 /
/ 
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 400 点
問題文
N 頂点 M 辺の(単純とは限らない)有向グラフがあり、頂点は頂点 1, 2, \ldots, N と番号付けられています。
i 番目 (1\leq i\leq M) の辺は頂点 U_i から頂点 V_i へ向かう辺で、コストは C_i です。
また、各頂点の出次数は 4 以下です。
次の条件をみたす頂点 v (1\leq v\leq N) をすべて求めてください。
頂点 1 から頂点 v への経路であって、次の条件をともにみたすものが存在する。
- ちょうど L 回辺を通る。このとき、同じ辺を複数回通っても良いが、通るたびに回数にカウントされる。
- 通った辺のコストの総和が S 以上 T 以下である。(同じ辺を複数回通った場合、通るたびに総和に加算されるものとする。)
出次数 とは
頂点 u の出次数は、頂点 u から出て行く辺の数を指します。辺の向かう先が同じ頂点であるような辺であっても重ねて数えられます。制約
- 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq M\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq L \leq 10
- 1\leq S\leq T \leq 10^9
- 1\leq U_i,V_i\leq N
- 1\leq C_i\leq 10^8
- 各頂点の出次数は高々 4 である。
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M L S T U_1 V_1 C_1 U_2 V_2 C_2 \vdots U_M V_M C_M
出力
条件をみたす頂点を 昇順に 空白区切りで出力せよ。
条件をみたす頂点が存在しない場合は空行を出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 8 3 80 100 1 2 20 1 3 70 2 1 30 2 5 10 3 2 10 3 4 30 3 5 20 5 1 70
出力例 1
1 5
与えられるグラフは下図左のようになっています。各辺のコストはその辺の始点のそばに示されています。
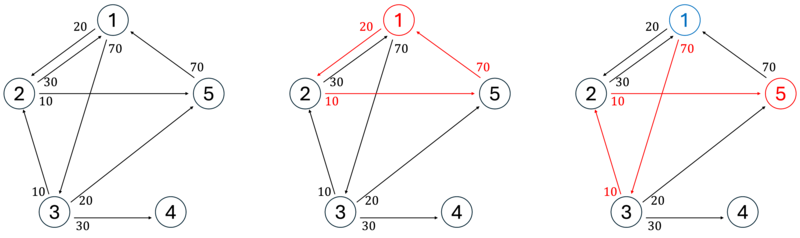
このとき、以下のようになります。
- 頂点 1 から頂点 1 への経路について、頂点 1 \to 頂点 2 \to 頂点 5 \to 頂点 1 (上図中央)を考えると、これはちょうど 3 本の辺を通り、通る辺のコストの総和は 20+10+70=100 であるため、条件をみたしています。
- 頂点 1 から頂点 2 への経路であって、条件をみたすような経路は存在しません。ちょうど 3 本の辺を通るような経路としては、頂点 1 \to 頂点 2 \to 頂点 1 \to 頂点 2 が存在しますが、この経路において通る辺のコストの総和は 20+30+20=70 であり特に 80 より小さいため、条件をみたしていません。
- 頂点 1 から頂点 3 への経路であって、条件をみたすような経路は存在しません。ちょうど 3 本の辺を通るような経路としては、頂点 1 \to 頂点 2 \to 頂点 1 \to 頂点 3 が存在しますが、この経路において通る辺のコストの総和は 20+30+70=120 であり特に 100 より大きいため、条件をみたしていません。
- 頂点 1 から頂点 4 への経路であって、条件をみたすような経路は存在しません。
- 頂点 1 から頂点 5 への経路について、頂点 1 \to 頂点 3 \to 頂点 2 \to 頂点 5 (上図右)を考えると、これはちょうど 3 本の辺を通り、通る辺のコストの総和は 70+10+10=90 であるため、条件をみたしています。
よって、1, 5 をこの順に出力します。条件をみたす頂点を昇順に出力する必要があることに注意してください。
入力例 2
10 1 1 1 100 2 3 1
出力例 2
条件をみたす頂点が存在しない場合は空行を出力してください。
入力例 3
2 5 3 1 100 1 1 1 2 2 100 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 100
出力例 3
1 2
グラフは自己ループや多重辺を含む可能性があります。
なお、このテストケースにおけるグラフの頂点 1,2 からの出次数はそれぞれ 4,1 です。
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
There is a directed graph (not necessarily simple) with N vertices and M edges, where the vertices are numbered as vertices 1, 2, \ldots, N.
The i-th (1\leq i\leq M) edge goes from vertex U_i to vertex V_i with cost C_i.
Additionally, the out-degree of each vertex is at most 4.
Find all vertices v (1\leq v\leq N) that satisfy the following condition:
There exists a path from vertex 1 to vertex v that satisfies both of the following conditions:
- It traverses exactly L edges. If the same edge is traversed multiple times, each traversal is counted.
- The sum of the costs of the traversed edges is at least S and at most T. (If the same edge is traversed multiple times, the cost is added to the sum each time.)
What is out-degree?
The out-degree of vertex u refers to the number of edges going out from vertex u. Even if multiple edges go to the same vertex, they are counted separately.Constraints
- 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq M\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq L \leq 10
- 1\leq S\leq T \leq 10^9
- 1\leq U_i,V_i\leq N
- 1\leq C_i\leq 10^8
- The out-degree of each vertex is at most 4.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M L S T U_1 V_1 C_1 U_2 V_2 C_2 \vdots U_M V_M C_M
Output
Print the vertices that satisfy the condition in ascending order, separated by spaces.
If there are no vertices that satisfy the condition, print an empty line.
Sample Input 1
5 8 3 80 100 1 2 20 1 3 70 2 1 30 2 5 10 3 2 10 3 4 30 3 5 20 5 1 70
Sample Output 1
1 5
The given graph is as shown in the left figure below. The cost of each edge is shown near the starting vertex of that edge.

Here, the following holds:
- For the path from vertex 1 to vertex 1, consider vertex 1 \to vertex 2 \to vertex 5 \to vertex 1 (center of the figure above). This traverses exactly three edges, and the sum of the costs of the traversed edges is 20+10+70=100, so it satisfies the condition.
- There is no path from vertex 1 to vertex 2 that satisfies the condition. One path that traverses exactly three edges is vertex 1 \to vertex 2 \to vertex 1 \to vertex 2, but the sum of the costs of the edges traversed in this path is 20+30+20=70, which is less than 80, so it does not satisfy the condition.
- There is no path from vertex 1 to vertex 3 that satisfies the condition. One path that traverses exactly three edges is vertex 1 \to vertex 2 \to vertex 1 \to vertex 3, but the sum of the costs of the edges traversed in this path is 20+30+70=120, which is greater than 100, so it does not satisfy the condition.
- There is no path from vertex 1 to vertex 4 that satisfies the condition.
- For the path from vertex 1 to vertex 5, consider vertex 1 \to vertex 3 \to vertex 2 \to vertex 5 (right of the figure above). This traverses exactly three edges, and the sum of the costs of the traversed edges is 70+10+10=90, so it satisfies the condition.
Therefore, print 1, 5 in this order. Note that you need to print those vertices that satisfy the condition in ascending order.
Sample Input 2
10 1 1 1 100 2 3 1
Sample Output 2
If there are no vertices that satisfy the condition, print an empty line.
Sample Input 3
2 5 3 1 100 1 1 1 2 2 100 1 2 1 1 2 1 1 2 100
Sample Output 3
1 2
The graph may contain self-loops and multiple edges.
In this test case, the out-degrees from vertices 1 and 2 are 4 and 1, respectively.