Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
高橋君の家には、高橋君、高橋君の父、高橋君の母の 3 人が住んでおり、全員が毎晩風呂で髪を洗います。
風呂には、高橋君の父、高橋君の母、高橋君の順に入り、それぞれシャンプーを A,B,C ミリリットル使います。
今朝の時点で、ボトルには V ミリリットルのシャンプーが残っていました。このまま補充しない時、初めてシャンプーが不足するのは誰が使おうとした時ですか?
制約
- 1 \leq V,A,B,C \leq 10^5
- 入力に含まれる値は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
V A B C
出力
初めてシャンプーが不足するのが、高橋君の父が使おうとしたときならば F、高橋君の母が使おうとしたときならば M、高橋君が使おうとしたときならば T を出力せよ。
入力例 1
25 10 11 12
出力例 1
T
シャンプーは 25 ミリリットル残っています。
- まず高橋君の父が 10 ミリリットル使い、残りは 15 ミリリットルになります。
- 次に高橋君の母が 11 ミリリットル使い、残りは 4 ミリリットルになります。
- 最後に高橋君が 12 ミリリットル使おうとしますが、4 ミリリットルしか残っておらず、不足しています。
入力例 2
30 10 10 10
出力例 2
F
シャンプーは 30 ミリリットル残っています。
- まず高橋君の父が 10 ミリリットル使い、残りは 20 ミリリットルになります。
- 次に高橋君の母が 10 ミリリットル使い、残りは 10 ミリリットルになります。
- 続いて高橋君が 10 ミリリットル使い、残りは 0 ミリリットルになります。
- 翌日、高橋君の父が 10 ミリリットル使おうとしますが、0 ミリリットルしか残っておらず、不足しています。
入力例 3
100000 1 1 1
出力例 3
M
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
Three people live in Takahashi's house: Takahashi, his father, and his mother. All of them wash their hair in the bathroom each night.
His father, his mother, and Takahashi take a bath in this order and use A, B, and C milliliters of shampoo, respectively.
This morning, the bottle contained V milliliters of shampoo. Without refilling, who will be the first to run short of shampoo to wash their hair?
Constraints
- 1 \leq V,A,B,C \leq 10^5
- All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
V A B C
Output
If the first person to run short of shampoo to wash their hair is Takahashi's father, print F; if it is Takahashi's mother, print M; if it is Takahashi, print T.
Sample Input 1
25 10 11 12
Sample Output 1
T
Now, they have 25 milliliters of shampoo.
- First, Takahashi's father uses 10 milliliters, leaving 15.
- Next, Takahashi's mother uses 11 milliliters, leaving 4.
- Finally, Takahashi tries to use 12 milliliters and runs short of shampoo since only 4 is remaining.
Sample Input 2
30 10 10 10
Sample Output 2
F
Now, they have 30 milliliters of shampoo.
- First, Takahashi's father uses 10 milliliters, leaving 20.
- Next, Takahashi's mother uses 10 milliliters, leaving 10.
- Then, Takahashi uses 10 milliliters, leaving 0.
- Next day, Takahashi's father tries to use 10 milliliters and runs short of shampoo since only 0 is remaining.
Sample Input 3
100000 1 1 1
Sample Output 3
M
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
整数 K が与えられます。
英大文字を A から昇順に K 個繋げて得られる文字列を答えてください。
制約
- K は 1 以上 26 以下の整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
K
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3
出力例 1
ABC
英大文字は A から昇順に A, B, C, ... です。
A から昇順に 3 個繋げて得られる文字列は ABC です。
入力例 2
1
出力例 2
A
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
You are given an integer K.
Print a string that is a concatenation of the first K uppercase English letters in ascending order, starting from A.
Constraints
- K is an integer between 1 and 26, inclusive.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
K
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
3
Sample Output 1
ABC
The uppercase English letters in ascending order are A, B, C, ...
By concatenating the first three uppercase English letters, we get ABC.
Sample Input 2
1
Sample Output 2
A
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
英小文字および英大文字のみからなる文字列 S, T が与えられます。
文字列 S が以下の条件を満たしているか判定してください。
- S の先頭でない英大文字の直前の文字はすべて T に含まれる。より形式的には、2 \leq i \leq |S| なる整数 i について S の i 番目の文字が英大文字ならば、S の i-1 番目の文字は T に含まれる。
制約
- S, T は長さ 1 以上 100 以下の英小文字および英大文字のみからなる文字列
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
S T
出力
S が問題文中の条件を満たしているとき Yes と出力せよ。そうでないとき、No と出力せよ。
入力例 1
AtCoder Total
出力例 1
Yes
S の先頭でない英大文字は 3 番目の文字の C のみです。この直前の文字である t は T に含まれているため、Yes と出力すればよいです。
入力例 2
aBCdE abcdcba
出力例 2
No
S の 3 番目の文字は英大文字 C であり、その直前の文字は B ですが、B は T に含まれていません。
入力例 3
abcde XYZ
出力例 3
Yes
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
You are given strings S and T consisting of lowercase and uppercase English letters.
Determine whether the string S satisfies the following condition:
- Every uppercase letter in S that is not at the beginning is immediately preceded by a character contained in T. More formally, for all integers i such that 2 \leq i \leq |S|, if the i-th character of S is uppercase, then the (i-1)-th character of S is contained in T.
Constraints
- Each of S and T is a string consisting of lowercase and uppercase English letters with length between 1 and 100, inclusive.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S T
Output
If S satisfies the condition in the problem statement, output Yes. Otherwise, output No.
Sample Input 1
AtCoder Total
Sample Output 1
Yes
The only uppercase letter in S that is not at the beginning is the 3rd character C. The immediately preceding character t is contained in T, so output Yes.
Sample Input 2
aBCdE abcdcba
Sample Output 2
No
The 3rd character of S is the uppercase letter C, and its immediately preceding character is B, but B is not contained in T.
Sample Input 3
abcde XYZ
Sample Output 3
Yes
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
この問題は 1 つの入力ファイルに複数のテストケースが含まれる問題です。
はじめに整数 T が与えられます。T 個のテストケースについて次の問題を解いてください。
- N 個の正整数 A_1, A_2, ..., A_N があります。このうち奇数は何個ありますか?
制約
- 1 \leq T \leq 100
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- 1 \leq A_i \leq 10^9
- 入力される値はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。ここで \text{test}_i は i 番目のテストケースを意味する。
T
\text{test}_1
\text{test}_2
\vdots
\text{test}_T
各テストケースは以下の形式で与えられる。
N A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
出力
T 行出力せよ。i 行目には i 番目のテストケースに対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 3 1 2 3 2 20 23 10 6 10 4 1 5 9 8 6 5 1 1 1000000000
出力例 1
2 1 5 0
この入力は 4 個のテストケースが含まれています。
入力の 2 行目と 3 行目が 1 番目のテストケースに対応する入力で、N = 3, A_1 = 1, A_2 = 2, A_3 = 3 になります。
A_1, A_2, A_3 のうち奇数は全部で 2 個なので 1 行目に 2 を出力します。
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
In this problem, an input file contains multiple test cases.
You are first given an integer T. Solve the following problem for T test cases.
- We have N positive integers A_1, A_2, ..., A_N. How many of them are odd?
Constraints
- 1 \leq T \leq 100
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- 1 \leq A_i \leq 10^9
- All values in the input are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format, where \text{test}_i represents the i-th test case:
T
\text{test}_1
\text{test}_2
\vdots
\text{test}_T
Each test case is in the following format:
N A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
Output
Print T lines. The i-th line should contain the answer for the i-th test case.
Sample Input 1
4 3 1 2 3 2 20 23 10 6 10 4 1 5 9 8 6 5 1 1 1000000000
Sample Output 1
2 1 5 0
This input contains four test cases.
The second and third lines correspond to the first test case, where N = 3, A_1 = 1, A_2 = 2, A_3 = 3.
We have two odd numbers in A_1, A_2, and A_3, so the first line should contain 2.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 250 点
問題文
長さ N の数列 A が与えられます。
A のうち丁度 K 要素を自由に選んで消し、残った要素を順序を保って連結した数列を B とします。
( B の最大値 ) - ( B の最小値 ) としてありうる最小値を求めてください。
制約
- 入力は全て整数
- 1 \le K < N \le 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \le A_i \le 10^9
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N K A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
出力
答えを整数として出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 2 3 1 5 4 9
出力例 1
2
A=(3,1,5,4,9) から丁度 2 要素を自由に選んで消すことを考えます。
- 例えば 2 要素目の 1 、 5 要素目の 9 を消すと、消した後の数列 B=(3,5,4) となります。
- このとき B の最大値は 5 、最小値は 3 なので ( B の最大値 ) - ( B の最小値 ) =2 となり、これは達成可能な最小値です。
入力例 2
6 5 1 1 1 1 1 1
出力例 2
0
入力例 3
8 3 31 43 26 6 18 36 22 13
出力例 3
18
Score : 250 points
Problem Statement
You are given a sequence A of length N.
Freely choose exactly K elements from A and remove them, then concatenate the remaining elements in their original order to form a new sequence B.
Find the minimum possible value of this: the maximum value of B minus the minimum value of B.
Constraints
- All inputs are integers.
- 1 \le K < N \le 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \le A_i \le 10^9
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N K A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
Output
Print the answer as an integer.
Sample Input 1
5 2 3 1 5 4 9
Sample Output 1
2
Consider removing exactly two elements from A=(3,1,5,4,9).
- For example, if you remove the 2nd element 1 and the 5th element 9, the resulting sequence is B=(3,5,4).
- In this case, the maximum value of B is 5 and the minimum value is 3, so (maximum value of B) - (minimum value of B) =2, which is the minimum possible value.
Sample Input 2
6 5 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output 2
0
Sample Input 3
8 3 31 43 26 6 18 36 22 13
Sample Output 3
18
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
ある地方に、1 から N の番号がついた N 個の街と、1 から M の番号がついた M 本の道路があります。
i 番目の道路は街 A_i と街 B_i を双方向に結び、長さは C_i です。
好きな街からスタートして同じ街を二度以上通らずに別の街へ移動するときの、通る道路の長さの和としてありえる最大値を求めてください。
制約
- 2 \leq N \leq 10
- 1 \leq M \leq \frac{N(N-1)}{2}
- 1\leq A_i < B_i \leq N
- (A_i,B_i) は相異なる
- 1\leq C_i \leq 10^8
- 入力は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M A_1 B_1 C_1 \vdots A_M B_M C_M
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 4 1 2 1 2 3 10 1 3 100 1 4 1000
出力例 1
1110
4\to 1\to 3\to 2 と移動すると、通る道路の長さの和は 1110 となります。
入力例 2
10 1 5 9 1
出力例 2
1
道路と繋がっていない街が存在するかもしれません。
入力例 3
10 13 1 2 1 1 10 1 2 3 1 3 4 4 4 7 2 4 8 1 5 8 1 5 9 3 6 8 1 6 9 5 7 8 1 7 9 4 9 10 3
出力例 3
20
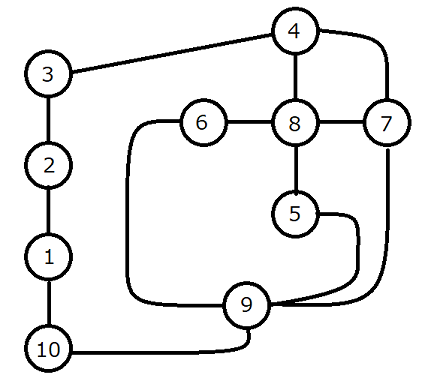
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
A region has N towns numbered 1 to N, and M roads numbered 1 to M.
The i-th road connects town A_i and town B_i bidirectionally with length C_i.
Find the maximum possible total length of the roads you traverse when starting from a town of your choice and getting to another town without passing through the same town more than once.
Constraints
- 2 \leq N \leq 10
- 1 \leq M \leq \frac{N(N-1)}{2}
- 1 \leq A_i < B_i \leq N
- The pairs (A_i,B_i) are distinct.
- 1\leq C_i \leq 10^8
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M A_1 B_1 C_1 \vdots A_M B_M C_M
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
4 4 1 2 1 2 3 10 1 3 100 1 4 1000
Sample Output 1
1110
If you travel as 4\to 1\to 3\to 2, the total length of the roads you traverse is 1110.
Sample Input 2
10 1 5 9 1
Sample Output 2
1
There may be a town that is not connected to a road.
Sample Input 3
10 13 1 2 1 1 10 1 2 3 1 3 4 4 4 7 2 4 8 1 5 8 1 5 9 3 6 8 1 6 9 5 7 8 1 7 9 4 9 10 3
Sample Output 3
20

Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 400 点
問題文
頂点 1, 頂点 2,\ldots, 頂点 N の N 個の頂点からなる木が与えられます。 i 番目 (1\leq i\lt N) の辺は頂点 u _ i と v _ i を結んでいます。
次の操作を好きな回数繰り返すことを考えます。
- 葉である頂点 v を 1 つ選び、頂点 v およびそれに接続する辺をすべて削除する。
頂点 1 を削除するまでに最小で操作を何回行う必要があるか求めてください。
木とは?
木とは、無向グラフのうち連結であって閉路がないものです。 詳しくはこちらをご覧ください: Wikipedia「木 (数学)」葉とは?
木の葉とは、木の頂点のうち次数がたかだか 1 であるものです。制約
- 2\leq N\leq3\times10^5
- 1\leq u _ i\lt v _ i\leq N\ (1\leq i\lt N)
- 与えられるグラフは木
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N
u _ 1 v _ 1
u _ 2 v _ 2
\vdots
u _ {N-1} v _ {N-1}
出力
答えを 1 行で出力せよ。
入力例 1
9 1 2 2 3 2 4 2 5 1 6 6 7 7 8 7 9
出力例 1
5
与えられるグラフは次のようになります。

たとえば、頂点 9,8,7,6,1 の順に選んで操作を行うことで、5 回の操作で頂点 1 を削除することができます。

4 回以下の操作では頂点 1 を削除することはできないため、5 を出力してください。
入力例 2
6 1 2 2 3 2 4 3 5 3 6
出力例 2
1
与えられたグラフにおいて、頂点 1 は葉です。 よって、1 回目の操作で頂点 1 を選んで削除することができます。
入力例 3
24 3 6 7 17 7 20 7 11 14 18 17 21 6 19 5 22 9 24 11 14 6 23 8 17 9 12 4 17 2 15 1 17 3 9 10 16 7 13 2 16 1 16 5 7 1 3
出力例 3
12
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
You are given a tree with N vertices: vertex 1, vertex 2, \ldots, vertex N. The i-th edge (1\leq i\lt N) connects vertex u _ i and vertex v _ i.
Consider repeating the following operation some number of times:
- Choose one leaf vertex v and delete it along with all incident edges.
Find the minimum number of operations required to delete vertex 1.
What is a tree?
A tree is an undirected graph that is connected and has no cycles. For more details, see: Wikipedia "Tree (graph theory)".What is a leaf?
A leaf in a tree is a vertex with a degree of at most 1.Constraints
- 2\leq N\leq3\times10^5
- 1\leq u _ i\lt v _ i\leq N\ (1\leq i\lt N)
- The given graph is a tree.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
u _ 1 v _ 1
u _ 2 v _ 2
\vdots
u _ {N-1} v _ {N-1}
Output
Print the answer in a single line.
Sample Input 1
9 1 2 2 3 2 4 2 5 1 6 6 7 7 8 7 9
Sample Output 1
5
The given graph looks like this:

For example, you can choose vertices 9,8,7,6,1 in this order to delete vertex 1 in five operations.

Vertex 1 cannot be deleted in four or fewer operations, so print 5.
Sample Input 2
6 1 2 2 3 2 4 3 5 3 6
Sample Output 2
1
In the given graph, vertex 1 is a leaf. Hence, you can choose and delete vertex 1 in the first operation.
Sample Input 3
24 3 6 7 17 7 20 7 11 14 18 17 21 6 19 5 22 9 24 11 14 6 23 8 17 9 12 4 17 2 15 1 17 3 9 10 16 7 13 2 16 1 16 5 7 1 3
Sample Output 3
12
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 450 点
問題文
(1,2,3,\ldots,2^{N}) の順列 P=(P_0,P_1,\ldots,P_{2^{N}-1}) が与えられます。
あなたは次の操作を何回でも(0 回でもよい)行うことができます。
- 0 \leq a \times 2^{b} < (a+1) \times 2^{b} \leq 2^{N} を満たす非負整数 a,b を選び、P_{a \times 2^{b}}, P_{a\times 2^{b}+1},\ldots,P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1} を反転する。ここで、P_{a \times 2^{b}},P_{a \times 2^{b}+1},\ldots,P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1} を反転するとは、P_{a \times 2^{b}}, P_{a\times 2^{b}+1},\ldots,P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1} を P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1}, P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-2},\ldots,P_{a \times 2^{b}} に同時に置き換えることを意味する。
操作を繰り返して得られる P のうち、辞書順最小のものを求めてください。
T 個のテストケースが与えられるので、それぞれについて答えを求めてください。
制約
- 1 \leq T \leq 10^{5}
- 1 \leq N \leq 18
- P は (1,2,3,\ldots,2^{N}) の順列
- 各入力ファイルについて、すべてのテストケースの 2^N の総和は 3 \times 10^{5} 以下
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
T
\textrm{case}_1
\textrm{case}_2
\vdots
\textrm{case}_T
\textrm{case}_i は i 番目のテストケースを表し、以下の形式で与えられる。
N
P_0 P_1 \ldots P_{2^N-1}
出力
T 行出力せよ。i 行目 (1 \leq i \leq T) には i 番目のテストケースに対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 1 1 2 2 1 3 4 2 2 2 3 4 1 3 8 3 4 2 1 5 7 6
出力例 1
1 2 1 3 2 4 1 4 2 3 1 5 6 7 2 4 3 8
1 番目のテストケースにおいて、P に対して操作を一回も行わないとき、P=(1,2) となります。これは辞書順で最小の順列です。よって答えは(1,2) です。
2 番目のテストケースにおいて、a=1,b=1 を選んで操作を行うと P=(1,3,2,4) となります。P に対して何回操作を行っても (1,3,2,4) より辞書順で小さい順列を得られません。よって答えは (1,3,2,4) です。
3 番目のテストケースにおいて、以下の順番で操作を行うことで、P=(1,4,2,3) が得られます。
- a=0,b=1 を選んで操作を行う。P=(3,2,4,1) となる。
- a=0,b=2 を選んで操作を行う。P=(1,4,2,3) となる。
P に対して何回操作を行っても (1,4,2,3) より辞書順で小さい順列を得られません。よって答えは (1,4,2,3) です。
Score : 450 points
Problem Statement
You are given a permutation P=(P_0,P_1,\ldots,P_{2^{N}-1}) of (1,2,3,\ldots,2^{N}).
You can perform the following operation any number of times (possibly zero):
- Choose non-negative integers a,b satisfying 0 \leq a \times 2^{b} < (a+1) \times 2^{b} \leq 2^{N}, and reverse P_{a \times 2^{b}}, P_{a\times 2^{b}+1},\ldots,P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1}. Here, reversing P_{a \times 2^{b}}, P_{a\times 2^{b}+1},\ldots,P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1} means simultaneously replacing P_{a \times 2^{b}}, P_{a\times 2^{b}+1},\ldots,P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1} with P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-1}, P_{(a+1) \times 2^{b}-2},\ldots,P_{a \times 2^{b}}.
Find the lexicographically smallest permutation P that can be obtained by repeating the operation.
You are given T test cases, so find the answer for each.
Constraints
- 1 \leq T \leq 10^{5}
- 1 \leq N \leq 18
- P is a permutation of (1,2,3,\ldots,2^{N}).
- For each input file, the sum of 2^N over all test cases is at most 3 \times 10^{5}.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from standard input in the following format:
T
\textrm{case}_1
\textrm{case}_2
\vdots
\textrm{case}_T
\textrm{case}_i represents the i-th test case and is given in the following format:
N
P_0 P_1 \ldots P_{2^N-1}
Output
Output T lines. The i-th line (1 \leq i \leq T) should contain the answer to the i-th test case.
Sample Input 1
4 1 1 2 2 1 3 4 2 2 2 3 4 1 3 8 3 4 2 1 5 7 6
Sample Output 1
1 2 1 3 2 4 1 4 2 3 1 5 6 7 2 4 3 8
In the first test case, when no operation is performed on P, P=(1,2). This is the lexicographically smallest permutation. Thus, the answer is (1,2).
In the second test case, when we perform the operation with a=1,b=1, P becomes (1,3,2,4). No matter how many operations we perform on P, we cannot obtain a permutation lexicographically smaller than (1,3,2,4). Thus, the answer is (1,3,2,4).
In the third test case, by performing operations in the following order, we can obtain P=(1,4,2,3):
- Perform the operation with a=0,b=1. P becomes (3,2,4,1).
- Perform the operation with a=0,b=2. P becomes (1,4,2,3).
No matter how many operations we perform on P, we cannot obtain a permutation lexicographically smaller than (1,4,2,3). Thus, the answer is (1,4,2,3).
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 525 点
問題文
すぬけくんは、AtCoder Land の新たな目玉アトラクションとして迷路を建設しようと考えています。 迷路は縦 N 行・横 M 列のグリッドとして表され、右上のマスの上端が入口、右下のマスの下端が出口です。 すぬけくんは、隣接するマスの間に適切に壁を配置することで迷路を作ります。
すぬけくんは簡単な迷路が大好きなので、入口から出口までの道順は枝分かれを一切持たずにちょうど K マスを通るようなものにしたいです。 そのような迷路を作ることが可能か判定し、可能ならば 1 つ構築してください。
例えば以下の図では、N=3,M=3 であり、実線で書かれているところに壁が配置されています(入口と出口を除く外周部には必ず壁が配置されるものとします)。 このとき、入口から出口までの道順は枝分かれを一切持たずにちょうど 7 マスを通っています。

厳密には以下の通りです。
縦 N 行・横 M 列のグリッドがあります。 上から i 行目、左から j 列目のマスを (i,j) と表記します。 あなたは、辺で隣接する任意の 2 マスの間それぞれについて壁を置くか置かないか決めることができます。 壁を置く場所をうまく定めることで以下の条件を満たすことができるか判定し、できるならば実際に 1 つ構築してください。
NM 頂点からなる無向グラフ G を考える。G の各頂点は 2 つの整数の組 (i,j)\ (1\leq i\leq N, 1\leq j\leq M) によって互いに相異なるラベルが付けられている。 相異なる 2 頂点 (i_1,j_1),(i_2,j_2) は、|i_1-i_2|+|j_1-j_2|=1 かつグリッド上の 2 マス (i_1,j_1),(i_2,j_2) の間に壁が置かれていない場合、またその場合に限り辺で結ばれている。
条件:K 頂点からなり 2 頂点 (1,M),(N,M) を結ぶような単純パスが存在し、また 2 頂点 (1,M),(N,M) を含む連結成分はこのパスのみからなる。
制約
- 2\leq N \leq 100
- 1\leq M \leq 100
- 1\leq K\leq NM
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M K
出力
条件を満たす壁の配置が存在しないならば No を出力し、存在するならばそのうちの 1 つを以下の形式で出力せよ。
条件を満たす壁の配置が複数存在する場合は、そのどれを出力してもよい。
複雑な出力形式のため、下記の出力例も参考にしてください。
Yes +++++ \dots +++S+ +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +?+?+ \dots +?+?+ +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +?+?+ \dots +?+?+ \vdots +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +?+?+ \dots +?+?+ +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +++++ \dots +++G+
ここで、S, G, +, o はそれぞれ入口、出口、壁、マスを表し、マスとマスの間にある ? は壁を置くことができる場所である。
横に隣接する 2 マスの間にある ? は、壁を置くならば | で、壁を置かないならば . で置き換えよ。
縦に隣接する 2 マスの間にある ? は、壁を置くならば - で、壁を置かないならば . で置き換えよ。
厳密には以下の通りである。
- 出力は 2N+2 行からなり、1 行目には文字列
Yesを、2 行目から 2N+2 行目には以下で説明されるように長さ 2M+1 の文字列を出力する。- 2 行目には、2M-1 個の
+,S,+をこの順に連結して出力する。 - 1+2i 行目 (1\leq i\leq N) には、
+,o, c_{i,1},o, c_{i,2}, \dots, c_{i,M-1},o,+をこの順に連結して出力する。 ここで、c_{i,j} はマス (i,j),(i,j+1) の間に壁を置くならば|、置かないならば.である。 - 2+2i 行目 (1\leq i\leq N-1) には、
+, r_{i,1},+, r_{i,2},+, \dots,+, r_{i,M},+をこの順に連結して出力する。 ここで、r_{i,j} はマス (i,j),(i+1,j) の間に壁を置くならば-、置かないならば.である。 - 2N+2 行目には、2M-1 個の
+,G,+をこの順に連結して出力する。
- 2 行目には、2M-1 個の
入力例 1
3 3 7
出力例 1
Yes +++++S+ +o.o.o+ +.+-+-+ +o.o.o+ +-+-+.+ +o.o|o+ +++++G+
問題文中の図と同じ壁の配置です。
入力例 2
3 3 2
出力例 2
No
入力例 3
4 1 4
出力例 3
Yes +S+ +o+ +.+ +o+ +.+ +o+ +.+ +o+ +G+
Score : 525 points
Problem Statement
Snuke is planning to build a maze as a new attraction in AtCoder Land. The maze is represented as a grid with N rows and M columns, with the top edge of the top-right cell being the entrance and the bottom edge of the bottom-right cell being the exit. He will create the maze by appropriately placing walls between adjacent cells.
He loves simple mazes, so he wants the path from the entrance to the exit to pass through exactly K cells without any branches. Determine if it is possible to create such a maze, and if possible, construct one.
For example, in the following figure, N=3 and M=3, and walls are placed at the solid lines (walls are always placed around the outer perimeter except for the entrance and exit). In this case, the path from the entrance to the exit passes through exactly 7 cells without any branches.

Below is a formal statement.
There is a grid with N rows and M columns. Let (i, j) denote the cell at the i-th row from the top and j-th column from the left. For each pair of side-adjacent cells, you can decide whether to place a wall between them. Determine whether it is possible to place walls to satisfy the following condition, and if it is possible, construct one such placement.
Consider an undirected graph G with NM vertices. Each vertex of G is uniquely labeled by a pair of integers (i,j)\ (1\leq i\leq N, 1\leq j\leq M). Two distinct vertices (i_1,j_1) and (i_2,j_2) are connected by an edge if and only if |i_1-i_2|+|j_1-j_2|=1 and there is no wall between the corresponding cells (i_1,j_1) and (i_2,j_2) on the grid.
Condition: there exists a simple path with K vertices that connects the two vertices (1,M) and (N,M), and the connected component containing the vertices (1,M) and (N,M) consists only of this path.
Constraints
- 2\leq N \leq 100
- 1\leq M \leq 100
- 1\leq K\leq NM
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M K
Output
If there is no placement of walls that satisfies the condition, print No. Otherwise, print one such placement in the following format. If multiple valid placements exist, any of them can be printed.
See also the sample outputs below to better understand the complicated output format.
Yes +++++ \dots +++S+ +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +?+?+ \dots +?+?+ +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +?+?+ \dots +?+?+ \vdots +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +?+?+ \dots +?+?+ +o?o? \dots ?o?o+ +++++ \dots +++G+
Here, S, G, +, and o represent the entrance, exit, a wall, and a cell, respectively, and ? between cells represents a position where a wall can be placed. Replace ? between two horizontally adjacent cells with | if a wall is placed, and . otherwise. Replace ? between two vertically adjacent cells with - if a wall is placed, and . otherwise.
Below is a formal instruction.
- The output should consist of 2N+2 lines. Line 1 should contain the string
Yes, and lines 2 to 2N+2 should contain strings of length 2M+1 as described below.- Line 2 should be a concatenation of
+repeated 2M-1 times,S, and+, in this order. - Line 1+2i (1\leq i\leq N) should be a concatenation of
+,o, c_{i,1},o, c_{i,2}, \dots, c_{i,M-1},o,+, in this order. Here, c_{i,j} is|if a wall is placed between cells (i,j) and (i,j+1), and.otherwise. - Line 2+2i (1\leq i\leq N-1) should be a concatenation of
+, r_{i,1},+, r_{i,2},+, \dots,+, r_{i,M},+, in this order. Here, r_{i,j} is-if a wall is placed between cells (i,j) and (i+1,j), and.otherwise. - Line 2N+2 should be a concatenation of
+repeated 2M-1 times,G, and+, in this order.
- Line 2 should be a concatenation of
Sample Input 1
3 3 7
Sample Output 1
Yes +++++S+ +o.o.o+ +.+-+-+ +o.o.o+ +-+-+.+ +o.o|o+ +++++G+
This is the same placement of walls as in the figure in the problem statement.
Sample Input 2
3 3 2
Sample Output 2
No
Sample Input 3
4 1 4
Sample Output 3
Yes +S+ +o+ +.+ +o+ +.+ +o+ +.+ +o+ +G+