Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
高橋君はティーポットです。
高橋君はティーポットなので、紅茶なら喜んで受け入れますが、それ以外の液体を入れようとすると拒否してしまいます。
高橋君に S という名前の液体を入れることが出来るか判定してください。
英小文字からなる長さ N の文字列 S が与えられます。
S が tea で終わる文字列であるかどうかを判定してください。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 20
- N は整数
- S は英小文字からなる長さ N の文字列
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N S
出力
S が tea で終わる文字列であれば Yes を、そうでなければ No を出力せよ。
入力例 1
8 greentea
出力例 1
Yes
greentea は tea で終わる文字列です。
入力例 2
6 coffee
出力例 2
No
coffee は tea で終わる文字列ではありません。
入力例 3
3 tea
出力例 3
Yes
入力例 4
1 t
出力例 4
No
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
Takahashi is a teapot.
Since he is a teapot, he will gladly accept tea, but will refuse any other liquid.
Determine whether you can pour a liquid named S into him.
You are given a string S of length N consisting of lowercase English letters.
Determine whether S is a string that ends with tea.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 20
- N is an integer.
- S is a string of length N consisting of lowercase English letters.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N S
Output
If S is a string that ends with tea, print Yes; otherwise, print No.
Sample Input 1
8 greentea
Sample Output 1
Yes
greentea is a string that ends with tea.
Sample Input 2
6 coffee
Sample Output 2
No
coffee is not a string that ends with tea.
Sample Input 3
3 tea
Sample Output 3
Yes
Sample Input 4
1 t
Sample Output 4
No
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
I begin with T and end with T, and I am full of T. What am I?
文字列 t について、充填率を以下のように定義します。
- t の先頭と末尾の文字がともに
tであり、かつ |t| \geq 3 である場合: t に含まれるtの個数を x とすると、t の充填率は \displaystyle\frac{x-2}{|t|-2} である。ここで、|t| は t の長さを表す。 - そうでない場合: t の充填率は 0 である。
文字列 S が与えられます。S の部分文字列の充填率としてありうる最大値を求めてください。
部分文字列とは
S の部分文字列とは、S の先頭から 0 文字以上、末尾から 0 文字以上削除して得られる文字列のことをいいます。 例えば、ab, bc, bcd は abcd の部分文字列ですが、ac, dc, e は abcd の部分文字列ではありません。
制約
- 1 \leq |S| \leq 100
- S は英小文字からなる文字列。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
S
出力
S の部分文字列の充填率としてありうる最大値を出力せよ。
出力された値と真の値との絶対誤差が 10^{-9} 以下のとき、正答と判定される。
入力例 1
attitude
出力例 1
0.50000000000000000
ttit は S の部分文字列であり、その充填率は \displaystyle\frac{3-2}{4-2} = \frac{1}{2} です。
充填率が \frac{1}{2} より高い部分文字列は存在しないので、答えは \frac{1}{2} です。
入力例 2
ottottott
出力例 2
0.66666666666666667
ttottott は S の部分文字列であり、その充填率は \displaystyle\frac{6-2}{8-2} = \frac{2}{3} です。
充填率が \frac{2}{3} より高い部分文字列は存在しないので、答えは \frac{2}{3} です。
入力例 3
coffeecup
出力例 3
0.00000000000000000
ff は S の部分文字列であり、その充填率は 0 です。
充填率が 0 より高い部分文字列は存在しないので、答えは 0 です。
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
I begin with T and end with T, and I am full of T. What am I?
For a string t, define the filling rate as follows:
- If the first and last characters of t are both
tand |t| \geq 3: Let x be the number oftin t. Then the filling rate of t is \displaystyle\frac{x-2}{|t|-2}, where |t| denotes the length of t. - Otherwise: the filling rate of t is 0.
You are given a string S. Find the maximum possible filling rate of a substring of S.
What is a substring?
A substring of S is a string obtained by removing zero or more characters from the beginning and the end of S. For example,ab, bc, and bcd are substrings of abcd, while ac, dc, and e are not substrings of abcd.
Constraints
- 1 \leq |S| \leq 100
- S is a string consisting of lowercase English letters.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S
Output
Print the maximum possible filling rate of a substring of S.
Your output will be judged as correct when the absolute error from the true value is at most 10^{-9}.
Sample Input 1
attitude
Sample Output 1
0.50000000000000000
ttit is a substring of S, and its filling rate is \displaystyle\frac{3-2}{4-2} = \frac{1}{2}.
There is no substring with a filling rate greater than \frac{1}{2}, so the answer is \frac{1}{2}.
Sample Input 2
ottottott
Sample Output 2
0.66666666666666667
ttottott is a substring of S, and its filling rate is \displaystyle\frac{6-2}{8-2} = \frac{2}{3}.
There is no substring with a filling rate greater than \frac{2}{3}, so the answer is \frac{2}{3}.
Sample Input 3
coffeecup
Sample Output 3
0.00000000000000000
ff is a substring of S, and its filling rate is 0.
There is no substring with a filling rate greater than 0, so the answer is 0.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 350 点
問題文
ポーカーテーブルの上に N 種類のフレーバーのティーバッグが置かれています。フレーバーには 1 から N までの番号が付けられており、フレーバー i (1 \leq i \leq N) のティーバッグは A_i 個あります。
あなたはこれらのティーバッグを使ったゲームに参加します。ゲームには 1 以上 A_1 + \dots + A_N 以下の難易度が設定されており,難易度 b のゲームは以下の流れで行われます。
- あなたは整数 x を宣言する。このとき、b \leq x \leq A_1 + \dots + A_N を満たす必要がある。
- ディーラーはポーカーテーブルの上にあるティーバッグの中からちょうど x 個を選び、あなたに渡す。
- あなたは渡された x 個のティーバッグのフレーバーを確認し、その中から b 個のティーバッグを選ぶ。
- あなたが選んだ b 個のティーバッグがすべて同じフレーバーであれば、あなたは勝利する。そうでなければ、あなたは敗北する。
ディーラーはあなたが敗北するように最善を尽くすものとします。
Q 個の質問が与えられるので、それぞれに答えてください。j 番目の質問は以下の通りです。
- 難易度 B_j のゲームに勝利するためにはじめに宣言する必要がある整数 x の最小値を答えよ。勝利が不可能であれば、代わりに -1 と答えよ。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 3 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq Q \leq 3 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq A_i \leq 10^6 (1 \leq i \leq N)
- 1 \leq B_j \leq \min(10^6, A_1 + \dots + A_N) (1 \leq j \leq Q)
- 入力される値は全て整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N Q A_1 \cdots A_N B_1 \vdots B_Q
出力
Q 行出力せよ。
j 行目 (1 \leq j \leq Q) には、j 番目のクエリに対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 5 4 1 8 4 1 8 5 2 10
出力例 1
1 17 14 5 -1
1 番目のクエリにおいて、x=1 を宣言すれば、ディーラーがどの 1 個のティーバッグを選んで渡しても、その中から適切に 1 個を選ぶことで勝利条件を満たすことが可能です。 1 より小さい整数を x として宣言することはできないので、答えは 1 です。
2 番目のクエリにおいて、x=17 を宣言すれば、ディーラーがどの 17 個のティーバッグを選んで渡しても、その中から適切に 8 個を選ぶことで勝利条件を満たすことが可能です。 逆に x < 17 のとき、ディーラーはあなたを敗北させるようにティーバッグを選んで渡すことが可能です。したがって、答えは 17 です。
3 番目のクエリにおいて、x=14 を宣言すれば、ディーラーがどの 14 個のティーバッグを選んで渡しても、その中から適切に 5 個を選ぶことで勝利条件を満たすことが可能です。 逆に x < 14 のとき、ディーラーはあなたを敗北させるようにティーバッグを選んで渡すことが可能です。したがって、答えは 14 です。
4 番目のクエリにおいて、x=5 を宣言すれば、ディーラーがどの 5 個のティーバッグを選んで渡しても、その中から適切に 2 個を選ぶことで勝利条件を満たすことが可能です。 逆に x < 5 のとき、ディーラーはあなたを敗北させるようにティーバッグを選んで渡すことが可能です。したがって、答えは 5 です。
5 番目のクエリにおいて、どのように x を宣言しても、ディーラーはあなたを敗北させるようにティーバッグを選んで渡すことが可能です。したがって、-1 を出力します。
入力例 2
5 3 13 13 13 13 2 5 12 13
出力例 2
19 47 51
Score : 350 points
Problem Statement
On the poker table, there are tea bags of N different flavors. The flavors are numbered from 1 through N, and there are A_i tea bags of flavor i (1 \leq i \leq N).
You will play a game using these tea bags. The game has a parameter called difficulty between 1 and A_1 + \dots + A_N, inclusive. A game of difficulty b proceeds as follows:
- You declare an integer x. Here, it must satisfy b \leq x \leq A_1 + \dots + A_N.
- The dealer chooses exactly x tea bags from among those on the table and gives them to you.
- You check the flavors of the x tea bags you received, and choose b tea bags from them.
- If all b tea bags you chose are of the same flavor, you win. Otherwise, you lose.
The dealer will do their best to make you lose.
You are given Q queries, so answer each of them. The j-th query is as follows:
- For a game of difficulty B_j, report the minimum integer x you must declare at the start to guarantee a win. If it is impossible to win, report -1 instead.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 3 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq Q \leq 3 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq A_i \leq 10^6 (1 \leq i \leq N)
- 1 \leq B_j \leq \min(10^6, A_1 + \dots + A_N) (1 \leq j \leq Q)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N Q A_1 \cdots A_N B_1 \vdots B_Q
Output
Print Q lines.
The j-th line (1 \leq j \leq Q) should contain the answer to the j-th query.
Sample Input 1
4 5 4 1 8 4 1 8 5 2 10
Sample Output 1
1 17 14 5 -1
For the 1-st query, if you declare x=1, then no matter which 1 bag the dealer chooses, you can satisfy the winning condition by choosing appropriate 1 bag among them. Since you cannot choose an integer x less than 1, the answer is 1.
For the 2-nd query, if you declare x=17, then no matter which 17 bags the dealer chooses, you can satisfy the winning condition by choosing appropriate 8 bags among them. Conversely, if x < 17, the dealer can choose bags to prevent your victory. Thus, the answer is 17.
For the 3-rd query, if you declare x=14, then no matter which 14 bags the dealer chooses, you can satisfy the winning condition by choosing appropriate 5 bags among them. Conversely, if x < 14, the dealer can choose bags to prevent your victory. Thus, the answer is 14.
For the 4-th query, if you declare x=5, then no matter which 5 bags the dealer chooses, you can satisfy the winning condition by choosing appropriate 2 bags among them. Conversely, if x < 5, the dealer can choose bags to prevent your victory. Thus, the answer is 5.
For the 5-th query, no matter what x you declare, the dealer can choose bags to prevent your victory. Thus, print -1.
Sample Input 2
5 3 13 13 13 13 2 5 12 13
Sample Output 2
19 47 51
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 425 点
問題文
この問題は G 問題の部分問題です。
0 と 1 からなる空でない文字列 S が次の条件を満たす時、S を美しい文字列と呼びます。
- (条件) 次の一連の操作を S の長さが 1 になるまで行い、S に残った唯一の文字を
1にすることができる。- 1 \leq i \leq |S| - 1 を満たす整数 i を自由に選ぶ。
- 整数 x を次のように定義する。
- S_i =
0かつ S_{i+1}=0である場合、x = 1 とする。 - S_i =
0かつ S_{i+1}=1である場合、x = 0 とする。 - S_i =
1かつ S_{i+1}=0である場合、x = 0 とする。 - S_i =
1かつ S_{i+1}=1である場合、x = 1 とする。
- S_i =
- S_i と S_{i+1} を取り除き、それらがあった場所に x を数字とみなしたものを 1 個挿入する。
例えば S=10101に対して i=2 を選んで操作を行った場合、操作後の文字列は1001になる。
0 と 1 からなる長さ N の文字列 T があります。
T の部分文字列である美しい文字列の個数を求めてください。ただし、2 つの部分文字列が文字列として同じでも、取り出す位置が異なるならば別々に数えます。
部分文字列とは
S の部分文字列とは、S の先頭から 0 文字以上、末尾から 0 文字以上削除して得られる文字列のことをいいます。例えば、
10 は 101 の部分文字列ですが、11 は 101 の部分文字列ではありません。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- N は整数
- T は
0と1からなる長さ N の文字列
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N T
出力
T の部分文字列である美しい文字列の個数を出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 110
出力例 1
3
T の 1 文字目から 2 文字目までを取り出してできる文字列 11 は美しい文字列です。なぜならば、i=1 として操作を行うと、操作後の文字列は 1 になるからです。
T の部分文字列である美しい文字列は次の 3 個です。
- T の 1 文字目を取り出してできる文字列
1 - T の 2 文字目を取り出してできる文字列
1 - T の 1 文字目から 2 文字目までを取り出してできる文字列
11
入力例 2
4 0000
出力例 2
4
入力例 3
30 011011100101110111100010011010
出力例 3
225
Score : 425 points
Problem Statement
This problem is a subproblem of Problem G.
A non-empty string S consisting of 0 and 1 is called a beautiful string when it satisfies the following condition:
- (Condition) You can perform the following sequence of operations until the length of S becomes 1 and make the only character remaining in S be
1.- Choose any integer i satisfying 1 \leq i \leq |S| - 1.
- Define an integer x as follows:
- If S_i =
0and S_{i+1} =0, let x = 1. - If S_i =
0and S_{i+1} =1, let x = 0. - If S_i =
1and S_{i+1} =0, let x = 0. - If S_i =
1and S_{i+1} =1, let x = 1.
- If S_i =
- Remove S_i and S_{i+1}, and insert the digit corresponding to x in their place.
For example, if S=10101and you choose i=2, the string after the operation is1001.
You are given a string T of length N consisting of 0 and 1.
Find the number of beautiful strings that are substrings of T. Even if two substrings are identical as strings, count them separately if they are taken from different positions.
What are substrings?
A substring of S is a string obtained by deleting zero or more characters from the beginning and zero or more characters from the end of S.For example,
10 is a substring of 101, but 11 is not a substring of 101.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- N is an integer.
- T is a string of length N consisting of
0and1.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N T
Output
Print the number of beautiful strings that are substrings of T.
Sample Input 1
3 110
Sample Output 1
3
The string 11 obtained by taking the 1st through 2nd characters of T is a beautiful string, because if you choose i=1 and perform the operation, the string becomes 1.
The beautiful strings that are substrings of T are the following three strings:
- The string
1obtained by taking the 1st character of T. - The string
1obtained by taking the 2nd character of T. - The string
11obtained by taking the 1st through 2nd characters of T.
Sample Input 2
4 0000
Sample Output 2
4
Sample Input 3
30 011011100101110111100010011010
Sample Output 3
225
Time Limit: 4 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 475 点
問題文
二次元平面上に N 個の点があり、i 番目の点は座標 (X_i, Y_i) にあります。どの 2 点も相異なる位置にあり、どの 3 点も同一直線上にないことが保証されます。
これらの点から 4 点を選ぶ組合せのうち、その 4 点を頂点とする多角形として台形がとれるものは何通りありますか?
制約
- 4 \leq N \leq 2\,000
- 0 \leq X_i, Y_i \leq 10^7 (1 \leq i \leq N)
- どの 2 点も相異なる位置にある。
- どの 3 点も同一直線上にない。
- 入力される値は全て整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N X_1 Y_1 \vdots X_N Y_N
出力
答えを 1 行に出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 0 2 0 5 1 0 2 1 2 4
出力例 1
3
与えられた点は、以下の図のような配置になっています。
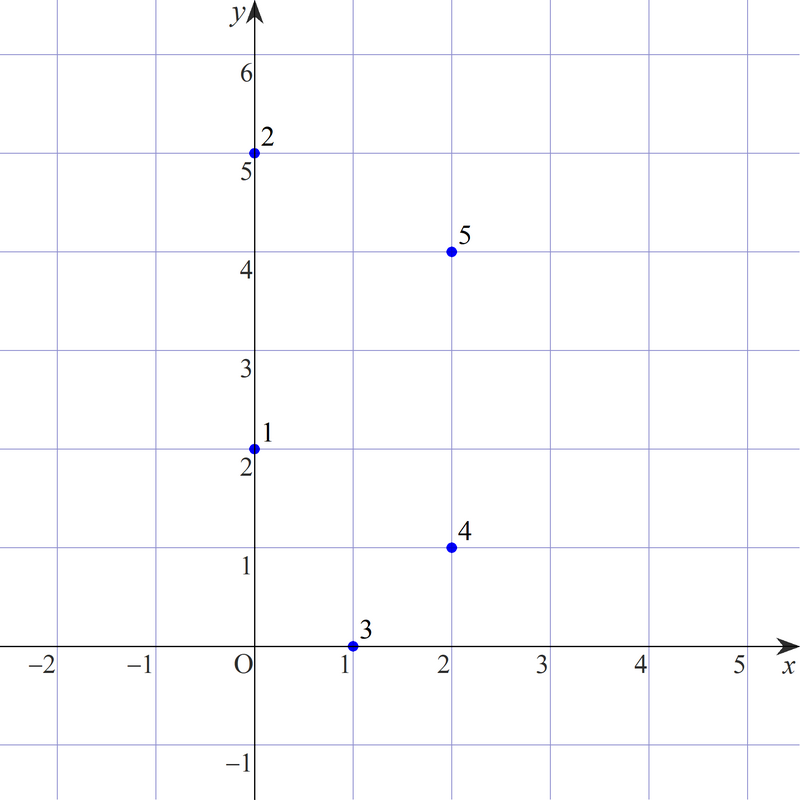
ここから 4 点を選ぶ組合せのうち、それらを頂点とする台形がとれるものは以下の 3 通りです。
- 1,5,4,3 番目の点。
- 1,3,4,2 番目の点。
- 1,2,5,4 番目の点。
平行四辺形や長方形も台形の一種として扱うことに注意してください。
入力例 2
8 0 1 1 3 2 3 3 1 0 2 1 0 2 0 3 2
出力例 2
22
Score : 475 points
Problem Statement
There are N points on a two-dimensional plane, with the i-th point at coordinates (X_i, Y_i). It is guaranteed that no two points are at the same position, and no three points are collinear.
Among the combinations of four points from these points, how many combinations can form a trapezoid as a polygon with those four points as vertices?
Constraints
- 4 \leq N \leq 2\,000
- 0 \leq X_i, Y_i \leq 10^7 (1 \leq i \leq N)
- No two points are at the same location.
- No three points are collinear.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N X_1 Y_1 \vdots X_N Y_N
Output
Print the answer on one line.
Sample Input 1
5 0 2 0 5 1 0 2 1 2 4
Sample Output 1
3
The given points are arranged as shown in the figure below.

Among the combinations of four points, the following three combinations can form a trapezoid as a polygon with those points as vertices:
- The 1st, 5th, 4th, 3rd points.
- The 1st, 3rd, 4th, 2nd points.
- The 1st, 2nd, 5th, 4th points.
Note that parallelograms and rectangles are also treated as trapezoids.
Sample Input 2
8 0 1 1 3 2 3 3 1 0 2 1 0 2 0 3 2
Sample Output 2
22
Time Limit: 3 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 550 点
問題文
N 個のティーポットが横一列に並んでおり、左から順に 1 から N までの番号が付けられています。
整数列 (a_1, \dots, a_N) があり、はじめその値は a_1 = \dots = a_N = -1 です。
あなたは以下の条件をすべて満たすように、それぞれのティーポットに紅茶かコーヒーのいずれか 1 つを入れます。
- どの隣り合う 2 つのティーポットについても、少なくとも片方には紅茶を入れる。
- 1 \leq i \leq N を満たす整数 i について、a_i \neq -1 である場合、ティーポット 1, \dots, i のうちちょうど a_i 個にコーヒーを入れる。
クエリが Q 個与えられるので、与えられた順に処理してください。
j 番目のクエリ (1 \leq j \leq Q) は以下の通りです。
- a_{X_j} の値を Y_j に変更する。その後、条件を満たすようなティーポットの満たし方の個数を 998244353 で割ったあまりを出力する。
制約
- 2 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq Q \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq X_j \leq N (1 \leq j \leq Q)
- -1 \leq Y_j \leq X_j (1 \leq j \leq Q)
- 入力される値は全て整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N Q X_1 Y_1 \vdots X_Q Y_Q
出力
Q 行出力せよ。
j 行目 (1 \leq j \leq Q) には、j 番目のクエリで出力するべき値を出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 6 1 1 4 2 1 0 4 -1 5 1 5 5
出力例 1
5 3 1 8 4 0
- 1 番目のクエリでの操作後、a = (1,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1) となります。条件を満たす入れ方は以下の 5 通りです。
- ティーポット 1 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 1, 3 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 1, 3, 5 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 1, 4 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 1, 5 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- 2 番目のクエリでの操作後、a = (1,\ -1,\ -1,\ 2,\ -1) となります。条件を満たす入れ方は以下の 3 通りです。
- ティーポット 1, 3 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 1, 3, 5 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 1, 4 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- 3 番目のクエリでの操作後、a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ 2,\ -1) となります。条件を満たす入れ方は以下の 1 通りです。
- ティーポット 2, 4 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- 4 番目のクエリでの操作後、a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1) となります。条件を満たす入れ方は以下の 8 通りです。
- どのティーポットにもコーヒーを入れず、すべてのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 2 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 2, 4 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 2, 5 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 3 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 3, 5 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 4 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 5 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- 5 番目のクエリでの操作後、a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ 1) となります。条件を満たす入れ方は以下の 4 通りです。
- ティーポット 2 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 3 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 4 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- ティーポット 5 にコーヒーを入れ、ほかのティーポットに紅茶を入れる。
- 6 番目のクエリでの操作後、a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ 5) となります。条件を満たす入れ方は 0 通りです。
Score : 550 points
Problem Statement
There are N teapots arranged in a row, numbered from 1 to N from left to right.
There is a sequence of integers (a_1, \dots, a_N), initially with values a_1 = \dots = a_N = -1.
You will fill each teapot with either tea or coffee so that the following conditions are all satisfied:
- For any two adjacent teapots, at least one of them contains tea.
- For any integer i satisfying 1 \leq i \leq N, if a_i \neq -1, then exactly a_i of teapots 1, \dots, i contain coffee.
You are given Q queries, which you should process in the given order.
The j-th query (1 \leq j \leq Q) is as follows:
- Change the value of a_{X_j} to Y_j. Then, print the number, modulo 998244353, of ways to fill the teapots satisfying the conditions.
Constraints
- 2 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq Q \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 1 \leq X_j \leq N (1 \leq j \leq Q)
- -1 \leq Y_j \leq X_j (1 \leq j \leq Q)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N Q X_1 Y_1 \vdots X_Q Y_Q
Output
Print Q lines.
The j-th line (1 \leq j \leq Q) should contain the value to be printed for the j-th query.
Sample Input 1
5 6 1 1 4 2 1 0 4 -1 5 1 5 5
Sample Output 1
5 3 1 8 4 0
- After the operation in the first query, a = (1,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1). The ways to fill the teapots satisfying the conditions are the following five ways:
- Put coffee in teapot 1, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 1, 3, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 1, 3, 5, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 1, 4, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 1, 5, and tea in the others.
- After the operation in the second query, a = (1,\ -1,\ -1,\ 2,\ -1). The ways to fill the teapots satisfying the conditions are the following three ways:
- Put coffee in teapots 1, 3, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 1, 3, 5, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 1, 4, and tea in the others.
- After the operation in the third query, a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ 2,\ -1). The ways to fill the teapots satisfying the conditions are the following one way:
- Put coffee in teapots 2, 4, and tea in the others.
- After the operation in the fourth query, a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1). The ways to fill the teapots satisfying the conditions are the following eight ways:
- Put coffee in none of the teapots and tea in all of them.
- Put coffee in teapot 2, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 2, 4, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 2, 5, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapot 3, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapots 3, 5, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapot 4, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapot 5, and tea in the others.
- After the operation in the fifth query, a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ 1). The ways to fill the teapots satisfying the conditions are the following four ways:
- Put coffee in teapot 2, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapot 3, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapot 4, and tea in the others.
- Put coffee in teapot 5, and tea in the others.
- After the operation in the sixth query, a = (0,\ -1,\ -1,\ -1,\ 5). The number of ways to fill the teapots satisfying the conditions is zero.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 650 点
問題文
A, B, C, D \in \lbrace 0, 1 \rbrace を満たす整数の組 (A, B, C, D) は 16 通りあります。それぞれに対して次の問題を解いてください。
0と1からなる空でない文字列 S が次の条件を満たす時、S を美しい文字列と呼びます。
- (条件) 次の一連の操作を S の長さが 1 になるまで行い、S に残った唯一の文字を
1にすることができる。
- 1 \leq i \leq |S| - 1 を満たす整数 i を自由に選ぶ。
- 整数 x を次のように定義する。
- S_i =
0かつ S_{i+1}=0である場合、x = A とする。- S_i =
0かつ S_{i+1}=1である場合、x = B とする。- S_i =
1かつ S_{i+1}=0である場合、x = C とする。- S_i =
1かつ S_{i+1}=1である場合、x = D とする。- S_i と S_{i+1} を取り除き、それらがあった場所に x を数字とみなしたものを 1 個挿入する。
例えば S=10101に対して i=2 を選んで操作を行った場合、操作後の文字列は B=0 の場合1001に、B=1 の場合1101になる。
0と1からなる長さ N の文字列 T があります。
- T の部分文字列である美しい文字列のうち最長のものの長さを L (ただし、T の部分文字列である美しい文字列が存在しない場合は L = -1 とする)、
- T の部分文字列である美しい文字列の個数を M
とします。L および M を求めてください。ただし、2 つの部分文字列が文字列として同じでも、取り出す位置が異なるならば別々に数えます。
部分文字列とは
S の部分文字列とは、S の先頭から 0 文字以上、末尾から 0 文字以上削除して得られる文字列のことをいいます。例えば、
10 は 101 の部分文字列ですが、11 は 101 の部分文字列ではありません。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- N は整数
- T は
0と1からなる長さ N の文字列
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N T
出力
16 行出力せよ。i 行目には i-1 = 8A + 4B + 2C + D を満たす (A,B,C,D) における L と M を空白区切りで出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 110
出力例 1
1 2 2 3 2 3 3 5 1 2 2 3 2 3 3 5 3 3 2 3 3 4 3 5 3 3 2 3 3 4 3 5
(A,B,C,D)=(0,0,0,1) の場合を説明します。
T の 1 文字目から 2 文字目までを取り出してできる文字列 11 は美しい文字列です。なぜならば、i=1 として操作を行うと、操作後の文字列は 1 になるからです。
(A,B,C,D)=(0,0,0,1) の場合、T の部分文字列である美しい文字列は次の 3 個です。
- T の 1 文字目を取り出してできる文字列
1 - T の 2 文字目を取り出してできる文字列
1 - T の 1 文字目から 2 文字目までを取り出してできる文字列
11
入力例 2
4 0000
出力例 2
-1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 4 4 4 4 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6
入力例 3
30 011011100101110111100010011010
出力例 3
1 17 4 31 29 263 29 280 29 232 29 247 30 240 30 447 30 418 29 225 30 435 30 435 30 435 30 435 30 439 30 452
Score : 650 points
Problem Statement
There are 16 integer tuples (A, B, C, D) satisfying A, B, C, D \in \lbrace 0, 1 \rbrace. For each of them, solve the following problem.
A non-empty string S consisting of
0and1is called a beautiful string when it satisfies the following condition:
- (Condition) You can perform the following sequence of operations until the length of S becomes 1 and make the only character remaining in S be
1.
- Choose any integer i satisfying 1 \leq i \leq |S| - 1.
- Define an integer x as follows:
- If S_i =
0and S_{i+1} =0, let x = A.- If S_i =
0and S_{i+1} =1, let x = B.- If S_i =
1and S_{i+1} =0, let x = C.- If S_i =
1and S_{i+1} =1, let x = D.- Remove S_i and S_{i+1}, and insert the digit corresponding to x in their place.
For example, if S=10101and you choose i=2, the string after the operation is1001if B=0, and1101if B=1.You are given a string T of length N consisting of
0and1.
- Let L be the length of the longest beautiful string that is a substring of T (if no substring of T is a beautiful string, let L = -1),
- Let M be the number of beautiful strings that are substrings of T.
Find L and M. Even if two substrings are identical as strings, count them separately if they are taken from different positions.
What are substrings?
A substring of S is a string obtained by deleting zero or more characters from the beginning and zero or more characters from the end of S.For example,
10 is a substring of 101, but 11 is not a substring of 101.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- N is an integer.
- T is a string of length N consisting of
0and1.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N T
Output
Print 16 lines. The i-th line should contain L and M separated by a space for (A,B,C,D) satisfying i-1 = 8A + 4B + 2C + D.
Sample Input 1
3 110
Sample Output 1
1 2 2 3 2 3 3 5 1 2 2 3 2 3 3 5 3 3 2 3 3 4 3 5 3 3 2 3 3 4 3 5
We explain the case (A,B,C,D)=(0,0,0,1).
The string 11 obtained by taking the 1st through 2nd characters of T is a beautiful string, because if you choose i=1 and perform the operation, the string becomes 1.
In the case (A,B,C,D)=(0,0,0,1), the beautiful strings that are substrings of T are the following three strings:
- The string
1obtained by taking the 1st character of T. - The string
1obtained by taking the 2nd character of T. - The string
11obtained by taking the 1st through 2nd characters of T.
Sample Input 2
4 0000
Sample Output 2
-1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 -1 0 4 4 4 4 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6 4 6
Sample Input 3
30 011011100101110111100010011010
Sample Output 3
1 17 4 31 29 263 29 280 29 232 29 247 30 240 30 447 30 418 29 225 30 435 30 435 30 435 30 435 30 439 30 452