Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
AtCoder マンションには 1 号室から N 号室までの N 個の部屋があります。
各 i 号室には S_i さんが 1 人で住んでいます。
あなたは X 号室の Y さん宛に荷物を届けようとしています。宛先が正しいかどうかを判定してください。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- 1 \leq X \leq N
- N,X は整数
- S_i および Y は英小文字のみからなる長さ 1 以上 10 以下の文字列
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N S_1 S_2 \vdots S_N X Y
出力
X 号室に住んでいる人の名前が Y であるとき Yes、そうでないとき No と出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 sato suzuki takahashi 3 takahashi
出力例 1
Yes
3 号室に住んでいるのは takahashi さんであり、荷物の宛名と一致しています。
入力例 2
3 sato suzuki takahashi 1 aoki
出力例 2
No
1 号室に住んでいるのは sato さんであり、荷物の宛名である aoki と一致しません。
入力例 3
2 smith smith 1 smith
出力例 3
Yes
AtCoder マンションには異なる部屋に同じ名前の人が住んでいることがあります。
入力例 4
2 wang li 2 wang
出力例 4
No
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
Mansion AtCoder has N rooms numbered from room 1 to room N.
Each room i is inhabited by one person named S_i.
You are to deliver a package addressed to Mr./Ms. Y in room X. Determine whether the destination is correct.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- 1 \leq X \leq N
- N and X are integers.
- S_i and Y are strings consisting of lowercase English letters with length between 1 and 10, inclusive.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N S_1 S_2 \vdots S_N X Y
Output
Print Yes if the name of the person living in room X is Y, and No otherwise.
Sample Input 1
3 sato suzuki takahashi 3 takahashi
Sample Output 1
Yes
The person living in room 3 is takahashi, which matches the name on the package.
Sample Input 2
3 sato suzuki takahashi 1 aoki
Sample Output 2
No
The person living in room 1 is sato, which does not match the name on the package, aoki.
Sample Input 3
2 smith smith 1 smith
Sample Output 3
Yes
Mansion AtCoder may have people with the same name living in different rooms.
Sample Input 4
2 wang li 2 wang
Sample Output 4
No
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
正整数 x に対し、f(x) を以下のように定義します。
- x を(先頭に余分な 0 をつけずに)十進表記して得られる文字列を s_x、s_x を反転して得られる文字列を \text{rev}(s_x) とおく。 f(x) の値は、\text{rev}(s_x) を整数の十進表記としてみなすことで得られる整数である。
例えば、x=13 のとき \text{rev}(s_x)=\ 31 より f(x)=31 であり、x=10 のとき \text{rev}(s_x)=\ 01 より f(x)=1 です。
特に、どのような正整数 x に対しても f(x) の値は正整数です。
正整数 X,Y が与えられます。 正整数列 A=(a_1,a_2,\dots,a_{10}) を以下のように定義します。
- a_1 = X
- a_2 = Y
- a_i = f(a_{i-1}+a_{i-2})\ (i\geq 3)
a_{10} の値を求めてください。
制約
- 1\leq X,Y \leq 10^5
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
X Y
出力
a_{10} の値を出力せよ。
入力例 1
1 1
出力例 1
415
A の各要素の値は以下の通りです。
- a_1=1
- a_2=1
- a_3=2
- a_4=3
- a_5=5
- a_6=8
- a_7=31
- a_8=93
- a_9=421
- a_{10}=415
よって 415 を出力します。
入力例 2
3 7
出力例 2
895
入力例 3
90701 90204
出力例 3
9560800101
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
For a positive integer x, define f(x) as follows:
- Let s_x be the string obtained by representing x in decimal notation (without leading zeros), and let \text{rev}(s_x) be the string obtained by reversing s_x. The value of f(x) is the integer obtained by interpreting \text{rev}(s_x) as a decimal representation of an integer.
For example, when x=13, we have \text{rev}(s_x)= 31, so f(x)=31; when x=10, we have \text{rev}(s_x)= 01, so f(x)=1.
Particularly, for any positive integer x, the value of f(x) is a positive integer.
You are given positive integers X and Y. Define a sequence of positive integers A=(a_1,a_2,\dots,a_{10}) as follows:
- a_1 = X
- a_2 = Y
- a_i = f(a_{i-1}+a_{i-2})\ (i\geq 3)
Find the value of a_{10}.
Constraints
- 1\leq X,Y \leq 10^5
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
X Y
Output
Print the value of a_{10}.
Sample Input 1
1 1
Sample Output 1
415
The values of the elements of A are as follows:
- a_1=1
- a_2=1
- a_3=2
- a_4=3
- a_5=5
- a_6=8
- a_7=31
- a_8=93
- a_9=421
- a_{10}=415
Thus, print 415.
Sample Input 2
3 7
Sample Output 2
895
Sample Input 3
90701 90204
Sample Output 3
9560800101
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 350 点
問題文
長さ 2N の文字列 S が与えられます。 S は A, B を N 個ずつ含みます。
S に対して隣り合う文字を入れ替える操作を好きな回数( 0 回でもよい)行って、同じ文字が隣り合う箇所がない状態にするために必要な操作回数の最小値を求めてください。
制約
- 1\leq N \leq 5\times 10^5
- N は整数
- S は長さ 2N の文字列であり、N 個の
Aと N 個のBからなる
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N S
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 AABBBA
出力例 1
2
次のように操作することで 2 回の操作で同じ文字が隣り合う箇所がない状態にすることができます。
- 2 文字目と 3 文字目を入れ替える。S は
ABABBAになる。 - 5 文字目と 6 文字目を入れ替える。S は
ABABABになる。
入力例 2
3 AAABBB
出力例 2
3
入れ替えることができるのは隣り合う文字に限ることに注意してください。
入力例 3
17 AAABABABBBABABBABABABABBAAABABABBA
出力例 3
15
Score : 350 points
Problem Statement
You are given a string S of length 2N. S contains exactly N occurrences of A and N occurrences of B.
Find the minimum number of operations (possibly zero) needed to make S have no adjacent identical characters, where an operation consists of swapping two adjacent characters in S.
Constraints
- 1\leq N \leq 5\times 10^5
- N is an integer.
- S is a string of length 2N consisting of N occurrences of
Aand N occurrences ofB.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N S
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
3 AABBBA
Sample Output 1
2
By performing operations as follows, you can achieve a state with no adjacent identical characters in two operations:
- Swap the 2nd and 3rd characters. S becomes
ABABBA. - Swap the 5th and 6th characters. S becomes
ABABAB.
Sample Input 2
3 AAABBB
Sample Output 2
3
Note that you can only swap adjacent characters.
Sample Input 3
17 AAABABABBBABABBABABABABBAAABABABBA
Sample Output 3
15
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 425 点
問題文
無限に広いグリッドがあります。グリッドのあるマスはマス (0,0) と名前がついています。
マス (0,0) から下に r マス、右に c マスの移動した位置にあるマスをマス (r,c) と呼びます。
ここで、「下に r マス移動する」は r が負のときは「上に |r| マス移動する」ことを表し、「右に c マス移動する」は c が負のときには「左に |c| マス移動する」ことを表すものとします。
具体的には、マス (0,0) の周辺にあるマスは以下のようになります。
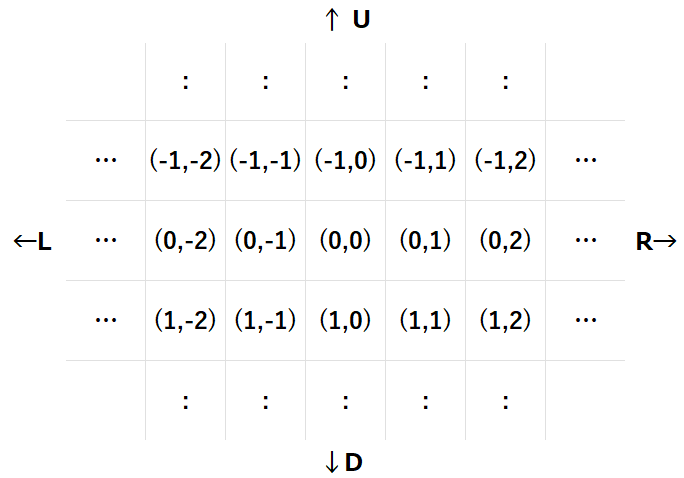
最初、高橋君はマス (R_t,C_t) に、青木君はマス (R_a,C_a) にいます。二人はそれぞれ U,D,L,R からなる長さ N の文字列 S,T に従って N 回移動を行います。
各 i について、高橋君と青木君の i 回目の移動は同時に行われます。具体的には、高橋君は S の i 文字目が U のとき上、D のとき下、L のとき左、R のとき右へ 1 マス移動し、青木君は T の i 文字目によって同様に移動します。
N 回の移動の中で、移動直後に高橋君と青木君が同じマスにいた回数を求めてください。
ただし、N は非常に大きいため S,T は ( (S'_1, A_1),\ldots(S'_M,A_M) ), ( (T'_1,B_1),\ldots,(T'_L,B_L) ) の形で与えられ、 S は「文字 S'_1 を A_1 個、\dots、文字 S'_M を A_M 個」をこの順に連結した文字列であり、T も同様です。
制約
- -10^9 \leq R_t,C_t,R_a,C_a \leq 10^9
- 1\leq N \leq 10^{14}
- 1\leq M,L \leq 10^5
- S'_i,T'_i は
U,D,L,Rのいずれか - 1 \leq A_i,B_i \leq 10^9
- A_1+\dots+A_M=B_1+\dots+B_L=N
- 与えられる数値は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
R_t C_t R_a C_a N M L S'_1 A_1 \vdots S'_M A_M T'_1 B_1 \vdots T'_L B_L
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
0 0 4 2 3 2 1 R 2 D 1 U 3
出力例 1
1
このケースでは S= RRD、T= UUU であり、移動は次のように行われます。
- 最初、高橋君はマス (0,0) に、青木君はマス (4,2) にいる。
- 1 回目の移動後、高橋君はマス (0,1)、青木君はマス (3,2) にいる。
- 2 回目の移動後、高橋君はマス (0,2)、青木君はマス (2,2) にいる。
- 3 回目の移動後、高橋君はマス (1,2)、青木君はマス (1,2) にいる。
よって、高橋君と青木君が移動直後に同じマスにいた回数は 1 です。
入力例 2
1000000000 1000000000 -1000000000 -1000000000 3000000000 3 3 L 1000000000 U 1000000000 U 1000000000 D 1000000000 R 1000000000 U 1000000000
出力例 2
1000000001
2000000000 回目の移動から 3000000000 回目の移動までの 1000000001 回で高橋君と青木君は移動直後に同じマスにいます。
入力例 3
3 3 3 2 1 1 1 L 1 R 1
出力例 3
0
入力例 4
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 L 1 R 1
出力例 4
0
Score : 425 points
Problem Statement
There is an infinitely large grid. One cell of the grid is named cell (0,0).
The cell located r cells down and c cells right from cell (0,0) is called cell (r,c).
Here, "r cells down" means "|r| cells up" when r is negative, and "c cells right" means "|c| cells left" when c is negative.
Specifically, the cells around cell (0,0) are as follows:

Initially, Takahashi is at cell (R_t,C_t) and Aoki is at cell (R_a,C_a). They will each make N moves according to strings S and T of length N consisting of U, D, L, R.
For each i, Takahashi's and Aoki's i-th moves occur simultaneously: Takahashi moves one cell up if the i-th character of S is U, down if D, left if L, and right if R; Aoki moves similarly according to the i-th character of T.
Find the number of times Takahashi and Aoki are at the same cell immediately after a move during the N moves.
Since N is very large, S and T are given in the form ((S'_1, A_1),\ldots,(S'_M,A_M)) and ((T'_1,B_1),\ldots,(T'_L,B_L)), where S is the string obtained by concatenating "A_1 copies of character S'_1, \dots, A_M copies of character S'_M" in this order, and T is given similarly.
Constraints
- -10^9 \leq R_t,C_t,R_a,C_a \leq 10^9
- 1\leq N \leq 10^{14}
- 1\leq M,L \leq 10^5
- Each of S'_i and T'_i is one of
U,D,L,R. - 1 \leq A_i,B_i \leq 10^9
- A_1+\dots+A_M=B_1+\dots+B_L=N
- All given values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
R_t C_t R_a C_a N M L S'_1 A_1 \vdots S'_M A_M T'_1 B_1 \vdots T'_L B_L
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
0 0 4 2 3 2 1 R 2 D 1 U 3
Sample Output 1
1
In this case, S= RRD and T= UUU, and the movements proceed as follows:
- Initially, Takahashi is at cell (0,0) and Aoki is at cell (4,2).
- After the 1st move, Takahashi is at cell (0,1) and Aoki is at cell (3,2).
- After the 2nd move, Takahashi is at cell (0,2) and Aoki is at cell (2,2).
- After the 3rd move, Takahashi is at cell (1,2) and Aoki is at cell (1,2).
Thus, the number of times Takahashi and Aoki are at the same cell immediately after a move is 1.
Sample Input 2
1000000000 1000000000 -1000000000 -1000000000 3000000000 3 3 L 1000000000 U 1000000000 U 1000000000 D 1000000000 R 1000000000 U 1000000000
Sample Output 2
1000000001
From the 2000000000-th move to the 3000000000-th move, Takahashi and Aoki are at the same cell immediately after a move for 1000000001 times.
Sample Input 3
3 3 3 2 1 1 1 L 1 R 1
Sample Output 3
0
Sample Input 4
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 L 1 R 1
Sample Output 4
0
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 475 点
問題文
5 個の 6 面ダイスがあります。どのダイスも各面に書かれた数は A_1,\ldots,A_6 の 6 個であり、各面が出る確率は \frac{1}{6} です。
あなたはこれらのダイスを使って次の手順で 1 人ゲームを行います。
- 5 個のダイスを全て振り、その結果を見て、好きな個数(0 個でもよい)のダイスをキープする。
- キープされていないダイスを全て振り直し、その結果を見て、振り直したダイスのうち好きな個数(0 個でもよい)のダイスを追加でキープする。前のステップでキープしたダイスはキープしたままとなる。
- キープされていないダイスを全て振り直し、その結果を見る。
- 好きな数 X を選ぶ。5 個のダイスのうち X の目が出ているダイスの個数を n として、このゲームの得点は nX 点となる。
ゲームの得点の期待値を最大化するように行動するときの、ゲームの得点の期待値を求めてください。
制約
- A_i は 1 以上 100 以下の整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
A_1 A_2 A_3 A_4 A_5 A_6
出力
答えを出力せよ。真の解との相対誤差または絶対誤差が 10^{-5} 以下のとき正解とみなされる。
入力例 1
1 2 3 4 5 6
出力例 1
14.6588633742
例えばゲームは次のように進行します。(最適な行動とは限りません)
- 5 個のダイスを全て振り、それぞれ 3,3,1,5,6 の目が出る。3 の目が出た 2 個のダイスをキープする。
- キープされていない 3 個のダイスを振り、それぞれ 6,6,2 の目が出る。6 の目が出た 2 個のダイスを追加でキープする。
- キープされていない 1 個のダイスを振り、4 の目が出る。
- X として 6 を選ぶ。5 個のダイスの出目はそれぞれ 3,3,6,6,4 なので、6 の目が出ているダイスの個数は 2 であり、このゲームの得点は 12 となる。
このケースでは最適に行動した場合の期待値は \frac{143591196865}{9795520512}=14.6588633742\ldots となります。
入力例 2
1 1 1 1 1 1
出力例 2
5.0000000000
ダイスは同じ値が書かれた面を持つことがあります。
入力例 3
31 41 59 26 53 58
出力例 3
159.8253021021
Score : 475 points
Problem Statement
There are five six-sided dice. Each die has the numbers A_1,\ldots,A_6 written on its faces, and each face appears with probability \frac{1}{6}.
You will play a single-player game using these dice with the following procedure:
- Roll all five dice, observe the results, and keep any number (possibly zero) of dice.
- Re-roll all dice that are not kept, observe the results, and additionally keep any number (possibly zero) of the re-rolled dice. The dice kept in the previous step remain kept.
- Re-roll all dice that are not kept and observe the results.
- Choose any number X. Let n be the number of dice among the five dice that show X. The score of this game is nX points.
Find the expected value of the game score when you act to maximize the expected value of the game score.
Constraints
- A_i is an integer between 1 and 100, inclusive.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
A_1 A_2 A_3 A_4 A_5 A_6
Output
Print the answer. Your answer will be considered correct if the relative or absolute error from the true value is at most 10^{-5}.
Sample Input 1
1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output 1
14.6588633742
For example, the game may proceed as follows (not necessarily optimal):
- Roll all five dice and get 3,3,1,5,6. Keep the two dice that show 3.
- Re-roll the three dice that are not kept and get 6,6,2. Additionally keep the two dice that show 6.
- Re-roll the one die that is not kept and get 4.
- Choose X = 6. The dice show 3,3,6,6,4, so the number of dice showing 6 is 2, and the score of this game is 12.
In this case, the expected value when acting optimally is \frac{143591196865}{9795520512}=14.6588633742\ldots.
Sample Input 2
1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output 2
5.0000000000
The dice may have faces with the same value written on them.
Sample Input 3
31 41 59 26 53 58
Sample Output 3
159.8253021021
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 525 点
問題文
数列 A があります。 はじめ、A=(0) です。 (すなわち、A は 0 を唯一の要素として含む長さ 1 の数列です)。
クエリが Q 個与えられるので、順に処理してください。 i 番目 (1\leq i\leq Q) のクエリは以下のいずれかの形式です。
1 x:A の中で x が現れる場所の直後に i を挿入する。- 具体的には、現在の A の j 番目の要素を A_j、A の長さを n としたとき、A_p=x なる p に対して A を (A_1,\dots,A_p,i,A_{p+1},\dots,A_n) で更新する。 ここで、このクエリを処理する直前の時点で A には x が含まれていることが保証される。
2 x y:A の中で x と y の間にある要素の値の合計を出力し、それらの要素を全て削除する。- 具体的には、現在の A の j 番目の要素を A_j、A の長さを n としたとき、A_p=x,A_q=y なる p,q に対して、A_{\min(p,q)+1} + \dots + A_{\max(p,q)-1} を出力し、 A を (A_1,\dots,A_{\min(p,q)},A_{\max(p,q)},\dots,A_n) で更新する。 ここで、このクエリを処理する直前の時点で A には x および y が共に含まれていることが保証される。
なお、どのようなクエリの列に対しても、クエリを処理する過程で A の中に同じ値が複数回現れることはなく、ゆえに A の中である値が現れる場所は(存在するならば)一意であることに注意してください。
制約
- 1\leq Q \leq 5\times 10^5
- i 番目のクエリについて、
- 1 種類目のクエリのとき:
- 0\leq x < i
- クエリを処理する直前の時点で A には x が含まれる
- 2 種類目のクエリのとき:
- 0\leq x < y < i
- クエリを処理する直前の時点で A には x,y が共に含まれる
- 1 種類目のクエリのとき:
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
Q
\text{query}_{1}
\text{query}_{2}
\vdots
\text{query}_{Q}
ここで \text{query}_{i} は i 番目のクエリを表し、以下のいずれかの形式で与えられる。
1 x
2 x y
出力
2 種類目のクエリの個数を q 個として、q 行出力せよ。 i 行目には、2 種類目のクエリのうち i 番目のものにおいて出力すべき値を出力せよ。
入力例 1
6 1 0 1 1 1 0 2 2 3 1 2 2 0 5
出力例 1
1 5
最初、A=(0) です。
- 1 番目のクエリ:0 の直後に 1 を挿入します。A=(0,1) になります。
- 2 番目のクエリ:1 の直後に 2 を挿入します。A=(0,1,2) になります。
- 3 番目のクエリ:0 の直後に 3 を挿入します。A=(0,3,1,2) になります。
- 4 番目のクエリ:2 と 3 の間にある要素、すなわち 1 を削除し、削除した値の合計である 1 を出力します。A=(0,3,2) になります。
- 5 番目のクエリ:2 の直後に 5 を挿入します。A=(0,3,2,5) になります。
- 6 番目のクエリ:0 と 5 の間にある要素、すなわち 3,2 を削除し、削除した値の合計である 5 を出力します。A=(0,5) になります。
入力例 2
2 1 0 2 0 1
出力例 2
0
2 番目のクエリでは 0 と 1 の間にある要素を全て削除しますが、実際にはそのような要素は一つも存在せず、要素の削除も行われないため、出力する値は 0 になります。
入力例 3
10 1 0 1 1 2 0 2 2 0 2 1 0 1 5 2 0 5 2 2 6 1 6 1 9
出力例 3
1 0 0 0
Score : 525 points
Problem Statement
There is a sequence A. Initially, A=(0). (That is, A is a sequence of length 1 containing 0 as its only element).
You are given Q queries to process in order. The i-th query (1\leq i\leq Q) has one of the following forms:
1 x: Insert i immediately after the location where x appears in A. Specifically, let A_j be the j-th element of the current A and n be the length of A. For p such that A_p=x, update A to (A_1,\dots,A_p,i,A_{p+1},\dots,A_n). It is guaranteed that A contains x immediately before processing this query.2 x y: Remove all elements between x and y in A, and output the sum of the values of the removed elements. Specifically, let A_j be the j-th element of the current A and n be the length of A. For p and q such that A_p=x and A_q=y, output A_{\min(p,q)+1} + \dots + A_{\max(p,q)-1} and update A to (A_1,\dots,A_{\min(p,q)},A_{\max(p,q)},\dots,A_n). It is guaranteed that A contains both x and y immediately before processing this query.
Note that for any sequence of queries, the same value never appears multiple times in A during the process of handling queries, and thus the position where a value appears in A is unique (if it exists).
Constraints
- 1\leq Q \leq 5\times 10^5
- For the i-th query:
- If it is a type 1 query:
- 0\leq x < i
- A contains x immediately before processing the query.
- If it is a type 2 query:
- 0\leq x < y < i
- A contains both x and y immediately before processing the query.
- If it is a type 1 query:
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
Q
\text{query}_{1}
\text{query}_{2}
\vdots
\text{query}_{Q}
Here, \text{query}_{i} represents the i-th query and is given in one of the following forms:
1 x
2 x y
Output
Let q be the number of type 2 queries. Output q lines. The i-th line should contain the value to be output for the i-th type 2 query.
Sample Input 1
6 1 0 1 1 1 0 2 2 3 1 2 2 0 5
Sample Output 1
1 5
Initially, A=(0).
- 1st query: Insert 1 immediately after 0. A becomes (0,1).
- 2nd query: Insert 2 immediately after 1. A becomes (0,1,2).
- 3rd query: Insert 3 immediately after 0. A becomes (0,3,1,2).
- 4th query: Remove the elements between 2 and 3, namely 1, and output the sum of the removed values, which is 1. A becomes (0,3,2).
- 5th query: Insert 5 immediately after 2. A becomes (0,3,2,5).
- 6th query: Remove the elements between 0 and 5, namely 3,2, and output the sum of the removed values, which is 5. A becomes (0,5).
Sample Input 2
2 1 0 2 0 1
Sample Output 2
0
In the 2nd query, we remove all elements between 0 and 1, but there are actually no such elements, so no elements are removed and the output value is 0.
Sample Input 3
10 1 0 1 1 2 0 2 2 0 2 1 0 1 5 2 0 5 2 2 6 1 6 1 9
Sample Output 3
1 0 0 0
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 600 点
問題文
長さ N の整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) が与えられます。 また、M 個の整数組 (L_1, R_1), (L_2, R_2), \dots, (L_M, R_M)\ (1\leq L_i\leq R_i\leq N) が与えられます。
あなたは数列 A に対して、以下の操作を好きな回数(0 回でも良い)行うことができます。
- 1 以上 M 以下の整数 i を選び、A_{L_i}, A_{L_i+1},\dots, A_{R_i} にそれぞれ 1 を足す。
A を広義単調増加にすることが可能かどうか判定し、可能ならば必要な操作回数の最小値を求めてください。
制約
- 1\leq N \leq 300
- 1\leq M \leq 300
- 1\leq A_i \leq 300
- 1\leq L_i\leq R_i\leq N
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M A_1 A_2 \dots A_N L_1 R_1 L_2 R_2 \vdots L_M R_M
出力
A を広義単調増加にすることが可能ならば必要な操作回数の最小値を、不可能ならば -1 を出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 3 4 2 3 2 2 2 2 3 4 4
出力例 1
4
例えば以下のように操作を 4 回行うと、A を広義単調増加にすることができます。
- i=1 を選んで操作する。A=(4,3,3,2) になる。
- i=3 を選んで操作する。A=(4,3,3,3) になる。
- i=3 を選んで操作する。A=(4,3,3,4) になる。
- i=2 を選んで操作する。A=(4,4,4,4) になる。
逆に、3 回以下の操作で A を広義単調増加にすることはできません。 よって 4 を出力します。
入力例 2
3 2 3 1 2 2 2 1 2
出力例 2
-1
どのように操作をしても、A を広義単調増加にすることはできません。
入力例 3
4 4 1 1 2 3 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
出力例 3
0
A は元から広義単調増加なので、1 回も操作をする必要はありません。
入力例 4
8 12 35 29 36 88 58 15 25 99 5 5 1 6 3 8 8 8 4 8 7 7 5 7 3 3 2 6 1 6 6 7 5 7
出力例 4
79
Score : 600 points
Problem Statement
You are given a length-N integer sequence A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N). You are also given M pairs of integers (L_1, R_1), (L_2, R_2), \dots, (L_M, R_M)\ (1\leq L_i\leq R_i\leq N).
You can perform the following operation on sequence A any number of times (possibly zero):
- Choose an integer i with 1 \leq i \leq M, and add 1 to each of A_{L_i}, A_{L_i+1},\dots, A_{R_i}.
Determine whether it is possible to make A non-decreasing, and if possible, find the minimum number of operations required.
Constraints
- 1\leq N \leq 300
- 1\leq M \leq 300
- 1\leq A_i \leq 300
- 1\leq L_i\leq R_i\leq N
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M A_1 A_2 \dots A_N L_1 R_1 L_2 R_2 \vdots L_M R_M
Output
If it is possible to make A non-decreasing, print the minimum number of operations required. If it is impossible, print -1.
Sample Input 1
4 3 4 2 3 2 2 2 2 3 4 4
Sample Output 1
4
For example, by performing operations four times as follows, you can make A non-decreasing:
- Choose i=1 and perform the operation. A becomes (4,3,3,2).
- Choose i=3 and perform the operation. A becomes (4,3,3,3).
- Choose i=3 and perform the operation. A becomes (4,3,3,4).
- Choose i=2 and perform the operation. A becomes (4,4,4,4).
Conversely, it is impossible to make A non-decreasing with three or fewer operations. Thus, print 4.
Sample Input 2
3 2 3 1 2 2 2 1 2
Sample Output 2
-1
No matter how you perform operations, it is impossible to make A non-decreasing.
Sample Input 3
4 4 1 1 2 3 1 1 2 2 3 3 4 4
Sample Output 3
0
A is already non-decreasing, so no operations are needed.
Sample Input 4
8 12 35 29 36 88 58 15 25 99 5 5 1 6 3 8 8 8 4 8 7 7 5 7 3 3 2 6 1 6 6 7 5 7
Sample Output 4
79