Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
N 問の問題からなるコンテストが開催され、i\ (1\leq i\leq N) 問目の配点は A_i 点でした。
すぬけくんはこのコンテストに参加し、B_1,B_2,\ldots,B_M 問目の M 問を解きました。 すぬけくんの総得点を求めてください。
ただし、総得点とは解いた問題の配点の総和を意味するものとします。
制約
- 1\leq M \leq N \leq 100
- 1\leq A_i \leq 100
- 1\leq B_1 < B_2 < \ldots < B_M \leq N
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M A_1 A_2 \dots A_N B_1 B_2 \dots B_M
出力
答えを整数として出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 2 10 20 30 1 3
出力例 1
40
すぬけくんは 1 問目と 3 問目を解きました。 配点はそれぞれ 10 点と 30 点なので、総得点は 10+30=40 点です。
入力例 2
4 1 1 1 1 100 4
出力例 2
100
入力例 3
8 4 22 75 26 45 72 81 47 29 4 6 7 8
出力例 3
202
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
There was a contest with N problems. The i-th (1\leq i\leq N) problem was worth A_i points.
Snuke took part in this contest and solved M problems: the B_1-th, B_2-th, \ldots, and B_M-th ones. Find his total score.
Here, the total score is defined as the sum of the points for the problems he solved.
Constraints
- 1\leq M \leq N \leq 100
- 1\leq A_i \leq 100
- 1\leq B_1 < B_2 < \ldots < B_M \leq N
- All values in the input are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M A_1 A_2 \dots A_N B_1 B_2 \dots B_M
Output
Print the answer as an integer.
Sample Input 1
3 2 10 20 30 1 3
Sample Output 1
40
Snuke solved the 1-st and 3-rd problems, which are worth 10 and 30 points, respectively. Thus, the total score is 10+30=40 points.
Sample Input 2
4 1 1 1 1 100 4
Sample Output 2
100
Sample Input 3
8 4 22 75 26 45 72 81 47 29 4 6 7 8
Sample Output 3
202
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
果物屋さんでりんごが売られています。
あなたは次の操作を好きな順で好きなだけ繰り返すことができます。
- X 円を払ってりんごを 1 個手に入れる。
- Y 円を払ってりんごを 3 個手に入れる。
りんごをちょうど N 個手に入れるには最低何円必要ですか?
制約
- 1 \leq X \leq Y \leq 100
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- 入力される値はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
X Y N
出力
答えを整数として出力せよ。
入力例 1
10 25 10
出力例 1
85
25 円払って 3 個のりんごを手に入れる操作を 3 回繰り返した後、10 円払って 1 個のりんごを手に入れると丁度 10 個のりんごを手に入れられます。このときあなたは 85 円を消費します。
これより少ない金額でちょうど 10 個のりんごを手に入れることはできないので、答えは 85 円になります。
入力例 2
10 40 10
出力例 2
100
10 円払って 1 個のりんごを手に入れる操作を 10 回繰り返すのが最適です。
入力例 3
100 100 2
出力例 3
200
100 円を払って 1 個のりんごを手に入れる操作を 2 回繰り返す以外に ちょうど 2 個のりんごを手に入れる方法はありません。
入力例 4
100 100 100
出力例 4
3400
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
A fruit store sells apples.
You may perform the following operations as many times as you want in any order:
- Buy one apple for X yen (the currency in Japan).
- Buy three apples for Y yen.
How much yen do you need to pay to obtain exactly N apples?
Constraints
- 1 \leq X \leq Y \leq 100
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
X Y N
Output
Print the answer as an integer.
Sample Input 1
10 25 10
Sample Output 1
85
Buy three apples for 25 yen three times and one apple for 10 yen, and you will obtain exactly 10 apples for a total of 85 yen.
You cannot obtain exactly 10 apples for a lower cost, so the answer is 85 yen.
Sample Input 2
10 40 10
Sample Output 2
100
It is optimal to buy an apple for 10 yen 10 times.
Sample Input 3
100 100 2
Sample Output 3
200
The only way to obtain exactly 2 apples is to buy an apple for 100 yen twice.
Sample Input 4
100 100 100
Sample Output 4
3400
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
縦 H マス、横 W マスのグリッドがあります。上から i 行目、左から j 列目のマスを (i,j) と表します。
各マスの状態は文字 C_{i,j} で表されます。C_{i,j} が . ならば (i, j) には何も置かれておらず、 # ならば箱が 1 個置かれています。
1 \leq j \leq W を満たす整数 j に対して、整数 X_j を次のように定義します。
- j 列目に置かれている箱の個数。言い換えると、C_{i,j} が
#であるような整数 i の個数。
X_1, X_2, \dots, X_W をすべて求めてください。
制約
- 1 \leq H \leq 1000
- 1 \leq W \leq 1000
- H, W は整数
- C_{i, j} は
.または#
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
H W
C_{1,1}C_{1,2}\dots C_{1,W}
C_{2,1}C_{2,2}\dots C_{2,W}
\vdots
C_{H,1}C_{H,2}\dots C_{H,W}
出力
X_1, X_2, \dots, X_W を以下の形式に従って出力せよ。
X_1 X_2 \dots X_W
入力例 1
3 4 #..# .#.# .#.#
出力例 1
1 2 0 3
1 列目の箱が置かれているマスは (1, 1) の 1 ヵ所です。よって X_1 = 1 です。
2 列目の箱が置かれているマスは (2, 2), (3, 2) の 2 ヵ所です。よって X_2 = 2 です。
3 列目の箱が置かれているマスは存在しません。よって X_3 = 0 です。
4 列目の箱が置かれているマスは (1, 4), (2, 4), (3, 4) の 3 ヵ所です。よって X_4 = 3 です。
よって (X_1, X_2, X_3, X_4) = (1, 2, 0, 3) が答えとなります。
入力例 2
3 7 ....... ....... .......
出力例 2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
箱が置かれているマスが存在しない場合もあります。
入力例 3
8 3 .#. ### .#. .#. .## ..# ##. .##
出力例 3
2 7 4
入力例 4
5 47 .#..#..#####..#...#..#####..#...#...###...##### .#.#...#.......#.#...#......##..#..#...#..#.... .##....#####....#....#####..#.#.#..#......##### .#.#...#........#....#......#..##..#...#..#.... .#..#..#####....#....#####..#...#...###...#####
出力例 4
0 5 1 2 2 0 0 5 3 3 3 3 0 0 1 1 3 1 1 0 0 5 3 3 3 3 0 0 5 1 1 1 5 0 0 3 2 2 2 2 0 0 5 3 3 3 3
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
There is a grid with H rows from top to bottom and W columns from left to right. Let (i, j) denote the square at the i-th row from the top and j-th column from the left.
The squares are described by characters C_{i,j}. If C_{i,j} is ., (i, j) is empty; if it is #, (i, j) contains a box.
For integers j satisfying 1 \leq j \leq W, let the integer X_j defined as follows.
- X_j is the number of boxes in the j-th column. In other words, X_j is the number of integers i such that C_{i,j} is
#.
Find all of X_1, X_2, \dots, X_W.
Constraints
- 1 \leq H \leq 1000
- 1 \leq W \leq 1000
- H and W are integers.
- C_{i, j} is
.or#.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
H W
C_{1,1}C_{1,2}\dots C_{1,W}
C_{2,1}C_{2,2}\dots C_{2,W}
\vdots
C_{H,1}C_{H,2}\dots C_{H,W}
Output
Print X_1, X_2, \dots, X_W in the following format:
X_1 X_2 \dots X_W
Sample Input 1
3 4 #..# .#.# .#.#
Sample Output 1
1 2 0 3
In the 1-st column, one square, (1, 1), contains a box. Thus, X_1 = 1.
In the 2-nd column, two squares, (2, 2) and (3, 2), contain a box. Thus, X_2 = 2.
In the 3-rd column, no squares contain a box. Thus, X_3 = 0.
In the 4-th column, three squares, (1, 4), (2, 4), and (3, 4), contain a box. Thus, X_4 = 3.
Therefore, the answer is (X_1, X_2, X_3, X_4) = (1, 2, 0, 3).
Sample Input 2
3 7 ....... ....... .......
Sample Output 2
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
There may be no square that contains a box.
Sample Input 3
8 3 .#. ### .#. .#. .## ..# ##. .##
Sample Output 3
2 7 4
Sample Input 4
5 47 .#..#..#####..#...#..#####..#...#...###...##### .#.#...#.......#.#...#......##..#..#...#..#.... .##....#####....#....#####..#.#.#..#......##### .#.#...#........#....#......#..##..#...#..#.... .#..#..#####....#....#####..#...#...###...#####
Sample Output 4
0 5 1 2 2 0 0 5 3 3 3 3 0 0 1 1 3 1 1 0 0 5 3 3 3 3 0 0 5 1 1 1 5 0 0 3 2 2 2 2 0 0 5 3 3 3 3
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
人 1 、人 2 、\ldots 、人 N の N 人の人がルーレットの賭けに参加しました。 このルーレットの出目は、0 から 36 までの 37 個の整数のうちいずれかです。 i = 1, 2, \ldots, N について、人 i は 37 個の目のうち C_i 個の目 A_{i, 1}, A_{i, 2}, \ldots, A_{i, C_i} に賭けました。
ルーレットが回され、出目は X でした。 X に賭けた人たちのうち、賭けた目の個数が最も少ない人たちの番号を昇順にすべて出力してください。
より形式的には、1 以上 N 以下の整数 i であって、下記の 2 つの条件をともに満たすものを昇順にすべて出力してください。
- 人 i は X に賭けている。
- 任意の j = 1, 2, \ldots, N について「人 j が X に賭けているならば、C_i \leq C_j 」が成り立つ。
出力するべき番号が 1 つも無い場合もあることに注意してください(入力例2を参照)。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- 1 \leq C_i \leq 37
- 0 \leq A_{i, j} \leq 36
- 任意の i = 1, 2, \ldots, N について、A_{i, 1}, A_{i, 2}, \ldots, A_{i, C_i} はすべて異なる。
- 0 \leq X \leq 36
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N
C_1
A_{1, 1} A_{1, 2} \ldots A_{1, C_1}
C_2
A_{2, 1} A_{2, 2} \ldots A_{2, C_2}
\vdots
C_N
A_{N, 1} A_{N, 2} \ldots A_{N, C_N}
X
出力
出力するべき番号を昇順にすベて並べた列を、B_1, B_2, \ldots, B_K とする。 下記の形式にしたがい、1 行目には出力するべき番号の個数 K を、 2 行目には B_1, B_2, \ldots, B_K を空白区切りで、それぞれ出力せよ。
K B_1 B_2 \ldots B_K
入力例 1
4 3 7 19 20 4 4 19 24 0 2 26 10 3 19 31 24 19
出力例 1
2 1 4
ルーレットが回され、出目は 19 でした。 19 に賭けた人は人 1 、人 2 、人 4 の 3 人であり、それぞれが賭けた目の個数は 3, 4, 3 です。 よって、19 に賭けた人のうち、賭けた目の個数が最も少ない人は人 1 と人 4 の 2 人です。
入力例 2
3 1 1 1 2 1 3 0
出力例 2
0
ルーレットが回され出目は 0 でしたが、0 に賭けた人は一人もいないため、 出力するべき番号は 1 つもありません。
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
N people, person 1, person 2, \ldots, person N, are playing roulette. The outcome of a spin is one of the 37 integers from 0 to 36. For each i = 1, 2, \ldots, N, person i has bet on C_i of the 37 possible outcomes: A_{i, 1}, A_{i, 2}, \ldots, A_{i, C_i}.
The wheel has been spun, and the outcome is X. Print the numbers of all people who have bet on X with the fewest bets, in ascending order.
More formally, print all integers i between 1 and N, inclusive, that satisfy both of the following conditions, in ascending order:
- Person i has bet on X.
- For each j = 1, 2, \ldots, N, if person j has bet on X, then C_i \leq C_j.
Note that there may be no number to print (see Sample Input 2).
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 100
- 1 \leq C_i \leq 37
- 0 \leq A_{i, j} \leq 36
- A_{i, 1}, A_{i, 2}, \ldots, A_{i, C_i} are all different for each i = 1, 2, \ldots, N.
- 0 \leq X \leq 36
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
C_1
A_{1, 1} A_{1, 2} \ldots A_{1, C_1}
C_2
A_{2, 1} A_{2, 2} \ldots A_{2, C_2}
\vdots
C_N
A_{N, 1} A_{N, 2} \ldots A_{N, C_N}
X
Output
Let B_1, B_2, \ldots, B_K be the sequence of numbers to be printed in ascending order. Using the following format, print the count of numbers to be printed, K, on the first line, and B_1, B_2, \ldots, B_K separated by spaces on the second line:
K B_1 B_2 \ldots B_K
Sample Input 1
4 3 7 19 20 4 4 19 24 0 2 26 10 3 19 31 24 19
Sample Output 1
2 1 4
The wheel has been spun, and the outcome is 19. The people who has bet on 19 are person 1, person 2, and person 4, and the number of their bets are 3, 4, and 3, respectively. Therefore, among the people who has bet on 19, the ones with the fewest bets are person 1 and person 4.
Sample Input 2
3 1 1 1 2 1 3 0
Sample Output 2
0
The wheel has been spun and the outcome is 0, but no one has bet on 0, so there is no number to print.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
1 以上 N 以下の整数からなる集合が M 個あり、順に S_1, S_2, \dots, S_M と呼びます。
S_i は C_i 個の整数 a_{i, 1}, a_{i, 2}, \dots, a_{i, C_i} からなります。
M 個の集合から 1 個以上の集合を選ぶ方法は 2^M-1 通りあります。
このうち、次の条件を満たす選び方は何通りありますか?
- 1 \leq x \leq N を満たす全ての整数 x に対して、選んだ集合の中に x を含む集合が少なくとも 1 個存在する。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 10
- 1 \leq M \leq 10
- 1 \leq C_i \leq N
- 1 \leq a_{i,1} \lt a_{i,2} \lt \dots \lt a_{i,C_i} \leq N
- 入力される値は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M
C_1
a_{1,1} a_{1,2} \dots a_{1,C_1}
C_2
a_{2,1} a_{2,2} \dots a_{2,C_2}
\vdots
C_M
a_{M,1} a_{M,2} \dots a_{M,C_M}
出力
問題文の条件を満たす集合の選び方の数を出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 3 2 1 2 2 1 3 1 2
出力例 1
3
入力で与えられている集合はそれぞれ S_1 = \lbrace 1, 2 \rbrace, S_2 = \lbrace 1, 3 \rbrace, S_3 = \lbrace 2 \rbrace です。
問題文の条件を満たす集合の選び方は次の 3 通りです。
- S_1, S_2 を選ぶ。
- S_1, S_2, S_3 を選ぶ。
- S_2, S_3 を選ぶ。
入力例 2
4 2 2 1 2 2 1 3
出力例 2
0
問題文の条件を満たす選び方が存在しない場合もあります。
入力例 3
6 6 3 2 3 6 3 2 4 6 2 3 6 3 1 5 6 3 1 3 6 2 1 4
出力例 3
18
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
There are M sets, called S_1, S_2, \dots, S_M, consisting of integers between 1 and N.
S_i consists of C_i integers a_{i, 1}, a_{i, 2}, \dots, a_{i, C_i}.
There are (2^M-1) ways to choose one or more sets from the M sets.
How many of them satisfy the following condition?
- For all integers x such that 1 \leq x \leq N, there is at least one chosen set containing x.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 10
- 1 \leq M \leq 10
- 1 \leq C_i \leq N
- 1 \leq a_{i,1} \lt a_{i,2} \lt \dots \lt a_{i,C_i} \leq N
- All values in the input are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M
C_1
a_{1,1} a_{1,2} \dots a_{1,C_1}
C_2
a_{2,1} a_{2,2} \dots a_{2,C_2}
\vdots
C_M
a_{M,1} a_{M,2} \dots a_{M,C_M}
Output
Print the number of ways to choose sets that satisfy the conditions in the Problem Statement.
Sample Input 1
3 3 2 1 2 2 1 3 1 2
Sample Output 1
3
The sets given in the input are S_1 = \lbrace 1, 2 \rbrace, S_2 = \lbrace 1, 3 \rbrace, S_3 = \lbrace 2 \rbrace.
The following three ways satisfy the conditions in the Problem Statement:
- choosing S_1, S_2;
- choosing S_1, S_2, S_3;
- choosing S_2, S_3.
Sample Input 2
4 2 2 1 2 2 1 3
Sample Output 2
0
There may be no way to choose sets that satisfies the conditions in the Problem Statement.
Sample Input 3
6 6 3 2 3 6 3 2 4 6 2 3 6 3 1 5 6 3 1 3 6 2 1 4
Sample Output 3
18
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
ある地方に、1 から N の番号がついた N 個の街と、1 から M の番号がついた M 本の道路があります。
i 番目の道路は街 A_i と街 B_i を双方向に結び、長さは C_i です。
好きな街からスタートして同じ街を二度以上通らずに別の街へ移動するときの、通る道路の長さの和としてありえる最大値を求めてください。
制約
- 2 \leq N \leq 10
- 1 \leq M \leq \frac{N(N-1)}{2}
- 1\leq A_i < B_i \leq N
- (A_i,B_i) は相異なる
- 1\leq C_i \leq 10^8
- 入力は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M A_1 B_1 C_1 \vdots A_M B_M C_M
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 4 1 2 1 2 3 10 1 3 100 1 4 1000
出力例 1
1110
4\to 1\to 3\to 2 と移動すると、通る道路の長さの和は 1110 となります。
入力例 2
10 1 5 9 1
出力例 2
1
道路と繋がっていない街が存在するかもしれません。
入力例 3
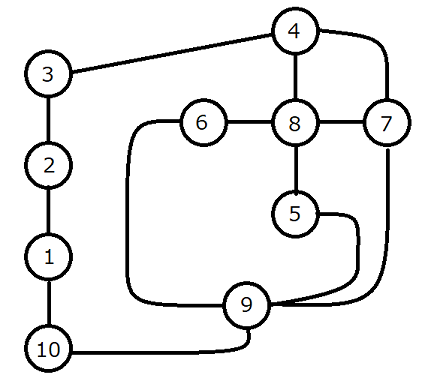
10 13 1 2 1 1 10 1 2 3 1 3 4 4 4 7 2 4 8 1 5 8 1 5 9 3 6 8 1 6 9 5 7 8 1 7 9 4 9 10 3
出力例 3
20
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
A region has N towns numbered 1 to N, and M roads numbered 1 to M.
The i-th road connects town A_i and town B_i bidirectionally with length C_i.
Find the maximum possible total length of the roads you traverse when starting from a town of your choice and getting to another town without passing through the same town more than once.
Constraints
- 2 \leq N \leq 10
- 1 \leq M \leq \frac{N(N-1)}{2}
- 1 \leq A_i < B_i \leq N
- The pairs (A_i,B_i) are distinct.
- 1\leq C_i \leq 10^8
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M A_1 B_1 C_1 \vdots A_M B_M C_M
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
4 4 1 2 1 2 3 10 1 3 100 1 4 1000
Sample Output 1
1110
If you travel as 4\to 1\to 3\to 2, the total length of the roads you traverse is 1110.
Sample Input 2
10 1 5 9 1
Sample Output 2
1
There may be a town that is not connected to a road.
Sample Input 3
10 13 1 2 1 1 10 1 2 3 1 3 4 4 4 7 2 4 8 1 5 8 1 5 9 3 6 8 1 6 9 5 7 8 1 7 9 4 9 10 3
Sample Output 3
20

Time Limit: 4 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 400 点
問題文
N = 2^{20} 項からなる数列 A = (A_0, A_1, \dots, A_{N - 1}) があります。はじめ、全ての要素は -1 です。
Q 個のクエリを順番に処理してください。i \, (1 \leq i \leq Q) 個目のクエリは t_i = 1 または t_i = 2 を満たす整数 t_i および整数 x_i で表され、内容は以下の通りです。
- t_i = 1 のとき、以下の処理を順番に行う。
- 整数 h を h = x_i で定める。
- A_{h \bmod N} \neq -1 である間、h の値を 1 増やすことを繰り返す。この問題の制約下でこの操作が有限回で終了することは証明できる。
- A_{h \bmod N} の値を x_i で書き換える。
- t_i = 2 のとき、その時点での A_{x_i \bmod N} の値を出力する。
なお、整数 a, b に対し、a を b で割った余りを a \bmod b と表します。
制約
- 1 \leq Q \leq 2 \times 10^5
- t_i \in \{ 1, 2 \} \, (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- 0 \leq x_i \leq 10^{18} \, (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- t_i = 2 であるような i \, (1 \leq i \leq Q) が 1 つ以上存在する。
- 入力は全て整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
Q
t_1 x_1
\vdots
t_{Q} x_{Q}
出力
t_i = 2 であるようなクエリに対し、それぞれ答えを 1 行に出力せよ。そのようなクエリが 1 つ以上存在することは保証される。
入力例 1
4 1 1048577 1 1 2 2097153 2 3
出力例 1
1048577 -1
x_1 \bmod N = 1 であるので、1 番目のクエリによって A_1 = 1048577 となります。
2 番目のクエリにおいて、はじめ h = x_2 ですが、A_{h \bmod N} = A_{1} \neq -1 であるので h の値を 1 増やします。すると A_{h \bmod N} = A_{2} = -1 となるので、このクエリによって A_2 = 1 となります。
3 番目のクエリにおいて、A_{x_3 \bmod N} = A_{1} = 1048577 を出力します。
4 番目のクエリにおいて、A_{x_4 \bmod N} = A_{3} = -1 を出力します。
この問題において N = 2^{20} = 1048576 は定数であり、入力では与えられないことに注意してください。
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
There is a sequence A = (A_0, A_1, \dots, A_{N - 1}) with N = 2^{20} terms. Initially, every term is -1.
Process Q queries in order. The i-th query (1 \leq i \leq Q) is described by an integer t_i such that t_i = 1 or t_i = 2, and another integer x_i, as follows.
- If t_i = 1, do the following in order.
- Define an integer h as h = x_i.
- While A_{h \bmod N} \neq -1, keep adding 1 to h. We can prove that this process ends after finite iterations under the Constraints of this problem.
- Replace the value of A_{h \bmod N} with x_i.
- If t_i = 2, print the value of A_{x_i \bmod N} at that time.
Here, for integers a and b, a \bmod b denotes the remainder when a is divided by b.
Constraints
- 1 \leq Q \leq 2 \times 10^5
- t_i \in \{ 1, 2 \} \, (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- 0 \leq x_i \leq 10^{18} \, (1 \leq i \leq Q)
- There is at least one i (1 \leq i \leq Q) such that t_i = 2.
- All values in input are integers.
Input
Input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
Q
t_1 x_1
\vdots
t_{Q} x_{Q}
Output
For each query with t_i = 2, print the response in one line. It is guaranteed that there is at least one such query.
Sample Input 1
4 1 1048577 1 1 2 2097153 2 3
Sample Output 1
1048577 -1
We have x_1 \bmod N = 1, so the first query sets A_1 = 1048577.
In the second query, initially we have h = x_2, for which A_{h \bmod N} = A_{1} \neq -1, so we add 1 to h. Now we have A_{h \bmod N} = A_{2} = -1, so this query sets A_2 = 1.
In the third query, we print A_{x_3 \bmod N} = A_{1} = 1048577.
In the fourth query, we print A_{x_4 \bmod N} = A_{3} = -1.
Note that, in this problem, N = 2^{20} = 1048576 is a constant and not given in input.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 475 点
問題文
高橋君と青木君は N 枚のカードを使ってとあるゲームをします。i 枚目のカードの表面には A_i が、裏面には B_i が書かれています。初めに場には N 枚のカードが並べられており、高橋君を先手として、2 人は以下の操作を交互に繰り返します。
- 場にあるカードの中から表面同士に同じ数が書かれている、または裏面同士に同じ数が書かれている 2 枚のカードの組を選び、そのカードを場から取り除く。このようなカードの組が存在しない場合、操作を行えない。
先に操作を行えなくなった方が負けとなり、もう一方が勝ちとなります。 両者がそれぞれ勝つために最適な操作を選ぶ時、どちらが勝つか求めてください。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 18
- 1 \leq A_i,B_i \leq 10^9
- 入力は全て整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N A_1 B_1 A_2 B_2 \vdots A_N B_N
出力
2 人とも最適に操作を行なったとき、高橋君が勝つ場合は Takahashi と、青木君が勝つ場合は Aoki と出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 1 9 2 5 4 9 1 4 2 5
出力例 1
Aoki
髙橋君が最初に取り除いた 2 枚が
-
1 枚目と 3 枚目のカードだった場合: 青木君は 2 枚目と 5 枚目のカードを取り除くことで勝つことができる。
-
1 枚目と 4 枚目のカードだった場合: 青木君は 2 枚目と 5 枚目のカードを取り除くことで勝つことができる。
-
2 枚目と 5 枚目のカードだった場合: 青木君は 1 枚目と 3 枚目のカードを取り除くことで勝つことができる。
髙橋君が最初の操作で取り除くことができるカードの組み合わせは以上の 3 通りのみで、髙橋君がどのような操作を行っても青木君が勝つことができるため、青木君が答えとなります。
入力例 2
9 3 2 1 7 4 1 1 8 5 2 9 8 2 1 6 8 5 2
出力例 2
Takahashi
Score : 475 points
Problem Statement
Takahashi and Aoki are playing a game using N cards. The front side of the i-th card has A_i written on it, and the back side has B_i written on it. Initially, the N cards are laid out on the table. With Takahashi going first, the two players take turns performing the following operation:
- Choose a pair of cards from the table such that either the numbers on their front sides are the same or the numbers on their back sides are the same, and remove these two cards from the table. If no such pair of cards exists, the player cannot perform the operation.
The player who is first to be unable to perform the operation loses, and the other player wins. Determine who wins if both players play optimally.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 18
- 1 \leq A_i, B_i \leq 10^9
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N A_1 B_1 A_2 B_2 \vdots A_N B_N
Output
Print Takahashi if Takahashi wins when both players play optimally, and Aoki otherwise.
Sample Input 1
5 1 9 2 5 4 9 1 4 2 5
Sample Output 1
Aoki
If Takahashi first removes
-
the first and third cards: Aoki can win by removing the second and fifth cards.
-
the first and fourth cards: Aoki can win by removing the second and fifth cards.
-
the second and fifth cards: Aoki can win by removing the first and third cards.
These are the only three pairs of cards Takahashi can remove in his first move, and Aoki can win in all cases. Therefore, the answer is Aoki.
Sample Input 2
9 3 2 1 7 4 1 1 8 5 2 9 8 2 1 6 8 5 2
Sample Output 2
Takahashi
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 500 点
問題文
1,\ldots,N の番号がついた N 個の街と、1,\ldots,M の番号がついた M 本の道路があります。
道路 i は街 A_i と B_i を結んでいます。道路を通行すると、所持している ポイント が次の通り増減します。
- 道路 i を使って、街 A_i から街 B_i に移動するときにはポイントが C_i 増加し、街 B_i から街 A_i に移動するときにはポイントが C_i 減少する。
所持しているポイントは負にもなりえます。
次の Q 個の質問に答えてください。
- 所持しているポイントが 0 である状態で街 X_i から移動を始めたとき、街 Y_i にいる状態で所持しているポイントの最大値を出力せよ。
ただし、街 X_i から街 Y_i に到達できないときはnan、街 Y_i にいる状態で所持しているポイントをいくらでも増やせるときはinfを代わりに出力せよ。
制約
- 2\leq N \leq 10^5
- 0\leq M \leq 10^5
- 1\leq Q \leq 10^5
- 1\leq A_i,B_i,X_i,Y_i \leq N
- 0\leq C_i \leq 10^9
- 入力は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M Q A_1 B_1 C_1 \vdots A_M B_M C_M X_1 Y_1 \vdots X_Q Y_Q
出力
問題文の指示通りに Q 行出力せよ。
i 行目には i 番目の質問に対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 5 3 1 2 1 1 2 2 3 4 1 4 5 1 3 5 2 5 3 1 2 3 1
出力例 1
-2 inf nan
1 番目の質問では、道路 5 を使って街 5 から街 3 に移動すると、ポイントを -2 所持している状態で街 3 にいることができます。
これ以上ポイントを大きくすることはできないので答えは -2 になります。
2 番目の質問では、「道路 2 を使って街 1 から街 2 に移動し、道路 1 を使って街 2 から街 1 に移動する」 という行動を好きなだけ繰り返したあと、道路 2 を使って街 1 から街 2 に移動することで、 街 2 にいる状態で所持しているポイントをいくらでも増やすことができます。
3 番目の質問では、街 3 から移動を始めて街 1 へ到達することはできません。
入力例 2
2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
出力例 2
inf
始点と終点が同じ街である道路や、始点と終点が同じ街である質問が含まれることもあります。
入力例 3
9 7 5 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 8 9 7 9 3 2 3 8 4 6 2 6 4 3 3 8 3 2 7 9
出力例 3
inf nan nan inf -9
Score : 500 points
Problem Statement
There are N towns numbered 1,\ldots,N and M roads numbered 1,\ldots,M.
Road i connects towns A_i and B_i. When you use a road, your score changes as follows:
- when you move from town A_i to town B_i using road i, your score increases by C_i; when you move from town B_i to town A_i using road i, your score decreases by C_i.
Your score may become negative.
Answer the following Q questions.
- If you start traveling from town X_i with initial score 0, find the maximum possible score when you are at town Y_i.
Here, if you cannot get from town X_i to town Y_i, printnaninstead; if you can have as large a score as you want when you are at town Y_i, printinfinstead.
Constraints
- 2\leq N \leq 10^5
- 0\leq M \leq 10^5
- 1\leq Q \leq 10^5
- 1\leq A_i,B_i,X_i,Y_i \leq N
- 0\leq C_i \leq 10^9
- All values in the input are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M Q A_1 B_1 C_1 \vdots A_M B_M C_M X_1 Y_1 \vdots X_Q Y_Q
Output
Print Q lines as specified in the Problem Statement.
The i-th line should contain the answer to the i-th question.
Sample Input 1
5 5 3 1 2 1 1 2 2 3 4 1 4 5 1 3 5 2 5 3 1 2 3 1
Sample Output 1
-2 inf nan
For the first question, if you use road 5 to move from town 5 to town 3, you can have a score -2 when you are at town 3.
Since you cannot make the score larger, the answer is -2.
For the second question, you can have as large a score as you want when you are at town 2 if you travel as follows: repeatedly "use road 2 to move from town 1 to town 2 and then use road 1 to move from town 2 to town 1" as many times as you want, and finally use road 2 to move from town 1 to town 2.
For the third question, you cannot get from town 3 to town 1.
Sample Input 2
2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output 2
inf
The endpoints of a road may be the same, and so may the endpoints given in a question.
Sample Input 3
9 7 5 3 1 4 1 5 9 2 6 5 3 5 8 9 7 9 3 2 3 8 4 6 2 6 4 3 3 8 3 2 7 9
Sample Output 3
inf nan nan inf -9