 /
/ 
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 1600 点
問題文
平衡ネットワーク とは、左から右へと延びる N 本のケーブルと、それぞれ 2 本のケーブルを繋ぐ M 個の 平衡器 からなる抽象機械です。 ケーブルには上から順に 1 から N までの番号が、平衡器には左から順に 1 から M までの番号がついています。平衡器 i はケーブル x_i, y_i (x_i < y_i) を繋ぎます。
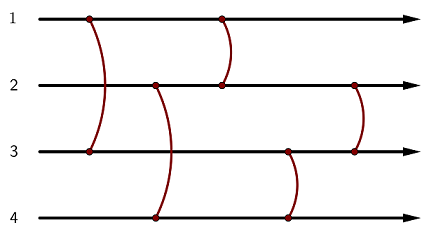
各平衡器は 上 または 下 のいずれかの状態に設定します。
1 枚のコインが、いずれかのケーブルに沿ってどの平衡器よりも左に位置する点から右へと流れ始めるとします。 これから、このコインはすべての平衡器のもとをちょうど一度ずつ通過します。 コインが平衡器 i の位置に来たとき、次のことが起こります。
- コインがケーブル x_i に沿って流れており、かつ平衡器 i の状態が下であるなら、コインはケーブル y_i に移ってから再び右へと流れる。
- コインがケーブル y_i に沿って流れており、かつ平衡器 i の状態が上であるなら、コインはケーブル x_i に移ってから再び右へと流れる。
- 上記のいずれでもないなら、コインが別のケーブルに移ることはない。
平衡ネットワークの状態とは、すべての平衡器の状態を表す長さ M の文字列です。
この文字列の i 文字目は、平衡器 i の状態が上なら ^、下なら v です。
平衡ネットワークの状態が 均一的 であるとは、あるケーブル w が存在して、コインがどのケーブルから流れ始めたとしてもケーブル w に行き着き、これに沿って永遠に流れることをいいます。それ以外の場合、平衡ネットワークの状態は 非均一的 であるといわれます。
整数 T (1 \le T \le 2) が与えられます。次の問いに答えてください。
- T = 1 の場合は、このネットワークの均一的な状態をいずれかひとつ求めるか、そのような状態が存在しないことを検出せよ。
- T = 2 の場合は、このネットワークの非均一的な状態をいずれかひとつ求めるか、そのような状態が存在しないことを検出せよ。
なお、いずれか 1 種類の問いにのみ正しく答えると部分点が得られます。
制約
- 2 \leq N \leq 50000
- 1 \leq M \leq 100000
- 1 \leq T \leq 2
- 1 \leq x_i < y_i \leq N
- 入力中のすべての値は整数である。
部分点
- T = 1 であるようなテストケースすべてに正解すると、800 点が与えられる。
- T = 2 であるようなテストケースすべてに正解すると、800 点が与えられる。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M T x_1 y_1 x_2 y_2 : x_M y_M
出力
T = 1 の場合は与えられたネットワークの均一的な状態をいずれかひとつ出力し、T = 2 の場合は非均一的な状態をいずれかひとつ出力せよ。ただし、そのような状態が存在しないなら -1 と出力せよ。
入力例 1
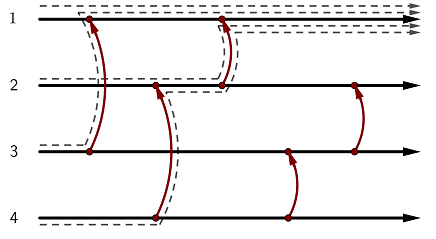
4 5 1 1 3 2 4 1 2 3 4 2 3
出力例 1
^^^^^
どのケーブルから流れ始めてもコインはケーブル 1 に行き着くため、この状態は均一的です。
入力例 2
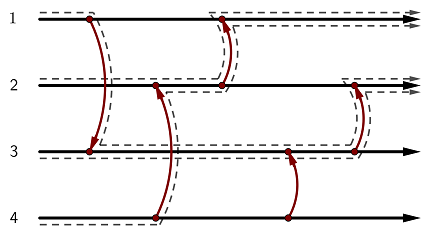
4 5 2 1 3 2 4 1 2 3 4 2 3
出力例 2
v^^^^
流れ始めるケーブル次第で、コインはケーブル 1 にもケーブル 2 にも行き着くことがあるため、この状態は非均一的です。
入力例 3
3 1 1 1 2
出力例 3
-1
均一的な状態が存在しません。
入力例 4
2 1 2 1 2
出力例 4
-1
非均一的な状態が存在しません。
Score : 1600 points
Problem Statement
A balancing network is an abstract device built up of N wires, thought of as running from left to right, and M balancers that connect pairs of wires. The wires are numbered from 1 to N from top to bottom, and the balancers are numbered from 1 to M from left to right. Balancer i connects wires x_i and y_i (x_i < y_i).

Each balancer must be in one of two states: up or down.
Consider a token that starts moving to the right along some wire at a point to the left of all balancers. During the process, the token passes through each balancer exactly once. Whenever the token encounters balancer i, the following happens:
- If the token is moving along wire x_i and balancer i is in the down state, the token moves down to wire y_i and continues moving to the right.
- If the token is moving along wire y_i and balancer i is in the up state, the token moves up to wire x_i and continues moving to the right.
- Otherwise, the token doesn't change the wire it's moving along.
Let a state of the balancing network be a string of length M, describing the states of all balancers.
The i-th character is ^ if balancer i is in the up state, and v if balancer i is in the down state.
A state of the balancing network is called uniforming if a wire w exists such that, regardless of the starting wire, the token will always end up at wire w and run to infinity along it. Any other state is called non-uniforming.
You are given an integer T (1 \le T \le 2). Answer the following question:
- If T = 1, find any uniforming state of the network or determine that it doesn't exist.
- If T = 2, find any non-uniforming state of the network or determine that it doesn't exist.
Note that if you answer just one kind of questions correctly, you can get partial score.
Constraints
- 2 \leq N \leq 50000
- 1 \leq M \leq 100000
- 1 \leq T \leq 2
- 1 \leq x_i < y_i \leq N
- All input values are integers.
Partial Score
- 800 points will be awarded for passing the testset satisfying T = 1.
- 800 points will be awarded for passing the testset satisfying T = 2.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M T x_1 y_1 x_2 y_2 : x_M y_M
Output
Print any uniforming state of the given network if T = 1, or any non-uniforming state if T = 2. If the required state doesn't exist, output -1.
Sample Input 1
4 5 1 1 3 2 4 1 2 3 4 2 3
Sample Output 1
^^^^^
This state is uniforming: regardless of the starting wire, the token ends up at wire 1.

Sample Input 2
4 5 2 1 3 2 4 1 2 3 4 2 3
Sample Output 2
v^^^^
This state is non-uniforming: depending on the starting wire, the token might end up at wire 1 or wire 2.

Sample Input 3
3 1 1 1 2
Sample Output 3
-1
A uniforming state doesn't exist.
Sample Input 4
2 1 2 1 2
Sample Output 4
-1
A non-uniforming state doesn't exist.