Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
1 から N の番号がついた N 人の人がいます。
人 i はキーエンス本社ビルの建築面積を S_i 平方メートルであると予想しました。
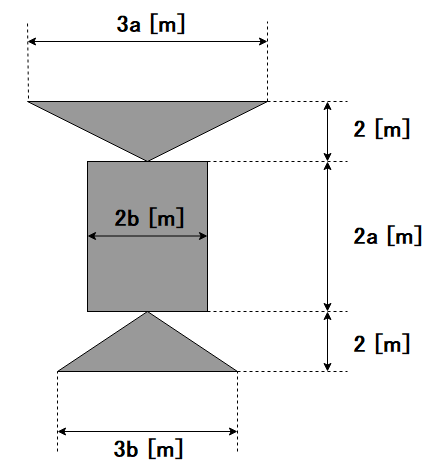
キーエンス本社ビルは下図のような形をしています。ただし、a,b はある 正の整数 です。
つまり、キーエンス本社ビルの建築面積は 4ab+3a+3b 平方メートルと表されます。
N 人のうち、この情報のみによって、予想した面積が確実に誤りであるとわかる人数を求めてください。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 20
- 1 \leq S_i \leq 1000
- 入力に含まれる値は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N S_1 \ldots S_N
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 10 20 39
出力例 1
1
a=1,b=1 のとき面積は 10 平方メートル、a=2,b=3 のとき面積は 39 平方メートルとなります。
しかし a,b がどのような正の整数であったとしても面積が 20 平方メートルになることはありません。
よって、人 2 の予想だけは確実に誤りであることがわかります。
入力例 2
5 666 777 888 777 666
出力例 2
3
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
There are N people numbered 1 to N.
Person i guessed the building area of KEYENCE headquarters building to be S_i square meters.
The shape of KEYENCE headquarters building is shown below, where a and b are some positive integers.
That is, the building area of the building can be represented as 4ab+3a+3b.
Based on just this information, how many of the N people are guaranteed to be wrong in their guesses?

Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 20
- 1 \leq S_i \leq 1000
- All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N S_1 \ldots S_N
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
3 10 20 39
Sample Output 1
1
The area would be 10 square meters if a=1,b=1, and 39 square meters if a=2,b=3.
However, no pair of positive integers a and b would make the area 20 square meters.
Thus, we can only be sure that Person 2 guessed wrong.
Sample Input 2
5 666 777 888 777 666
Sample Output 2
3
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
xy 平面上に N 人の人 1,2,\dots,N がおり、人 i は座標 (X_i,Y_i) にいます。
このうち、 K 人の人 A_1,A_2,\dots,A_K に同じ強さの明かりを持たせます。
座標 (x,y) にいる人が強さ R の明かりを持っている時、その明かりによって中心 (x,y) 、半径 R の円の内部全体(境界を含む)が照らされます。
すべての人が少なくとも 1 つの明かりによって照らされるために必要な明かりの強さの最小値を求めてください。
制約
- 入力は全て整数
- 1 \le K < N \le 1000
- 1 \le A_1 < A_2 < \dots < A_K \le N
- |X_i|,|Y_i| \le 10^5
- i \neq j ならば (X_i,Y_i) \neq (X_j,Y_j)
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N K A_1 A_2 \dots A_K X_1 Y_1 X_2 Y_2 \vdots X_N Y_N
出力
答えを実数として出力せよ。
出力された解と想定解との絶対誤差または相対誤差が 10^{-5} 以下であるならば、出力は正しいと見なされる。
入力例 1
4 2 2 3 0 0 0 1 1 2 2 0
出力例 1
2.23606797749978969
この入力では人が 4 人おり、そのうち人 2,3 が明かりを持ちます。
R \ge \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236068 である時、すべての人が少なくとも 1 つの明かりによって照らされます。
入力例 2
2 1 2 -100000 -100000 100000 100000
出力例 2
282842.712474619009
入力例 3
8 3 2 6 8 -17683 17993 93038 47074 58079 -57520 -41515 -89802 -72739 68805 24324 -73073 71049 72103 47863 19268
出力例 3
130379.280458974768
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
There are N people numbered 1, 2, \dots, N in the xy-plane. Person i is at the coordinates (X_i, Y_i).
K of these people, Persons A_1, A_2, \dots, A_K, will receive lights of the same strength.
When a person at coordinates (x, y) has a light of strength R, it lights up the interior of a circle of radius R centered at (x, y) (including the boundary).
Find the minimum strength of the lights needed for every person to be lit by at least one light.
Constraints
- All values in input are integers.
- 1 \le K < N \le 1000
- 1 \le A_1 < A_2 < \dots < A_K \le N
- |X_i|,|Y_i| \le 10^5
- (X_i,Y_i) \neq (X_j,Y_j), if i \neq j.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N K A_1 A_2 \dots A_K X_1 Y_1 X_2 Y_2 \vdots X_N Y_N
Output
Print the answer as a real number.
Your output will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error from the judge's output is at most 10^{-5}.
Sample Input 1
4 2 2 3 0 0 0 1 1 2 2 0
Sample Output 1
2.23606797749978969
This input contains four people. Among them, Persons 2 and 3 will have lights.
Every person will be lit by at least one light if R \ge \sqrt{5} \approx 2.236068.
Sample Input 2
2 1 2 -100000 -100000 100000 100000
Sample Output 2
282842.712474619009
Sample Input 3
8 3 2 6 8 -17683 17993 93038 47074 58079 -57520 -41515 -89802 -72739 68805 24324 -73073 71049 72103 47863 19268
Sample Output 3
130379.280458974768
Time Limit: 3 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
長さ N の数列 A = (a_1, a_2, \dots, a_N) があります。
以下で説明される Q 個のクエリに答えてください。
- クエリ i : 整数の組 (x_i, k_i) が与えられます。A の要素を a_1, a_2, \dots と前から順に見ていったときに、数 x_i が k_i 回目に登場するのは A の前から何番目の要素を見たときかを出力してください。
ただし条件を満たす要素が存在しない場合は -1 を出力してください。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq Q \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 0 \leq a_i \leq 10^9 (1 \leq i \leq N)
- 0 \leq x_i \leq 10^9 (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- 1 \leq k_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- 入力はすべて整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N Q a_1 a_2 \dots a_N x_1 k_1 x_2 k_2 \vdots x_Q k_Q
出力
Q 行出力せよ。i 行目ではクエリ i に対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
6 8 1 1 2 3 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 1 2 2 2 3 4 1
出力例 1
1 2 5 -1 3 6 -1 -1
A の中で 1 は a_1, a_2, a_5 に登場します。よって、クエリ 1 からクエリ 4 の答えは順に 1, 2, 5, -1 となります。
入力例 2
3 2 0 1000000000 999999999 1000000000 1 123456789 1
出力例 2
2 -1
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
We have a sequence of N numbers: A = (a_1, a_2, \dots, a_N).
Process the Q queries explained below.
- Query i: You are given a pair of integers (x_i, k_i). Let us look at the elements of A one by one from the beginning: a_1, a_2, \dots Which element will be the k_i-th occurrence of the number x_i?
Print the index of that element, or -1 if there is no such element.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq Q \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 0 \leq a_i \leq 10^9 (1 \leq i \leq N)
- 0 \leq x_i \leq 10^9 (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- 1 \leq k_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N Q a_1 a_2 \dots a_N x_1 k_1 x_2 k_2 \vdots x_Q k_Q
Output
Print Q lines. The i-th line should contain the answer to Query i.
Sample Input 1
6 8 1 1 2 3 1 2 1 1 1 2 1 3 1 4 2 1 2 2 2 3 4 1
Sample Output 1
1 2 5 -1 3 6 -1 -1
1 occurs in A at a_1, a_2, a_5. Thus, the answers to Query 1 through 4 are 1, 2, 5, -1 in this order.
Sample Input 2
3 2 0 1000000000 999999999 1000000000 1 123456789 1
Sample Output 2
2 -1
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 250 点
問題文
N 種類のビーンズが 1 粒ずつあります。 i 種類目のビーンズはおいしさが A_i で色が C_i です。ビーンズは混ぜられており、色でしか区別することができません。
あなたはビーンズの色を 1 つ選び、その色のビーンズをどれか 1 粒食べます。ビーンズの色をうまく選ぶことで、食べる可能性のあるビーンズのおいしさの最小値を最大化してください。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq A_i \leq 10^{9}
- 1 \leq C_i \leq 10^{9}
- 入力は全て整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N A_1 C_1 A_2 C_2 \vdots A_N C_N
出力
食べる可能性のあるビーンズのおいしさの最小値の最大値を整数として出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 100 1 20 5 30 5 40 1
出力例 1
40
同じ色のビーンズは互いに区別がつかないことに注意してください。
選ぶことができる色は 色 1 と 色 5 です。
- 色 1 のビーンズは 2 種類あり、美味しさはそれぞれ 100, 40 です。よって、色 1 を選んだときのおいしさの最小値は 40 です。
- 色 5 のビーンズは 2 種類あり、美味しさはそれぞれ 20, 30 です。よって、色 5 を選んだときのおいしさの最小値は 20 です。
おいしさの最小値を最大化するには 色 1 を選べばよいため、そのときの最小値である 40 を出力します。
入力例 2
10 68 3 17 2 99 2 92 4 82 4 10 3 100 2 78 1 3 1 35 4
出力例 2
35
Score: 250 points
Problem Statement
There are N types of beans, one bean of each type. The i-th type of bean has a deliciousness of A_i and a color of C_i. The beans are mixed and can only be distinguished by color.
You will choose one color of beans and eat one bean of that color. By selecting the optimal color, maximize the minimum possible deliciousness of the bean you eat.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq A_i \leq 10^{9}
- 1 \leq C_i \leq 10^{9}
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N A_1 C_1 A_2 C_2 \vdots A_N C_N
Output
Print as an integer the maximum value of the minimum possible deliciousness of the bean you eat.
Sample Input 1
4 100 1 20 5 30 5 40 1
Sample Output 1
40
Note that beans of the same color cannot be distinguished from each other.
You can choose color 1 or color 5.
- There are two types of beans of color 1, with deliciousness of 100 and 40. Thus, the minimum deliciousness when choosing color 1 is 40.
- There are two types of beans of color 5, with deliciousness of 20 and 30. Thus, the minimum deliciousness when choosing color 5 is 20.
To maximize the minimum deliciousness, you should choose color 1, so print the minimum deliciousness in that case: 40.
Sample Input 2
10 68 3 17 2 99 2 92 4 82 4 10 3 100 2 78 1 3 1 35 4
Sample Output 2
35
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 400 点
問題文
T 個のテストケースについて、以下の問題を解いてください。
非負整数 a,s が与えられます。以下の条件を両方とも満たす非負整数の組 (x,y) は存在しますか?
- x\ \text{AND}\ y=a
- x+y=s
\text{AND} とは
非負整数 n, m の bit ごとの論理積 n\ \text{AND}\ m は、以下のように定義されます。
- n\ \text{AND}\ m を二進表記した際の 2^k \, (k \geq 0) の位の数は、n, m を二進表記した際の 2^k の位の数のうち両方が 1 であれば 1、そうでなければ 0 である。
制約
- 1 \leq T \leq 10^5
- 0 \leq a,s \lt 2^{60}
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は標準入力から与えられる。入力の 1 行目は以下の形式である。
T
その後、 T 個のテストケースが続く。各テストケースは以下の形式で与えられる。
a s
出力
T 行出力せよ。i\ (1 \leq i \leq T) 行目には、i 番目に与えられるテストケースについて問題文中の条件を両方とも満たす非負整数の組 (x,y) が存在するなら Yes を、存在しないなら No を出力せよ。
入力例 1
2 1 8 4 2
出力例 1
Yes No
1 番目のテストケースにおいては、(x,y)=(3,5) などが条件を満たします。
2 番目のテストケースにおいては、条件を満たす非負整数の組 (x,y) は存在しません。
入力例 2
4 201408139683277485 381410962404666524 360288799186493714 788806911317182736 18999951915747344 451273909320288229 962424162689761932 1097438793187620758
出力例 2
No Yes Yes No
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
Solve the following problem for T test cases.
Given are non-negative integers a and s. Is there a pair of non-negative integers (x,y) that satisfies both of the conditions below?
- x\ \text{AND}\ y=a
- x+y=s
What is bitwise \mathrm{AND}?
The bitwise \mathrm{AND} of integers A and B, A\ \mathrm{AND}\ B, is defined as follows:
- When A\ \mathrm{AND}\ B is written in base two, the digit in the 2^k's place (k \geq 0) is 1 if those of A and B are both 1, and 0 otherwise.
Constraints
- 1 \leq T \leq 10^5
- 0 \leq a,s \lt 2^{60}
- All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input. The first line is in the following format:
T
Then, T test cases follow. Each test case is in the following format:
a s
Output
Print T lines. The i-th line (1 \leq i \leq T) should contain Yes if, in the i-th test case, there is a pair of non-negative integers (x,y) that satisfies both of the conditions in the Problem Statement, and No otherwise.
Sample Input 1
2 1 8 4 2
Sample Output 1
Yes No
In the first test case, some pairs such as (x,y)=(3,5) satisfy the conditions.
In the second test case, no pair of non-negative integers satisfies the conditions.
Sample Input 2
4 201408139683277485 381410962404666524 360288799186493714 788806911317182736 18999951915747344 451273909320288229 962424162689761932 1097438793187620758
Sample Output 2
No Yes Yes No