 /
/ 
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
Score: 100 points
Problem Statement
You are given a graph G consisting of N vertices numbered 1, 2, \ldots, N. Initially, G has no edges.
You will add M undirected edges to G. The final shape of the graph is predetermined, and the i-th edge to be added (1 ≤ i ≤ M) connects vertices u_i and v_i. We will refer to this as edge i.
It is guaranteed that the resulting graph will be simple.
Determine if there exists a permutation (P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_M) of (1, 2, \ldots, M) that satisfies the following conditions, and if such a permutation exists, show an example.
Conditions
You must be able to add all M edges to G by following this procedure:
- For i = 1, 2, \dots, M, repeat the following:
- If there is already a cycle in G containing either vertex u_{P_i} or vertex v_{P_i}, the condition is not satisfied, and the procedure ends.
- Add edge P_i (the undirected edge connecting u_{P_i} and v_{P_i}) to G.
You are given T test cases; solve each of them.
What is a cycle?
A cycle in G is defined as a sequence of vertices (v_0, \dots, v_{L - 1}) and a sequence of edges (e_0, \dots, e_{L - 1}) that satisfy the following conditions:
- L \ge 1
- i \neq j \implies v_i \neq v_j, e_i \neq e_j
- For 0 \le i \le L - 2, edge e_i connects vertices v_i and v_{i+1}
- Edge e_{L-1} connects vertices v_{L-1} and v_0
What does it mean for a graph to be simple?
A graph G is simple if it contains no self-loops or multiple edges.Constraints
- All input values are integers.
- 1 \le T \le 2000
- For each test case:
- 2 \le N \le 4000
- 1 \le M \le 4000
- 1 \le u_i, v_i \le N\ (1 ≤ i ≤ M)
- The graph formed by adding all given edges is simple.
- The sum of N over all test cases is at most 4000.
- The sum of M over all test cases is at most 4000.
Subtasks
30 points will be awarded for passing the test set satisfying:
- T \le 50
- For each test case:
- N \le 100
- M \le 100
- The sum of N over all test cases is at most 100.
- The sum of M over all test cases is at most 100.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
T
\text{case}_1
\text{case}_2
\vdots
\text{case}_T
Here, \text{case}_i\ (1 ≤ i ≤ T) represents the i-th test case. Each test case is given in the following format:
N M u_1 v_1 u_2 v_2 \vdots u_M v_M
Output
For each test case, if a permutation (P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_M) satisfying the conditions exists, output such a P separated by spaces. If no such permutation exists, output -1.
Sample Input 1
1 4 4 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 2
Sample Output 1
2 4 1 3
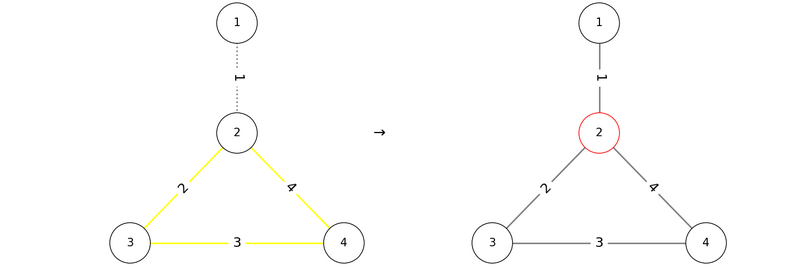
The given graph has the following shape:
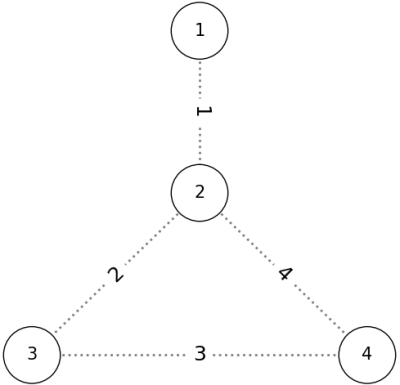
If we add the edges in the order P = (1, 2, 3, 4), the conditions are satisfied as shown below:
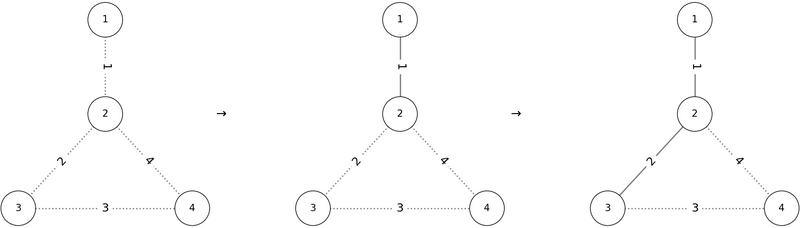
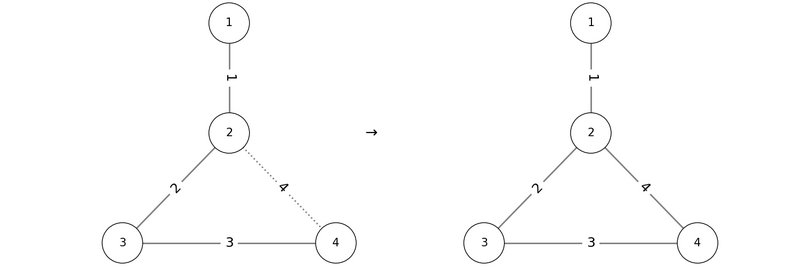
Thus, 1 2 3 4 is one valid output.
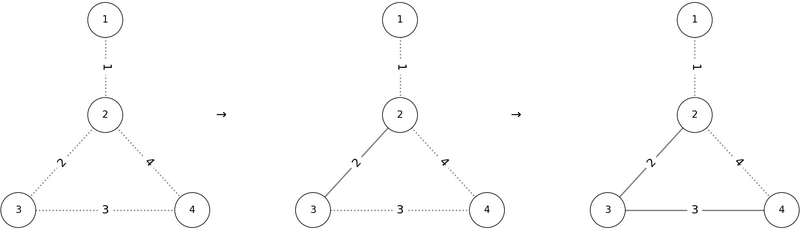
However, if we add edges in the order P = (2, 3, 4, 1), a cycle containing vertex 2 is created before edge 1 can be added, so the conditions are not satisfied.
Other valid outputs include P = (1, 4, 3, 2) or P = (2, 4, 1, 3).
Sample Input 2
4 4 5 1 2 2 3 3 4 3 1 1 4 5 3 1 2 2 3 3 4 9 10 3 5 1 8 5 8 4 9 6 7 7 9 1 2 1 4 2 4 4 6 8 10 1 4 3 8 2 5 3 4 1 5 5 8 2 8 5 7 4 5 3 7
Sample Output 2
-1 3 2 1 4 10 2 8 7 9 6 5 3 1 -1
If no valid P exists, output -1. Note that the graph is not necessarily connected.
配点 : 100 点
問題文
N 頂点からなるグラフ G があり、頂点には 1, 2, \ldots, N の番号がついています。はじめ、G には辺がありません。
これから、G に M 本の無向辺を追加します。追加後のグラフの形は決まっており、追加する辺のうち i 番目の辺 (1 ≤ i ≤ M) は頂点 u_i と頂点 v_i を結ぶ辺です。これを辺 i と呼ぶことにします。
追加後のグラフは単純であることが保証されます。
(1, 2, \ldots, M) の順列 (P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_M) であって以下の条件を満たすようなものが存在するかどうか判定し、存在する場合はその一例を示してください。
条件
以下の手順を行って、G に M 本の辺をすべて追加することができる。
- i = 1, 2, \dots, M の順に以下を繰り返す:
- G に頂点 u_{P_i} または頂点 v_{P_i} を含むサイクルが存在するとき、条件は満たされないものとして手順を終了する。
- G に辺 P_i(頂点 u_{P_i} と頂点 v_{P_i} を結ぶ無向辺)を追加する。
T 個のテストケースが与えられるので、それぞれについて解いて下さい。
サイクルとは?
G におけるサイクルとは、頂点の列 (v_0, \dots, v_{L - 1}) と 辺の列 (e_0, \dots, e_{L - 1}) であって以下の条件を満たすもののことを言います。
- L \ge 1
- i \neq j \implies v_i \neq v_j, e_i \neq e_j
- 0 \le i \le L - 2 に対して、辺 e_i は頂点 v_i と頂点 v_{i+1} を結ぶ
- 辺 e_{L-1} は頂点 v_{L-1} と頂点 v_0 を結ぶ
グラフが単純とは?
グラフ G が単純であるとは、G が自己ループ及び多重辺を含まない事を言います。制約
- 入力はすべて整数
- 1 \le T \le 2000
- 各テストケースについて:
- 2 \le N \le 4000
- 1 \le M \le 4000
- 1 \le u_i, v_i \le N\ (1 ≤ i ≤ M)
- 与えられるすべての辺を追加したグラフは単純
- 各入力ファイルについて、N, M の総和はそれぞれ 4000 を超えない
部分点
以下の制約を満たすデータセットに正解した場合は 30 点が与えられる。
- T \le 50
- 各テストケースについて:
- N \le 100
- M \le 100
- 各入力ファイルについて、N, M の総和はそれぞれ 100 を超えない
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
T
\text{case}_1
\text{case}_2
\vdots
\text{case}_T
ここで、\text{case}_i\ (1 ≤ i ≤ T) は i 番目のテストケースを表す。各テストケースは以下の形式で与えられる。
N M u_1 v_1 u_2 v_2 \vdots u_M v_M
出力
各テストケースについて、条件を満たす順列 (P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_M) が存在する場合は、そのような P を空白区切りで出力せよ。存在しない場合は、-1 を出力せよ。
入力例 1
1 4 4 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 2
出力例 1
2 4 1 3
与えられたグラフは以下の図のような形をしています。

これに対し、P = (1, 2, 3, 4) の順で辺を追加すると、以下の図のように条件を満たします。


したがって、1 2 3 4 は正しい出力の 1 つです。
しかし、P = (2, 3, 4, 1) の順で辺を追加すると、辺 1 を追加する際に頂点 2 を含むサイクルが存在するため、条件を満たしません。


他にも、P = (1, 4, 3, 2) や P = (2, 4, 1, 3) などが条件を満たします。
入力例 2
4 4 5 1 2 2 3 3 4 3 1 1 4 5 3 1 2 2 3 3 4 9 10 3 5 1 8 5 8 4 9 6 7 7 9 1 2 1 4 2 4 4 6 8 10 1 4 3 8 2 5 3 4 1 5 5 8 2 8 5 7 4 5 3 7
出力例 2
-1 3 2 1 4 10 2 8 7 9 6 5 3 1 -1
条件を満たす P が存在しない場合、-1 を出力して下さい。また、グラフは連結とは限らないことに注意してください。