the lower left part of the above figure (not to scale).
\[\sum_{X_{1} = 10^{A_{1} - 1}}^{10^{A_{1}} - 1} \max(0, 9 \times 10^{A_{2} - 1} - X_{1}) = \sum_{X_{1} = 10^{A_{1} - 1}}^{10^{A_{1}} - 1} (9 \times 10^{A_{2} - 1} - X_{1}) = 9 \times 10^{A_{1} - 1} \left(9 \times 10^{A_{2} - 1} - \dfrac{10^{A_{1} - 1} + 10^{A_{1}} - 1}{2}\right)\]
These two values modulo \(998244353\) can be calculated in \(O(\log(A_{2}))\) time.
If \(A_{3} = A_{2} + 1\)
We can find the count when \(A_{3} = A_{2}\) and subtract that value from \(81 \times 10^{A_{1} + A_{2} - 2}\).
Therefore, the answer can be found in \(O(\log(A_{2}))\) time per test case, for a total time complexity of \(O(T \log(A_{2}))\).
Python implementation example:
MOD = 998244353
# return 10 ^ a
def powten(a):
return pow(10, a, MOD)
def solve(a1, a2, a3):
# a1 <= a2
if a1 > a2:
a1, a2 = a2, a1
# impossible
if a2 != a3 and a2 + 1 != a3:
return 0
# a2 == a3
if a2 != a3:
return (81 * powten(a1 + a2 - 2) - solve(a1, a2, a2)) % MOD
# calc
if a1 == a2:
return 4 * powten(a1 - 1) * (8 * powten(a1 - 1) + 1) % MOD
else:
ans = (9 * powten(a2 - 1) - (11 * powten(a1 - 1) - 1) * pow(2, -1, MOD)) % MOD
ans = ans * 9 * powten(a1 - 1) % MOD
return ans
# I/O
T = int(input())
for _ in range(T):
a1, a2, a3 = map(int, input().split())
print(solve(a1, a2, a3))
posted:
last update: