実行時間制限: 2 sec / メモリ制限: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
長さ N の正整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) に対して,Q 回の操作を行います.1\leq q\leq Q に対して,q 回目の操作の情報は正整数 i_q, x_q (ただし 1\leq i_q\leq N)として与えられ,その内容は A_{i_q} に x_q を加算するというものです.
あなたの目標は,A の初期状態を適切に定めることで,どの時点においても(つまり,初期状態および各操作の直後においても)以下の条件が成り立つようにすることです.
- 0<A_1 < A_2 < \cdots < A_N が成り立つ.
この目標を達成するとき,A の初期状態における要素の総和として考えられる最小値を求めてください.
制約
- 2\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq Q\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq i_q\leq N
- 1\leq x_q\leq 10^5
- 入力される値はすべて整数.
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられます.
N Q i_1 x_1 \vdots i_Q x_Q
出力
目標を達成するとき,A の初期状態における要素の総和として考えられる最小値を出力してください.
入力例 1
4 2 1 2 2 3
出力例 1
22
初期状態の A が A=(1,4,8,9) であったとします.このとき,
- 1 回目の操作直後の A:A=(3,4,8,9)
- 2 回目の操作直後の A:A=(3,7,8,9)
となり,どの時点においても A は条件を満たしていることが確かめられます.
この場合,A の初期状態における要素の総和は \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^NA_i=1+4+8+9=22 です.
入力例 2
4 2 2 3 1 2
出力例 2
16
入力例 3
100000 1 1 100000
出力例 3
14999950000
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
You are given a sequence of positive integers A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) of length N, and you will perform Q operations on it. For 1\leq q\leq Q, the q-th operation is given as positive integers i_q, x_q (where 1\leq i_q\leq N), and it adds x_q to A_{i_q}.
Your goal is to appropriately determine the initial state of A so that the following condition holds at any point in time (that is, in the initial state and immediately after each operation).
- 0<A_1 < A_2 < \cdots < A_N holds.
When achieving this goal, find the minimum possible sum of elements in the initial state of A.
Constraints
- 2\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq Q\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq i_q\leq N
- 1\leq x_q\leq 10^5
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N Q i_1 x_1 \vdots i_Q x_Q
Output
Output the minimum possible sum of elements in the initial state of A when achieving the goal.
Sample Input 1
4 2 1 2 2 3
Sample Output 1
22
Suppose the initial state of A is A=(1,4,8,9). Then,
- A immediately after the 1-st operation: A=(3,4,8,9)
- A immediately after the 2-nd operation: A=(3,7,8,9)
and it can be verified that A satisfies the condition at any point in time.
In this case, the sum of elements in the initial state of A is \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^NA_i=1+4+8+9=22.
Sample Input 2
4 2 2 3 1 2
Sample Output 2
16
Sample Input 3
100000 1 1 100000
Sample Output 3
14999950000
実行時間制限: 3 sec / メモリ制限: 1024 MiB
配点 : 600 点
問題文
長さ N の整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) および,長さ M の整数列 B=(B_1,B_2,\ldots,B_M) が与えられます.ここで N は偶数です.
Q 個のクエリが与えられます.q 個目のクエリの情報は整数の 3 つ組 (t_q,i_q,x_q) として与えられ,その内容は以下の通りです.
- t_q=1 の場合:このとき 1\leq i_q\leq N である.このクエリでは A_{i_q} を x_q に変更する.
- t_q=2 の場合:このとき 1\leq i_q\leq M である.このクエリでは B_{i_q} を x_q に変更する.
クエリを処理するたびに,次の小問題の答を求めてください.
多重集合 X を X=\lbrace A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N\rbrace で初期化します. j=1,2,\ldots,M に対して次の操作を行います:
- X に B_j を挿入する.その後,X の中央値を X からひとつ削除する.
すべての操作が終了したときの X の要素の総和を求めてください.
中央値とは
N が偶数であるとき,N+1 個の要素を持つ多重集合 X の中央値とは,X の要素のうち昇順で \left(1+\frac{N}{2}\right) 番目の値です.
例えば X=\lbrace 1, 3, 4, 5, 8\rbrace の中央値は 4,X=\lbrace 2,2,2\rbrace の中央値は 2 です.
本問題において,中央値を考える多重集合は常に要素数が奇数であることに注意してください.
制約
- 1\leq N,M,Q\leq 2\times 10^5
- N は偶数.
- 1\leq A_i\leq 10^9
- 1\leq B_i\leq 10^9
- t_q\in\lbrace 1,2\rbrace
- t_q=1 ならば 1\leq i_q\leq N
- t_q=2 ならば 1\leq i_q\leq M
- 1\leq x_q\leq 10^9
- 入力される値はすべて整数.
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられます.
N M Q A_1 A_2 \cdots A_N B_1 B_2 \cdots B_M t_1 i_1 x_1 \vdots t_Q i_Q x_Q
出力
Q 行出力してください.q 行目には,q 個目のクエリを処理した直後における小問題の答を出力してください.
入力例 1
4 2 2 5 1 4 3 1 2 1 3 3 2 1 5
出力例 1
10 13
まず 1 個目のクエリによって,A=(5,1,3,3), B=(1,2) となります.この場合,小問題の操作は次のように進行します.
- X=\lbrace 5,1,3,3\rbrace=\lbrace 1,3,3,5\rbrace で初期化される.
- X に B_1=1 を挿入し,X=\lbrace 1,1,3,3,5\rbrace となる.その後,X の中央値をひとつ削除して X=\lbrace 1,1,3,5\rbrace となる.
- X に B_2=2 を挿入し,X=\lbrace 1,1,2,3,5\rbrace となる.その後,X の中央値をひとつ削除して X=\lbrace 1,1,3,5\rbrace となる.
すべての操作が終了した時点での X の要素の総和は 1+1+3+5=10 です.
次に 2 個目のクエリによって,A=(5,1,3,3), B=(5,2) となります.この場合,小問題の操作は次のように進行します.
- X=\lbrace 5,1,3,3\rbrace=\lbrace 1,3,3,5\rbrace で初期化される.
- X に B_1=5 を挿入し,X=\lbrace 1,3,3,5,5\rbrace となる.その後,X の中央値をひとつ削除して X=\lbrace 1,3,5,5\rbrace となる.
- X に B_2=2 を挿入し,X=\lbrace 1,2,3,5,5\rbrace となる.その後,X の中央値をひとつ削除して X=\lbrace 1,2,5,5\rbrace となる.
すべての操作が終了した時点での X の要素の総和は 1+2+5+5=13 です.
入力例 2
6 7 5 7 1 2 5 5 3 4 2 5 1 3 3 8 2 1 3 2 7 1 1 3 6 2 4 2 1 5 1
出力例 2
24 20 21 22 21
Score : 600 points
Problem Statement
You are given an integer sequence A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) of length N and an integer sequence B=(B_1,B_2,\ldots,B_M) of length M. Here, N is even.
You are given Q queries. The q-th query is given as a triple of integers (t_q,i_q,x_q), and it does the following.
- If t_q=1: In this case, 1\leq i_q\leq N. This query changes A_{i_q} to x_q.
- If t_q=2: In this case, 1\leq i_q\leq M. This query changes B_{i_q} to x_q.
After processing each query, find the answer to the following subproblem.
Initialize a multiset X with X=\lbrace A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N\rbrace. For j=1,2,\ldots,M, perform the following operation:
- Insert B_j into X. Then, remove one median of X from X.
Find the sum of elements in X when all operations are finished.
What is a median?
When N is even, the median of a multiset X with N+1 elements is the \left(1+\frac{N}{2}\right)-th value in ascending order among the elements of X.
For example, the median of X=\lbrace 1, 3, 4, 5, 8\rbrace is 4, and the median of X=\lbrace 2,2,2\rbrace is 2.
Note that in this problem, the multiset for which we consider the median always has an odd number of elements.
Constraints
- 1\leq N,M,Q\leq 2\times 10^5
- N is even.
- 1\leq A_i\leq 10^9
- 1\leq B_i\leq 10^9
- t_q\in\lbrace 1,2\rbrace
- If t_q=1, then 1\leq i_q\leq N
- If t_q=2, then 1\leq i_q\leq M
- 1\leq x_q\leq 10^9
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M Q A_1 A_2 \cdots A_N B_1 B_2 \cdots B_M t_1 i_1 x_1 \vdots t_Q i_Q x_Q
Output
Output Q lines. The q-th line should contain the answer to the subproblem immediately after processing the q-th query.
Sample Input 1
4 2 2 5 1 4 3 1 2 1 3 3 2 1 5
Sample Output 1
10 13
First, the 1-st query makes A=(5,1,3,3) and B=(1,2). In this case, the operations in the subproblem proceed as follows.
- Initialize X=\lbrace 5,1,3,3\rbrace=\lbrace 1,3,3,5\rbrace.
- Insert B_1=1 into X, making X=\lbrace 1,1,3,3,5\rbrace. Then, remove one median from X, making X=\lbrace 1,1,3,5\rbrace.
- Insert B_2=2 into X, making X=\lbrace 1,1,2,3,5\rbrace. Then, remove one median from X, making X=\lbrace 1,1,3,5\rbrace.
The sum of elements in X when all operations are finished is 1+1+3+5=10.
Next, the 2-nd query makes A=(5,1,3,3) and B=(5,2). In this case, the operations in the subproblem proceed as follows.
- Initialize X=\lbrace 5,1,3,3\rbrace=\lbrace 1,3,3,5\rbrace.
- Insert B_1=5 into X, making X=\lbrace 1,3,3,5,5\rbrace. Then, remove one median from X, making X=\lbrace 1,3,5,5\rbrace.
- Insert B_2=2 into X, making X=\lbrace 1,2,3,5,5\rbrace. Then, remove one median from X, making X=\lbrace 1,2,5,5\rbrace.
The sum of elements in X when all operations are finished is 1+2+5+5=13.
Sample Input 2
6 7 5 7 1 2 5 5 3 4 2 5 1 3 3 8 2 1 3 2 7 1 1 3 6 2 4 2 1 5 1
Sample Output 2
24 20 21 22 21
実行時間制限: 2 sec / メモリ制限: 1024 MiB
配点 : 700 点
問題文
N 種類のコインがあります.0\leq i\leq N-1 について (1+i) 種類目のコインは価値が 10^{i} で,あなたはこのコインを A_i 枚所持しています.
これらのコインを,M 人に配ることにしました.ただし,1 人あたりに配るコインの価値の総和が等しくなるようにします.また,配らないコインがあってもよいです.
1 人あたりに配るコインの価値の総和としてありうる最大値を求めてください.
T 個のテストケースが与えられるので,それぞれについて答えを求めてください.
制約
- 1\leq T\leq 10^5
- 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq M\leq 10^9
- 0\leq A_i\leq 10^9
- すべてのテストケースにわたる N の総和は 2\times 10^5 以下.
- 入力される値はすべて整数.
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられます.
T
\mathrm{case}_1
\mathrm{case}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{case}_T
各テストケースは以下の形式で与えられます.
N M
A_0 A_1 \ldots A_{N-1}
出力
1 人あたりに配るコインの価値の総和としてありうる最大値を出力してください.
入力例 1
5 3 1 123 456 789 3 1000 123 456 789 2 3 6 14 2 3 11 14 30 4 15 9 2 66 23 2 4 1 1 32 4 80 9 10 47 14 8 7 3 16 2 39 77 4 4 2 38 64 1 2
出力例 1
83583 0 42 50 19401302040124704218001124023
- 1 番目のテストケースについて,すべてのコインを 1 人に配ると,1 人あたりに配るコインの価値の総和は 123\times 10^0+456\times 10^1+789\times 10^2=83583 になります.
- 2 番目のテストケースについて,全員に 0 枚のコインを配るしかありません.
- 3 番目のテストケースについて,次のようにすることで 1 人あたりに配るコインの価値を 42 にすることができます.
- 1 番目の人に,価値 10^0 のコインを 2 枚,価値 10^1 のコインを 4 枚配る.
- 2 番目の人に,価値 10^0 のコインを 2 枚,価値 10^1 のコインを 4 枚配る.
- 3 番目の人に,価値 10^0 のコインを 2 枚,価値 10^1 のコインを 4 枚配る.
- 4 番目のテストケースについて,次のようにすることで 1 人あたりに配るコインの価値を 50 にすることができます.
- 1 番目の人に,価値 10^0 のコインを 0 枚,価値 10^1 のコインを 5 枚配る.
- 2 番目の人に,価値 10^0 のコインを 0 枚,価値 10^1 のコインを 5 枚配る.
- 3 番目の人に,価値 10^0 のコインを 10 枚,価値 10^1 のコインを 4 枚配る.
Score : 700 points
Problem Statement
There are N types of coins. For 0\leq i\leq N-1, the (1+i)-th type of coin has a value of 10^{i}, and you possess A_i of these coins.
You have decided to distribute these coins to M people. However, the total value of coins distributed to each person must be equal. It is allowed to have coins that are not distributed.
Find the maximum possible total value of coins distributed to each person.
You are given T test cases; solve each of them.
Constraints
- 1\leq T\leq 10^5
- 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq M\leq 10^9
- 0\leq A_i\leq 10^9
- The sum of N over all test cases is at most 2\times 10^5.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
T
\mathrm{case}_1
\mathrm{case}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{case}_T
Each test case is given in the following format:
N M
A_0 A_1 \ldots A_{N-1}
Output
Output the maximum possible total value of coins distributed to each person.
Sample Input 1
5 3 1 123 456 789 3 1000 123 456 789 2 3 6 14 2 3 11 14 30 4 15 9 2 66 23 2 4 1 1 32 4 80 9 10 47 14 8 7 3 16 2 39 77 4 4 2 38 64 1 2
Sample Output 1
83583 0 42 50 19401302040124704218001124023
- For the first test case, if all coins are distributed to one person, the total value of coins distributed to each person is 123\times 10^0+456\times 10^1+789\times 10^2=83583.
- For the second test case, there is no choice but to distribute 0 coins to everyone.
- For the third test case, the total value of coins distributed to each person can be made 42 as follows:
- To the 1-st person, distribute 2 coins of value 10^0 and 4 coins of value 10^1.
- To the 2-nd person, distribute 2 coins of value 10^0 and 4 coins of value 10^1.
- To the 3-rd person, distribute 2 coins of value 10^0 and 4 coins of value 10^1.
- For the fourth test case, the total value of coins distributed to each person can be made 50 as follows:
- To the 1-st person, distribute 0 coins of value 10^0 and 5 coins of value 10^1.
- To the 2-nd person, distribute 0 coins of value 10^0 and 5 coins of value 10^1.
- To the 3-rd person, distribute 10 coins of value 10^0 and 4 coins of value 10^1.
実行時間制限: 2 sec / メモリ制限: 1024 MiB
配点 : 800 点
問題文
頂点に 1 から N の番号が付いた N 頂点 M 辺の単純無向グラフ G が与えられます.i 番目の辺は頂点 u_i と頂点 v_i を結んでいます.
G の頂点にははじめ色が塗られていません.Alice と Bob が G を使ってゲームをします.Alice と Bob は t=1,\ldots,N の順に次の行動を行います.
- t が奇数ならば,Alice がまだ色の塗られていない頂点をひとつ選び,その頂点を黒色で塗る.
- t が偶数ならば,Bob がまだ色の塗られていない頂点をひとつ選び,その頂点を白色で塗る.
N 回すべての行動が終わった時点で,黒色で塗られた頂点全体が G の独立集合であれば Alice が勝者,そうでなければ Bob が勝者となります.両者が最適に行動した場合の勝者の名前を出力してください.
T 個のテストケースが与えられるので,それぞれについて解いてください.
独立集合とは
単純無向グラフ G の頂点からなる集合 S が G の独立集合であるとは,辺で結ばれた 2 頂点 u,v であって u\in S かつ v\in S となるものが存在しないことをいいます.制約
- 1\leq T\leq 2\times 10^5
- 2\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 0\leq M\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq u_i < v_i \leq N
- 与えられるグラフは単純無向グラフである.
- すべてのテストケースにわたる N の総和は 2\times 10^5 以下.
- すべてのテストケースにわたる M の総和は 2\times 10^5 以下.
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられます.
T
\mathrm{case}_1
\mathrm{case}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{case}_T
各ケースは以下の形式で与えられます.
N M u_1 v_1 \vdots u_M v_M
出力
T 行出力してください.i 行目には i 番目のテストケースについて,両者が最適に行動した場合の勝者の名前(Alice または Bob)を出力してください.
入力例 1
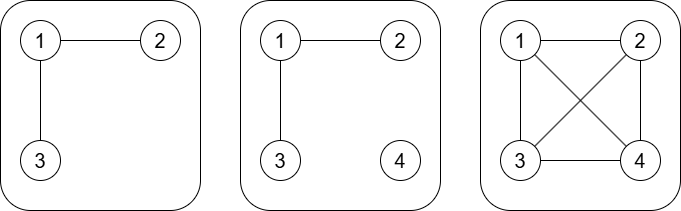
3 3 2 1 2 1 3 4 2 1 2 1 3 4 6 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 4 3 4
出力例 1
Bob Alice Bob
各テストケースで与えられるグラフを図示すると次のようになります.
Score : 800 points
Problem Statement
You are given a simple undirected graph G with N vertices and M edges, where vertices are numbered 1 to N. The i-th edge connects vertices u_i and v_i.
Initially, no vertices of G are colored. Alice and Bob will play a game using G. Alice and Bob perform the following actions in order for t=1,\ldots,N:
- If t is odd, Alice chooses one vertex that is not yet colored and colors that vertex black.
- If t is even, Bob chooses one vertex that is not yet colored and colors that vertex white.
After all N actions are completed, if the set of all vertices colored black is an independent set of G, Alice is the winner; otherwise, Bob is the winner. Output the name of the winner when both players play optimally.
You are given T test cases; solve each of them.
What is an independent set
A set S consisting of vertices of a simple undirected graph G is an independent set of G if there does not exist a pair of vertices u and v connected by an edge such that u\in S and v\in S.Constraints
- 1\leq T\leq 2\times 10^5
- 2\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 0\leq M\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq u_i < v_i \leq N
- The given graph is a simple undirected graph.
- The sum of N over all test cases is at most 2\times 10^5.
- The sum of M over all test cases is at most 2\times 10^5.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
T
\mathrm{case}_1
\mathrm{case}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{case}_T
Each case is given in the following format:
N M u_1 v_1 \vdots u_M v_M
Output
Output T lines. The i-th line should contain the name of the winner (Alice or Bob) for the i-th test case when both players play optimally.
Sample Input 1
3 3 2 1 2 1 3 4 2 1 2 1 3 4 6 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 3 2 4 3 4
Sample Output 1
Bob Alice Bob
The graph given in each test case is illustrated below:

実行時間制限: 2 sec / メモリ制限: 1024 MiB
配点 : 1000 点
問題文
正整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) が与えられます.
A の部分列は,要素の添字の違いを区別すれば,2^N 個あります.これらの各部分列の総和を昇順に列挙したものを,S_1, S_2, \ldots, S_{2^N} とします.
整数 k (1\leq k\leq 2^N-1)であって,1.01 \times S_k\leq S_{k+1} を満たすものすべてについて,S_k, S_{k+1}, (k\bmod 998244353) を出力してください.
部分列とは
数列 A の部分列とは,A の要素を 0 個以上選んで削除し,残った要素を元の順序を保って並べた数列のことを指します.制約
- 2\leq N\leq 5000
- 1\leq A_i\leq 10^{13}
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられます.
N A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N
出力
1 行目には,条件を満たす整数 k の個数を出力してください.
2 行目以降には各行に,条件を満たす整数 k それぞれについて,S_k, S_{k+1}, (k\bmod 998244353) を空白区切りで出力してください.
k について昇順に出力してください.
入力例 1
3 5 5 3
出力例 1
5 0 3 1 3 5 2 5 8 4 8 10 6 10 13 7
部分列は次の 8 個です.
- 空な部分列.総和は 0 である.
- (5).総和は 5 である.この部分列は 2 回現れる.
- (3).総和は 3 である.
- (5,5).総和は 10 である.
- (5,3).総和は 8 である.この部分列は 2 回現れる.
- (5,5,3).総和は 13 である.
S_1, S_2, \ldots, S_8 は順に 0,3,5,5,8,8,10,13 となります.
入力例 2
2 100 101
出力例 2
3 0 100 1 100 101 2 101 201 3
入力例 3
2 101 102
出力例 3
2 0 101 1 102 203 3
入力例 4
20 456 206 448 830 937 793 483 527 772 239 361 925 364 956 355 420 557 739 323 912
出力例 4
23 0 206 1 206 239 2 239 323 3 323 355 4 355 361 5 364 420 7 420 445 8 448 456 10 456 483 11 483 527 12 529 557 14 570 594 19 594 600 20 603 626 22 626 654 23 662 678 26 695 716 32 725 733 36 743 763 39 784 793 48 820 830 60 850 865 65 11397 11603 1048575
Score : 1000 points
Problem Statement
You are given a sequence of positive integers A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N).
There are 2^N subsequences of A when distinguishing subsequences by the indices of their elements. Let S_1, S_2, \ldots, S_{2^N} be the sums of these subsequences, enumerated in ascending order.
For all integers k (1\leq k\leq 2^N-1) that satisfy 1.01 \times S_k\leq S_{k+1}, output S_k, S_{k+1}, (k\bmod 998244353).
What is a subsequence
A subsequence of a sequence A is a sequence obtained by removing zero or more elements from A and arranging the remaining elements in their original order.Constraints
- 2\leq N\leq 5000
- 1\leq A_i\leq 10^{13}
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N
Output
On the first line, output the number of integers k that satisfy the condition.
From the second line onwards, for each integer k that satisfies the condition, output S_k, S_{k+1}, (k\bmod 998244353) separated by spaces on each line.
Output in ascending order of k.
Sample Input 1
3 5 5 3
Sample Output 1
5 0 3 1 3 5 2 5 8 4 8 10 6 10 13 7
We have the following eight subsequences:
- The empty subsequence. The sum is 0.
- (5). The sum is 5. This subsequence appears twice.
- (3). The sum is 3.
- (5,5). The sum is 10.
- (5,3). The sum is 8. This subsequence appears twice.
- (5,5,3). The sum is 13.
S_1, S_2, \ldots, S_8 are 0,3,5,5,8,8,10,13 in order.
Sample Input 2
2 100 101
Sample Output 2
3 0 100 1 100 101 2 101 201 3
Sample Input 3
2 101 102
Sample Output 3
2 0 101 1 102 203 3
Sample Input 4
20 456 206 448 830 937 793 483 527 772 239 361 925 364 956 355 420 557 739 323 912
Sample Output 4
23 0 206 1 206 239 2 239 323 3 323 355 4 355 361 5 364 420 7 420 445 8 448 456 10 456 483 11 483 527 12 529 557 14 570 594 19 594 600 20 603 626 22 626 654 23 662 678 26 695 716 32 725 733 36 743 763 39 784 793 48 820 830 60 850 865 65 11397 11603 1048575
実行時間制限: 10 sec / メモリ制限: 1024 MiB
配点 : 1100 点
問題文
整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) が与えられます.また,正整数 a,b,s,t が与えられます.ただし,a,b は互いに素であることが保証されます.
A に対して,次の 4 種の操作を行うことができます.
- 1\leq i\leq N を満たす整数 i をひとつ選び,A_i に a を足す.この操作にはコストが s かかる.
- 1\leq i\leq N を満たす整数 i をひとつ選び,A_i から a を引く.この操作にはコストが s かかる.
- 1\leq i\leq N を満たす整数 i をひとつ選び,A_i に b を足す.この操作にはコストが t かかる.
- 1\leq i\leq N を満たす整数 i をひとつ選び,A_i から b を引く.この操作にはコストが t かかる.
Q 個のクエリに答えてください.q 番目のクエリでは,整数 B_q が与えられるので,次の値を 998244353 で割った余りを求めてください.
- A_{1}=A_{2}=\cdots=A_{N}=B_q が成り立つようにするために必要なコストの総和の最小値.なお,A_{1}=A_{2}=\cdots=A_{N}=B_q が成り立つようにすることは可能であることが証明できる.
制約
- 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq Q\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq a,b,s,t\leq 5\times 10^8
- a,b は互いに素
- 1\leq A_i\leq 5\times 10^8
- 1\leq B_q\leq 5\times 10^8
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられます.
N Q a b s t A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N B_1 B_2 \ldots B_Q
出力
Q 個の値を空白区切りで出力してください.
q 番目には,A_{1}=A_{2}=\cdots=A_{N}=B_q が成り立つようにするために必要なコストの総和の最小値を,998244353 で割った余りを出力してください.
入力例 1
1 5 3 5 4 3 3 1 2 3 4 5
出力例 1
7 11 0 11 7
- A_1 に +a, -b する操作を順に行うことで,A=(1) にできます.コストの総和 4+3=7 です.
- A_1 に -a, -a, +b する操作を順に行うことで,A=(2) にできます.コストの総和 4+4+3=11 です.
- はじめから A=(3) です.コストの総和は 0 です.
- A_1 に +a, +a, -b する操作を順に行うことで,A=(4) にできます.コストの総和 4+4+3=11 です.
- A_1 に -a, +b する操作を順に行うことで,A=(5) にできます.コストの総和 4+3=7 です.
入力例 2
3 1 3 5 4 3 1 2 3 4
出力例 2
22
- A_1 に +a,A_2 に +b, -a,A_3 に +a,+a,-b という操作を順に行うことで,A=(4,4,4) にできます.コストの総和は 22 です.
入力例 3
5 5 1234 4321 5 5 1 10 100 1000 10000 123 4567 89012345 6 789
出力例 3
45340 42530 531725 35135 41690
Score : 1100 points
Problem Statement
You are given an integer sequence A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N). Also, you are given positive integers a,b,s,t. It is guaranteed that a and b are coprime.
You can perform the following four types of operations on A:
- Choose an integer i satisfying 1\leq i\leq N and add a to A_i. This operation costs s.
- Choose an integer i satisfying 1\leq i\leq N and subtract a from A_i. This operation costs s.
- Choose an integer i satisfying 1\leq i\leq N and add b to A_i. This operation costs t.
- Choose an integer i satisfying 1\leq i\leq N and subtract b from A_i. This operation costs t.
Answer Q queries. In the q-th query, you are given an integer B_q, so find the following value modulo 998244353:
- The minimum total cost required to make A_{1}=A_{2}=\cdots=A_{N}=B_q hold. It can be proved that it is possible to make A_{1}=A_{2}=\cdots=A_{N}=B_q hold.
Constraints
- 1\leq N\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq Q\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq a,b,s,t\leq 5\times 10^8
- a and b are coprime.
- 1\leq A_i\leq 5\times 10^8
- 1\leq B_q\leq 5\times 10^8
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N Q a b s t A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N B_1 B_2 \ldots B_Q
Output
Output Q values separated by spaces.
The q-th value should be the minimum total cost, modulo 998244353, required to make A_{1}=A_{2}=\cdots=A_{N}=B_q hold.
Sample Input 1
1 5 3 5 4 3 3 1 2 3 4 5
Sample Output 1
7 11 0 11 7
- By performing operations +a, -b on A_1 in order, we can make A=(1). The total cost is 4+3=7.
- By performing operations -a, -a, +b on A_1 in order, we can make A=(2). The total cost is 4+4+3=11.
- A=(3) from the beginning. The total cost is 0.
- By performing operations +a, +a, -b on A_1 in order, we can make A=(4). The total cost is 4+4+3=11.
- By performing operations -a, +b on A_1 in order, we can make A=(5). The total cost is 4+3=7.
Sample Input 2
3 1 3 5 4 3 1 2 3 4
Sample Output 2
22
- By performing operations +a on A_1, +b, -a on A_2, and +a,+a,-b on A_3 in order, we can make A=(4,4,4). The total cost is 22.
Sample Input 3
5 5 1234 4321 5 5 1 10 100 1000 10000 123 4567 89012345 6 789
Sample Output 3
45340 42530 531725 35135 41690