 /
/ 
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 475 点
問題文
N 頂点 M 辺の単純連結無向グラフ G が与えられます。
G の頂点は頂点 1, 頂点 2, \ldots, 頂点 N と番号付けられており、
i (1\leq i\leq M) 本目の辺は頂点 U_i と頂点 V_i を結んでいます。
G における頂点 X から頂点 Y への単純パスのうち辞書順最小のものを求めてください。
すなわち、以下の条件をみたす整数列 P=(P_1,P_2,\ldots,P_{\lvert P\rvert}) の中で辞書順最小のものを求めてください。
- 1\leq P_i\leq N
- i\neq j ならば P_i\neq P_j
- P_1=X かつ P_{\lvert P\rvert}=Y
- 1\leq i\leq \lvert P\rvert-1 について、頂点 P_i と頂点 P_{i+1} を結ぶ辺が存在する。
なお、本問題の制約下で条件をみたすようなものが必ず存在することが証明できます。
T 個のテストケースが与えられるので、それぞれについて答えを求めてください。
整数列の辞書順 とは
整数列 S=(S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_{\lvert S\rvert}) が整数列 T=(T_1,T_2,\ldots,T_{\lvert T\rvert}) より辞書順で小さいとは、下記の 1. と 2. のどちらかが成り立つことを言います。 ここで、\lvert S\rvert, \lvert T\rvert はそれぞれ S,T の長さを表します。- \lvert S\rvert<\lvert T\rvert かつ (S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_{\lvert S\rvert})=(T_1,T_2,\ldots,T_{\lvert S\rvert})。
- ある 1\leq i\leq \min(\lvert S\rvert,\lvert T\rvert) が存在して (S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_{i-1})=(T_1,T_2,\ldots,T_{i-1}) かつ S_i< T_i。
制約
- 1\leq T\leq 500
- 2\leq N\leq 1000
- N-1\leq M\leq \min\left( \frac{N(N-1)}{2},5\times 10^4\right)
- 1\leq X,Y \leq N
- X\neq Y
- 1\leq U_i<V_i \leq N
- i\neq j ならば (U_i,V_i)\neq (U_j,V_j)
- 与えられるグラフは連結である。
- 1 つの入力における N の総和は 1000 以下である。
- 1 つの入力における M の総和は 5\times 10^4 以下である。
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
T
\mathrm{case}_1
\mathrm{case}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{case}_T
\mathrm{case}_i は i 番目のテストケースを表す。 各テストケースは以下の形式で与えられる。
N M X Y U_1 V_1 U_2 V_2 \vdots U_M V_M
出力
T 行出力せよ。
i 行目 (1\leq i\leq T) には、i 個目のテストケースの答えとなる単純パス上の頂点番号を、順に空白区切りで出力せよ。
すなわち i 個目のテストケースに対する答えが P=(P_1,P_2,\ldots,P_{\lvert P\rvert}) であるとき、
P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_{\lvert P\rvert} を i 行目にこの順に空白区切りで出力せよ。
入力例 1
2 6 10 3 5 1 2 1 3 1 5 1 6 2 4 2 5 2 6 3 4 3 5 5 6 3 2 3 2 1 3 2 3
出力例 1
3 1 2 5 3 2
1 つめのテストケースについて、グラフ G は次のようになっています。
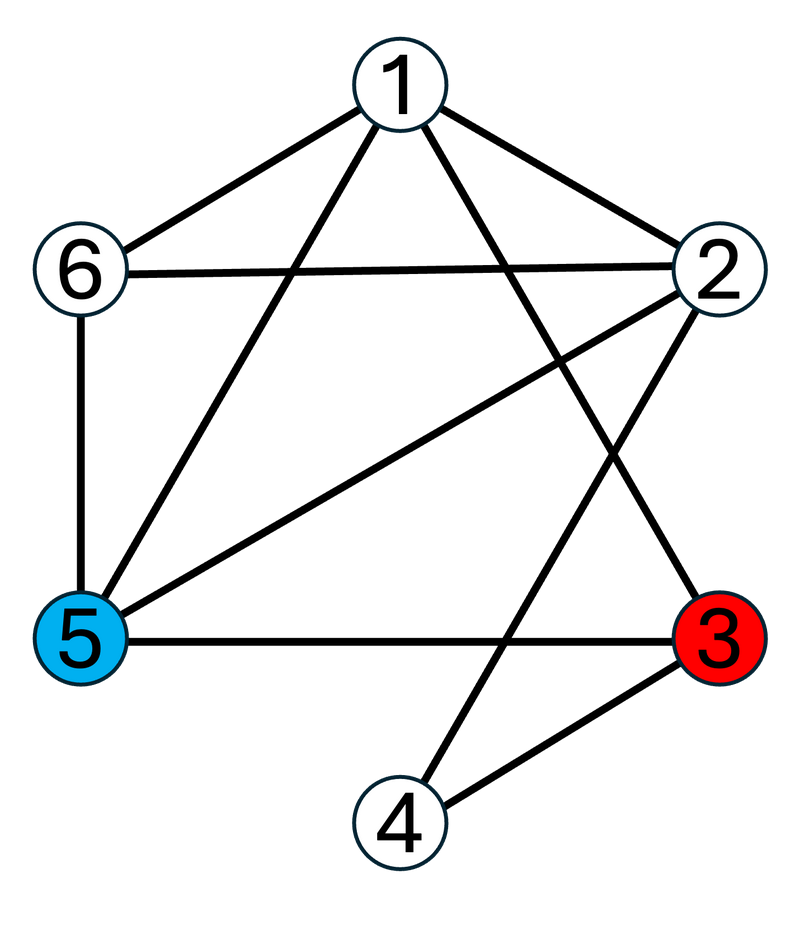
G 上の頂点 3 から頂点 5 への単純パスを辞書順に列挙すると、次のとおりになります。
- (3,1,2,5)
- (3,1,2,6,5)
- (3,1,5)
- (3,1,6,2,5)
- (3,1,6,5)
- (3,4,2,1,5)
- (3,4,2,1,6,5)
- (3,4,2,5)
- (3,4,2,6,1,5)
- (3,4,2,6,5)
- (3,5)
このうち、辞書順最小のものは (3,1,2,5) であるため、1 行目には 3,1,2,5 を空白区切りで出力します。
2 つめのテストケースにおいては、(3,2) が頂点 3 から頂点 2 への唯一の単純パスです。
Score : 475 points
Problem Statement
You are given a simple connected undirected graph G with N vertices and M edges.
The vertices of G are numbered vertex 1, vertex 2, \ldots, vertex N, and
the i-th (1\leq i\leq M) edge connects vertices U_i and V_i.
Find the lexicographically smallest simple path from vertex X to vertex Y in G.
That is, find the lexicographically smallest among the integer sequences P=(P_1,P_2,\ldots,P_{\lvert P\rvert}) that satisfy the following conditions:
- 1\leq P_i\leq N
- If i\neq j, then P_i\neq P_j.
- P_1=X and P_{\lvert P\rvert}=Y.
- For 1\leq i\leq \lvert P\rvert-1, there exists an edge connecting vertices P_i and P_{i+1}.
One can prove that such a path always exists under the constraints of this problem.
You are given T test cases, so find the answer for each.
Lexicographic order on integer sequences
An integer sequence S=(S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_{\lvert S\rvert}) is lexicographically smaller than an integer sequence T=(T_1,T_2,\ldots,T_{\lvert T\rvert}) if either of the following 1. or 2. holds. Here, \lvert S\rvert and \lvert T\rvert represent the lengths of S and T, respectively.- \lvert S\rvert<\lvert T\rvert and (S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_{\lvert S\rvert})=(T_1,T_2,\ldots,T_{\lvert S\rvert}).
- There exists some 1\leq i\leq \min(\lvert S\rvert,\lvert T\rvert) such that (S_1,S_2,\ldots,S_{i-1})=(T_1,T_2,\ldots,T_{i-1}) and S_i< T_i.
Constraints
- 1\leq T\leq 500
- 2\leq N\leq 1000
- N-1\leq M\leq \min\left( \frac{N(N-1)}{2},5\times 10^4\right)
- 1\leq X,Y \leq N
- X\neq Y
- 1\leq U_i<V_i \leq N
- If i\neq j, then (U_i,V_i)\neq (U_j,V_j).
- The given graph is connected.
- The sum of N over all test cases in each input is at most 1000.
- The sum of M over all test cases in each input is at most 5\times 10^4.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
T
\mathrm{case}_1
\mathrm{case}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{case}_T
\mathrm{case}_i represents the i-th test case. Each test case is given in the following format:
N M X Y U_1 V_1 U_2 V_2 \vdots U_M V_M
Output
Output T lines.
The i-th line (1\leq i\leq T) should contain the vertex numbers on the simple path that is the answer to the i-th test case, in order, separated by spaces.
That is, when the answer to the i-th test case is P=(P_1,P_2,\ldots,P_{\lvert P\rvert}),
output P_1, P_2, \ldots, P_{\lvert P\rvert} on the i-th line in this order, separated by spaces.
Sample Input 1
2 6 10 3 5 1 2 1 3 1 5 1 6 2 4 2 5 2 6 3 4 3 5 5 6 3 2 3 2 1 3 2 3
Sample Output 1
3 1 2 5 3 2
For the first test case, graph G is as follows:

The simple paths from vertex 3 to vertex 5 on G, listed in lexicographic order, are as follows:
- (3,1,2,5)
- (3,1,2,6,5)
- (3,1,5)
- (3,1,6,2,5)
- (3,1,6,5)
- (3,4,2,1,5)
- (3,4,2,1,6,5)
- (3,4,2,5)
- (3,4,2,6,1,5)
- (3,4,2,6,5)
- (3,5)
Among these, the lexicographically smallest is (3,1,2,5), so output 3,1,2,5 separated by spaces on the first line.
For the second test case, (3,2) is the only simple path from vertex 3 to vertex 2.