Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 150 点
問題文
正整数 A と正の奇数 B が与えられます。
実数 \dfrac AB との差が最小となる整数を出力してください。
ただし、制約のもとでそのような整数がただ一つ存在することが証明できます。
制約
- 1\leq A\leq407
- 1\leq B\leq407
- B は奇数
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
A B
出力
\dfrac AB との差が最小となる整数を出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 7
出力例 1
1
\dfrac AB=\dfrac47=0.5714\ldots です。 \dfrac AB と 1 との差は \dfrac37=0.4285\ldots で、これより差が小さい整数はありません。
よって、1 を出力してください。
入力例 2
407 29
出力例 2
14
\dfrac AB=\dfrac{407}{29}=14.0344\ldots です。 \dfrac AB と 14 との差は \dfrac1{29}=0.0344\ldots で、これより差が小さい整数はありません。
よって、14 を出力してください。
入力例 3
22 11
出力例 3
2
\dfrac AB が整数である場合もあります。
Score : 150 points
Problem Statement
You are given a positive integer A and a positive odd integer B.
Output the integer whose difference from the real number \dfrac AB is the smallest.
It can be proved that, under the constraints, such an integer is unique.
Constraints
- 1 \le A \le 407
- 1 \le B \le 407
- B is odd.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
A B
Output
Output the integer that minimizes the difference from \dfrac AB.
Sample Input 1
4 7
Sample Output 1
1
We have \dfrac AB = \dfrac47 = 0.5714\ldots. The difference between \dfrac AB and 1 is \dfrac37 = 0.4285\ldots, and no integer has a smaller difference.
Thus, print 1.
Sample Input 2
407 29
Sample Output 2
14
We have \dfrac AB = \dfrac{407}{29} = 14.0344\ldots. The difference between \dfrac AB and 14 is \dfrac1{29} = 0.0344\ldots, and no integer has a smaller difference.
Thus, print 14.
Sample Input 3
22 11
Sample Output 3
2
\dfrac AB may itself be an integer.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 250 点
問題文
1,2,3,4,5,6 の 6 種類の目が出るサイコロを 2 つ振ったときに、次の 2 つの条件の少なくとも一方を満たす確率を求めてください。
- 2 つの出目の合計が X 以上である。
- 2 つの出目の差の絶対値が Y 以上である。
ここで、どちらのサイコロについても 6 種類のどの目が出るかは同様に確からしく、それぞれのサイコロの出目は独立であるとします。
制約
- 2\leq X\leq13
- 0\leq Y\leq6
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
X Y
出力
2 つのサイコロの出目が 2 つの条件の少なくとも一方を満たす確率を出力せよ。 出力された値と真の値との絶対誤差が 10 ^ {-9} 以下のとき、正答と判定される。
入力例 1
9 3
出力例 1
0.555555555555555555555555555555
2 つのサイコロの出目がそれぞれ x と y であることを (x,y) で表すことにすると、それぞれの条件を満たすのは次の場合です。
- 2 つのサイコロの出目の和が 9 以上になるのは、(3,6),(4,5),(4,6),(5,4),(5,5),(5,6),(6,3),(6,4),(6,5),(6,6) のとき
- 2 つのサイコロの出目の差が 3 以上になるのは、(1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(2,5),(2,6),(3,6),(4,1),(5,1),(5,2),(6,1),(6,2),(6,3) のとき
これらの条件の少なくとも一方を満たすのは (1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(2,5),(2,6),(3,6),(4,1),(4,5),(4,6),(5,1),(5,2),(5,4),(5,5),(5,6),(6,1),(6,2),(6,3),(6,4),(6,5),(6,6) の 20 通りのいずれかのときです。
よって、求める答えは \dfrac{20}{36}=\dfrac59=0.5555555555\ldots です。
絶対誤差が 10 ^ {-9} 以下のとき正答と判定されるので、0.5555555565 や 0.55555555456789 などと出力しても正解となります。
入力例 2
13 6
出力例 2
0
2 つのサイコロの出目の和が 13 以上になることも、差が 6 以上になることもありません。
よって、求める答えは 0 です。
入力例 3
10 3
出力例 3
0.5
Score : 250 points
Problem Statement
Two dice, each with six faces 1,2,3,4,5,6, are rolled. Find the probability that at least one of the following two conditions holds:
- The sum of the two outcomes is at least X.
- The absolute difference of the two outcomes is at least Y.
Each face of each die is equally likely, and the two dice are independent.
Constraints
- 2 \le X \le 13
- 0 \le Y \le 6
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
X Y
Output
Output the probability that the two outcomes satisfy at least one of the two conditions. Your answer is accepted if its absolute error from the true value is at most 10^{-9}.
Sample Input 1
9 3
Sample Output 1
0.555555555555555555555555555555
Let (x,y) denote the event that the dice show x and y.
- The sum is at least 9 for (3,6),(4,5),(4,6),(5,4),(5,5),(5,6),(6,3),(6,4),(6,5),(6,6).
- The difference is at least 3 for (1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(2,5),(2,6),(3,6),(4,1),(5,1),(5,2),(6,1),(6,2),(6,3).
At least one of these conditions holds for the following 20 pairs: (1,4),(1,5),(1,6),(2,5),(2,6),(3,6),(4,1),(4,5),(4,6),(5,1),(5,2),(5,4),(5,5),(5,6),(6,1),(6,2),(6,3),(6,4),(6,5),(6,6).
Thus, the answer is \dfrac{20}{36}=\dfrac59=0.5555555555\ldots.
Because an absolute error of at most 10^{-9} is allowed, outputs such as 0.5555555565 or 0.55555555456789 are accepted.
Sample Input 2
13 6
Sample Output 2
0
Neither the sum of two dice can be 13 or greater, nor can their difference be 6 or greater.
Thus, the answer is 0.
Sample Input 3
10 3
Sample Output 3
0.5
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
AtCoder 社の入口には特殊なパスコード入力装置があり、 この装置は文字列を 1 つ表示する画面と 2 つのボタンからなります。
画面に表示される文字列を t とします。 t ははじめ空文字列であり、ボタンを押すことで t に以下の変化が起きます。
- ボタン A を押すと、t の末尾に
0が追加される。 - ボタン B を押すと、t に含まれるすべての数字が、それぞれ次の数字に置き換わる。ここで、
0から8までの数字については次の数字は 1 大きな数を表す数字とし、9の次の数字は0とする。
たとえば、t が 1984 のときにボタン A を押すと t は 19840 に変化し、さらにボタン B を押すと t は 20951 に変化します。
文字列 S が与えられます。t が空文字列である状態からボタンを 0 回以上押して t を S に一致させるとき、ボタンを最少で何回押す必要があるかを求めてください。
制約
- S は
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9からなる文字列 - 1 \leq |S| \leq 5 \times 10^5 (|S| は S の長さをあらわす)
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
S
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
21
出力例 1
4
以下の順にボタンを押せば、t が 21 になります。
- ボタン A を押す。t は
0になる。 - ボタン B を押す。t は
1になる。 - ボタン A を押す。t は
10になる。 - ボタン B を押す。t は
21になる。
4 回より少ない回数ボタンを押して t を 21 にすることはできないので、4 を出力します。
入力例 2
407
出力例 2
17
入力例 3
2025524202552420255242025524
出力例 3
150
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
At the entrance of AtCoder Inc., there is a special pass-code input device. The device consists of a screen displaying one string, and two buttons.
Let t be the string shown on the screen. Initially, t is the empty string. Pressing a button changes t as follows:
- Pressing button A appends
0to the end of t. - Pressing button B replaces every digit in t with the next digit: for digits
0through8the next digit is the one whose value is larger by 1; the next digit after9is0.
For example, if t is 1984 and button A is pressed, t becomes 19840; if button B is then pressed, t becomes 20951.
You are given a string S. Starting from the empty string, press the buttons zero or more times until t coincides with S. Find the minimum number of button presses required.
Constraints
- S is a string consisting of
0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8, and9. - 1 \le |S| \le 5 \times 10^{5}, where |S| is the length of S.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S
Output
Output the answer.
Sample Input 1
21
Sample Output 1
4
The following sequence of presses makes t equal to 21.
- Press button A. t becomes
0. - Press button B. t becomes
1. - Press button A. t becomes
10. - Press button B. t becomes
21.
It is impossible to obtain 21 with fewer than four presses, so output 4.
Sample Input 2
407
Sample Output 2
17
Sample Input 3
2025524202552420255242025524
Sample Output 3
150
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 425 点
問題文
H 行 W 列のマス目があります。 上から i 行目 (1\leq i\leq H)、左から j 列目 (1\leq j\leq W) のマスをマス (i,j) と呼ぶことにします。
マス (i,j)\ (1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\leq W) には非負整数 A _ {i,j} が書かれています。
このマス目にドミノを 0 個以上置きます。 1 つのドミノは隣り合う 2 つのマス、つまり
- 1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\lt W に対するマス (i,j) とマス (i,j+1)
- 1\leq i\lt H,1\leq j\leq W に対するマス (i,j) とマス (i+1,j)
のどれかに置くことができます。
ただし、同じマスに対して複数のドミノを置くことはできません。
ドミノの置き方に対して、置き方のスコアをドミノが置かれていないマスに書かれた整数すべてのビットごとの排他的論理和として定めます。
ドミノの置き方のスコアとしてありうる最大値を求めてください。
ビットごとの排他的論理和とは
非負整数 A, B のビットごとの排他的論理和 A \oplus B は、以下のように定義されます。
- A \oplus B を二進表記した際の 2^k (k \geq 0) の位の数は、A, B を二進表記した際の 2^k の位の数のうち一方のみが 1 であれば 1、そうでなければ 0 である。
一般に k 個の非負整数 p_1, p_2, p_3, \dots, p_k のビット単位 \mathrm{XOR} は (\dots ((p_1 \oplus p_2) \oplus p_3) \oplus \dots \oplus p_k) と定義され、これは p_1, p_2, p_3, \dots, p_k の順番によらないことが証明できます。
制約
- 1\leq H
- 1\leq W
- HW\leq20
- 0\leq A _ {i,j}\lt 2 ^ {60}\ (1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\leq W)
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
H W
A _ {1,1} A _ {1,2} \ldots A _ {1,W}
A _ {2,1} A _ {2,2} \ldots A _ {2,W}
\vdots
A _ {H,1} A _ {H,2} \ldots A _ {H,W}
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 4 1 2 3 8 4 0 7 10 5 2 4 2
出力例 1
15
与えられたマス目は以下のようになります。
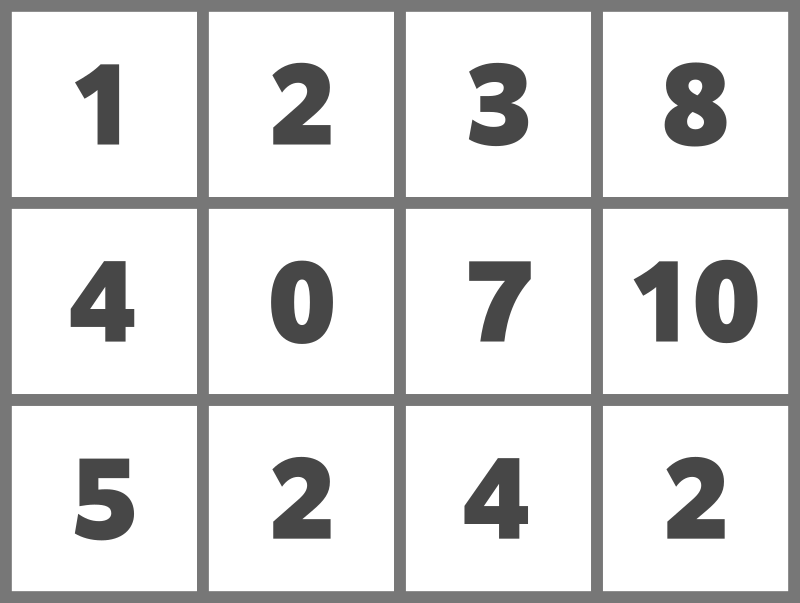
例えば、次のようにドミノを置くことでスコアを 15 とすることができます。
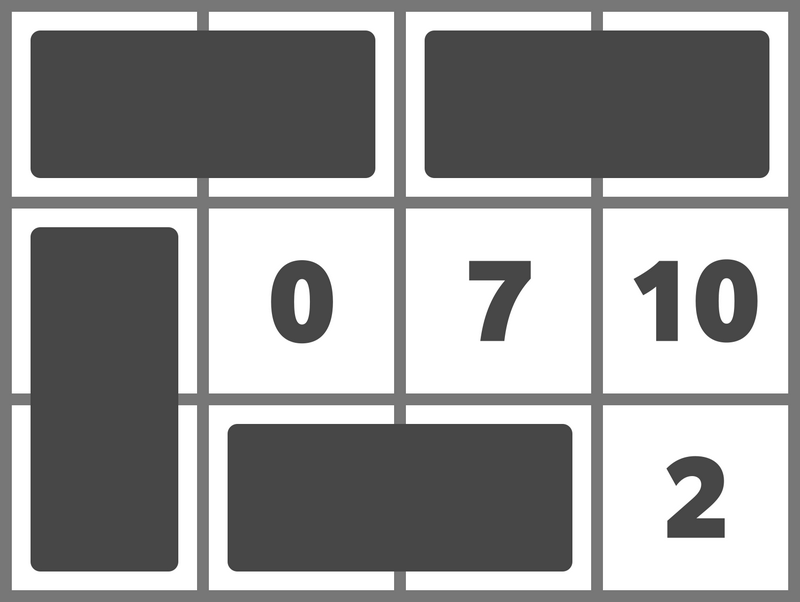
スコアを 16 以上にすることはできないため、15 を出力してください。
入力例 2
1 11 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024
出力例 2
2047
ドミノを 1 枚も置かないこともできます。
入力例 3
4 5 74832 16944 58683 32965 97236 52995 43262 51959 40883 58715 13846 24919 65627 11492 63264 29966 98452 75577 40415 77202
出力例 3
131067
Score : 425 points
Problem Statement
There is a grid with H rows and W columns. Let (i,j) denote the cell at the i-th row from the top (1\leq i\leq H) and the j-th column from the left (1\leq j\leq W).
Cell (i,j)\ (1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\leq W) has a non-negative integer A_{i,j} written on it.
Let us place zero or more dominoes on the grid. A domino covers two adjacent cells, namely one of the following pairs:
- cells (i,j) and (i,j+1) for 1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\lt W;
- cells (i,j) and (i+1,j) for 1\leq i\lt H,1\leq j\leq W.
No cell may be covered by more than one domino.
For a placement of dominoes, define its score as the bitwise XOR of all integers written in cells not covered by any domino.
Find the maximum possible score.
What is bitwise XOR?
For non-negative integers A and B, their bitwise XOR A \oplus B is defined as follows:
- In binary, the 2^k bit (k \ge 0) of A \oplus B is 1 if exactly one of A and B has 1 in that bit, and 0 otherwise.
For k non-negative integers p_1, p_2, p_3, \dots, p_k, their bitwise XOR is (\dots ((p_1 \oplus p_2) \oplus p_3) \oplus \dots \oplus p_k), which can be proved to be independent of the order of the operands.
Constraints
- 1 \le H
- 1 \le W
- HW \le 20
- 0 \le A_{i,j} < 2^{60} (1 \le i \le H,\ 1 \le j \le W)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
H W
A _ {1,1} A _ {1,2} \ldots A _ {1,W}
A _ {2,1} A _ {2,2} \ldots A _ {2,W}
\vdots
A _ {H,1} A _ {H,2} \ldots A _ {H,W}
Output
Output the answer.
Sample Input 1
3 4 1 2 3 8 4 0 7 10 5 2 4 2
Sample Output 1
15
The grid is as follows:

For example, the placement below yields a score of 15.

No placement achieves a score of 16 or higher, so output 15.
Sample Input 2
1 11 1 2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024
Sample Output 2
2047
You may also choose to place no dominoes.
Sample Input 3
4 5 74832 16944 58683 32965 97236 52995 43262 51959 40883 58715 13846 24919 65627 11492 63264 29966 98452 75577 40415 77202
Sample Output 3
131067
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 450 点
問題文
長さ 2N の非負整数列 A = (A_1, \dots, A_{2N}) が与えられます。
長さ 2N の括弧列 s のスコアを、以下で得られる値として定義します。
- s の i 文字目が
)であるようなすべての整数 i について A_i の値を 0 に変えた場合の、A の要素の総和。
長さ 2N の正しい括弧列のスコアとしてありうる最大値を求めてください。
T 個のテストケースが与えられるので、それぞれについて答えを求めてください。
正しい括弧列とは
正しい括弧列とは、() である部分文字列を削除することを 0 回以上繰り返して空文字列にできる文字列を指します。
制約
- 1 \leq T \leq 500
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 各入力ファイルについて、すべてのテストケースの N の総和は 2 \times 10^5 以下である。
- 0 \leq A_i \leq 10^9 (1 \leq i \leq 2N)
- 入力はすべて整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
T
\textrm{case}_1
\textrm{case}_2
\vdots
\textrm{case}_T
\textrm{case}_i は i 番目のテストケースを表す。各テストケースは以下の形式で与えられる。
N
A_1
A_2
\vdots
A_{2N}
出力
T 行出力せよ。i 行目 (1 \leq i \leq T) には i 番目のテストケースに対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
2 3 400 500 200 100 300 600 6 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000
出力例 1
1200 6000000000
1 番目のテストケースにおいて、正しい括弧列として (())() を選ぶと、そのスコアは 400+500+0+0+300+0=1200 となります。
1200 よりも高いスコアを得るような正しい括弧列は存在しないので、1 番目のテストケースの答えとして 1200 を出力します。
この入出力例における 2 番目のテストケースのように、答えが 32 bit 整数におさまらないことがあることに注意してください。
Score : 450 points
Problem Statement
You are given a sequence of non-negative integers A = (A_1,\dots,A_{2N}) of length 2N.
Define the score of a parenthesis sequence s of length 2N as follows:
- For every position i where the i-th character of s is
), set A_i to 0, then take the sum of all elements of A.
Find the maximum possible score of a correct parenthesis sequence of length 2N.
You are given T test cases; solve each.
What is a correct parenthesis sequence?
A correct parenthesis sequence is a string that can be reduced to the empty string by repeatedly removing substrings equal to().
Constraints
- 1 \le T \le 500
- 1 \le N \le 2 \times 10^{5}
- For each input file, the sum of N over all test cases is at most 2 \times 10^{5}.
- 0 \le A_i \le 10^{9} (1 \le i \le 2N)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
T
\textrm{case}_1
\textrm{case}_2
\vdots
\textrm{case}_T
\textrm{case}_i represents the i-th test case. Each test case is given in the following format:
N
A_1
A_2
\vdots
A_{2N}
Output
Output T lines. The i-th line (1 \le i \le T) should contain the answer for the i-th test case.
Sample Input 1
2 3 400 500 200 100 300 600 6 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000 1000000000
Sample Output 1
1200 6000000000
In the first test case, choosing the correct parenthesis string (())() gives a score of 400+500+0+0+300+0=1200.
No correct parenthesis string yields a higher score, so the answer is 1200.
Note that, as in the second test case of this sample, the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer range.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 550 点
問題文
長さ N の非負整数列 A = (A_1, \dots, A_N) が与えられます。
k = 1, \dots, N について、次の問題を解いてください。
- A の連続部分列のうち長さが k のものは N-k+1 個ある。それぞれの連続部分列について最大値を求めたとき、それらの合計を求めよ。
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 2 \times 10^5
- 0 \leq A_i \leq 10^7 (1 \leq i \leq N)
- 入力はすべて整数である。
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
出力
N 行出力せよ。i 行目 (1 \leq i \leq N) には、k = i に対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 5 3 4 2
出力例 1
14 13 9 5
k = 1 の場合、長さ k=1 の連続部分列は 4 個あり、それぞれについて
- (5) の最大値は 5
- (3) の最大値は 3
- (4) の最大値は 4
- (2) の最大値は 2
となり、これらの合計は 5+3+4+2 = 14 です。
k = 2 の場合、長さ k=2 の連続部分列は 3 個あります。それぞれについて
- (5,3) の最大値は 5
- (3,4) の最大値は 4
- (4,2) の最大値は 4
となり、これらの合計は 5+4+4 = 13 です。
k = 3 の場合、長さ k=3 の連続部分列は 2 個あります。それぞれについて
- (5,3,4) の最大値は 5
- (3,4,2) の最大値は 4
となり、これらの合計は 5+4 = 9 です。
k = 4 の場合、長さ k=4 の連続部分列は 1 個あります。それぞれについて
- (5,3,4,2) の最大値は 5
となり、これらの合計は 5 です。
入力例 2
8 2 0 2 5 0 5 2 4
出力例 2
20 28 27 25 20 15 10 5
入力例 3
11 9203973 9141294 9444773 9292472 5507634 9599162 497764 430010 4152216 3574307 430010
出力例 3
61273615 68960818 69588453 65590626 61592799 57594972 47995810 38396648 28797486 19198324 9599162
Score : 550 points
Problem Statement
You are given a sequence of non-negative integers A = (A_1,\dots,A_N) of length N.
For each k = 1,\dots,N, solve the following problem:
- A has N-k+1 (contiguous) subarrays of length k. Take the maximum of each of them, and output the sum of these maxima.
Constraints
- 1 \le N \le 2 \times 10^{5}
- 0 \le A_i \le 10^{7} (1 \le i \le N)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
Output
Output N lines. The i-th line (1 \le i \le N) should contain the answer for k = i.
Sample Input 1
4 5 3 4 2
Sample Output 1
14 13 9 5
For k = 1, there are four subarrays of length k=1:
- (5), whose maximum is 5;
- (3), whose maximum is 3;
- (4), whose maximum is 4;
- (2), whose maximum is 2.
The sum is 5 + 3 + 4 + 2 = 14.
For k = 2, there are three subarrays of length k=2:
- (5,3), whose maximum is 5;
- (3,4), whose maximum is 4;
- (4,2), whose maximum is 4.
The sum is 5 + 4 + 4 = 13.
For k = 3, there are two subarrays of length k=3:
- (5,3,4), whose maximum is 5;
- (3,4,2), whose maximum is 4.
The sum is 5 + 4 = 9.
For k = 4, there is one subarray of length k=4:
- (5,3,4,2), whose maximum is 5.
The sum is 5.
Sample Input 2
8 2 0 2 5 0 5 2 4
Sample Output 2
20 28 27 25 20 15 10 5
Sample Input 3
11 9203973 9141294 9444773 9292472 5507634 9599162 497764 430010 4152216 3574307 430010
Sample Output 3
61273615 68960818 69588453 65590626 61592799 57594972 47995810 38396648 28797486 19198324 9599162
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 600 点
問題文
H 行 W 列のマス目があります。 上から i 行目 (1\leq i\leq H)、左から j 列目 (1\leq j\leq W) のマスをマス (i,j) と呼ぶことにします。
マス (i,j)\ (1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\leq W) には整数 A _ {i,j} が書かれています。
このマス目にドミノを 0 個以上置きます。 1 つのドミノは隣り合う 2 つのマス、つまり
- 1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\lt W に対するマス (i,j) とマス (i,j+1)
- 1\leq i\lt H,1\leq j\leq W に対するマス (i,j) とマス (i+1,j)
のどれかに置くことができます。
ただし、同じマスに対して複数のドミノを置くことはできません。
ドミノの置き方に対して、置き方のスコアをドミノが置かれていないマスに書かれた整数すべての和として定めます。
ドミノの置き方のスコアとしてありうる最大値を求めてください。
制約
- 1\leq H
- 1\leq W
- HW\leq2000
- -10 ^ {12}\leq A _ {i,j}\leq10 ^ {12}\ (1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\leq W)
- 入力はすべて整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
H W
A _ {1,1} A _ {1,2} \ldots A _ {1,W}
A _ {2,1} A _ {2,2} \ldots A _ {2,W}
\vdots
A _ {H,1} A _ {H,2} \ldots A _ {H,W}
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 4 3 -1 -4 1 -5 9 -2 -6 -5 3 -5 8
出力例 1
23
与えられたマス目は以下のようになります。
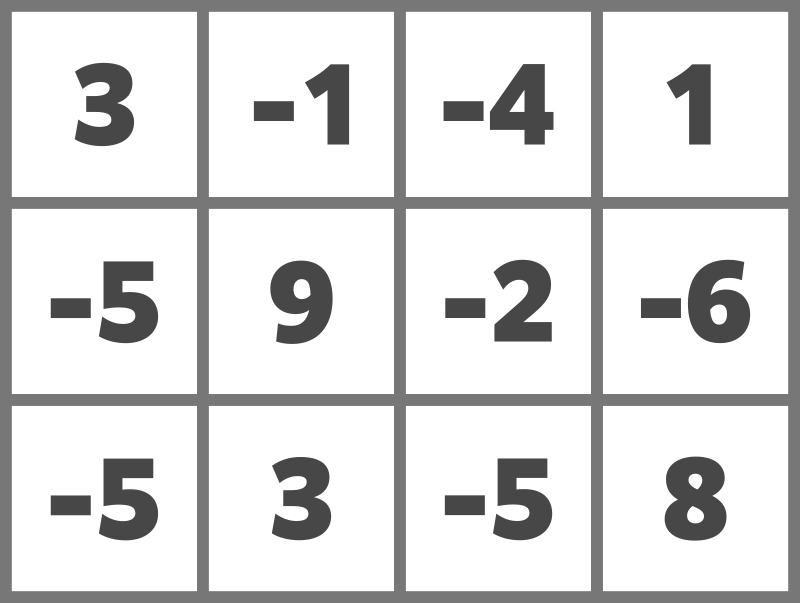
例えば、次のようにドミノを置くことでスコアを 23 とすることができます。
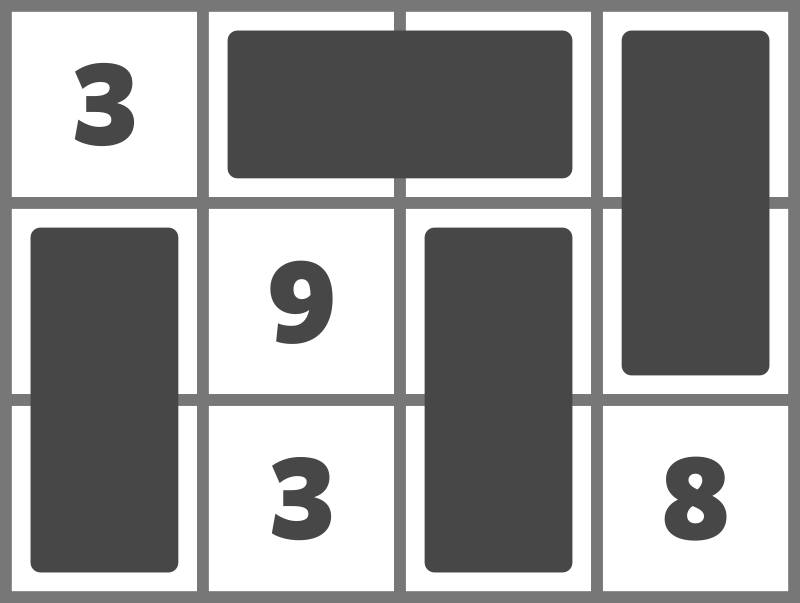
スコアを 24 以上にすることはできないため、23 を出力してください。
入力例 2
5 5 -70 11 -45 -54 -30 -99 39 -83 -69 -77 -48 -21 -43 -96 -24 -54 -65 21 -88 -44 -90 -33 -67 -29 -62
出力例 2
39
入力例 3
8 9 -74832 16944 58683 32965 97236 -52995 43262 -51959 40883 -58715 13846 24919 65627 -11492 -63264 29966 -98452 -75577 40415 77202 15542 -50602 83295 85415 -35304 46520 -38742 37482 56721 -38521 63127 55608 95115 42893 10484 70510 53019 40623 25885 -10246 70973 32528 -33423 19322 52097 79880 74931 -58277 -33783 91022 -53003 11085 -65924 -63548 78622 -77307 81181 46875 -81091 63881 11160 -82217 -55492 62770 39530 -95923 92440 -69899 77737 89392 -14281 84899
出力例 3
2232232
Score : 600 points
Problem Statement
There is a grid with H rows and W columns. Let (i,j) denote the cell at the i-th row from the top (1\leq i\leq H) and the j-th column from the left (1\leq j\leq W).
Cell (i,j)\ (1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\leq W) has an integer A_{i,j} written on it.
Let us place zero or more dominoes on the grid. A domino covers two adjacent cells, namely one of the following pairs:
- cells (i,j) and (i,j+1) for 1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\lt W;
- cells (i,j) and (i+1,j) for 1\leq i\lt H,1\leq j\leq W.
No cell may be covered by more than one domino.
For a placement of dominoes, define its score as the sum of all integers written in cells not covered by any domino.
Find the maximum possible score.
Constraints
- 1\leq H
- 1\leq W
- HW\leq2000
- -10 ^ {12}\leq A _ {i,j}\leq10 ^ {12}\ (1\leq i\leq H,1\leq j\leq W)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
H W
A _ {1,1} A _ {1,2} \ldots A _ {1,W}
A _ {2,1} A _ {2,2} \ldots A _ {2,W}
\vdots
A _ {H,1} A _ {H,2} \ldots A _ {H,W}
Output
Output the answer.
Sample Input 1
3 4 3 -1 -4 1 -5 9 -2 -6 -5 3 -5 8
Sample Output 1
23
The grid is as follows:

For example, the placement below yields a score of 23.

No placement achieves a score of 24 or higher, so output 23.
Sample Input 2
5 5 -70 11 -45 -54 -30 -99 39 -83 -69 -77 -48 -21 -43 -96 -24 -54 -65 21 -88 -44 -90 -33 -67 -29 -62
Sample Output 2
39
Sample Input 3
8 9 -74832 16944 58683 32965 97236 -52995 43262 -51959 40883 -58715 13846 24919 65627 -11492 -63264 29966 -98452 -75577 40415 77202 15542 -50602 83295 85415 -35304 46520 -38742 37482 56721 -38521 63127 55608 95115 42893 10484 70510 53019 40623 25885 -10246 70973 32528 -33423 19322 52097 79880 74931 -58277 -33783 91022 -53003 11085 -65924 -63548 78622 -77307 81181 46875 -81091 63881 11160 -82217 -55492 62770 39530 -95923 92440 -69899 77737 89392 -14281 84899
Sample Output 3
2232232