Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
長さ N の整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) が与えられます。
A の中に同じ要素が 3 つ以上連続する箇所が存在するか判定してください。
より厳密には、 1 以上 N-2 以下の整数 i であって A_i=A_{i+1}=A_{i+2} を満たすものが存在するか判定してください。
制約
- 3\le N\le 100
- 1\le A_i\le 100
- 入力される値は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N
出力
A の中に同じ要素が 3 つ以上連続する箇所が存在するならば Yes を、存在しないならば No を出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 1 4 4 4 2
出力例 1
Yes
A=(1,4,4,4,2) です。 4 が 3 つ連続している箇所が存在するので、 Yes を出力してください。
入力例 2
6 2 4 4 2 2 4
出力例 2
No
A=(2,4,4,2,2,4) です。同じ要素が 3 つ以上連続している箇所は存在しないので、 No を出力してください。
入力例 3
8 1 4 2 5 7 7 7 2
出力例 3
Yes
入力例 4
10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
出力例 4
No
入力例 5
13 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
出力例 5
Yes
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
You are given an integer sequence of length N: A = (A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N).
Determine whether there is a place in A where the same element appears three or more times in a row.
More formally, determine whether there exists an integer i with 1 \le i \le N-2 such that A_i = A_{i+1} = A_{i+2}.
Constraints
- 3 \le N \le 100
- 1 \le A_i \le 100
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N
Output
If there is a place in A where the same element appears three or more times in a row, print Yes. Otherwise, print No.
Sample Input 1
5 1 4 4 4 2
Sample Output 1
Yes
We have A=(1,4,4,4,2). There is a place where 4 appears three times in a row, so print Yes.
Sample Input 2
6 2 4 4 2 2 4
Sample Output 2
No
We have A=(2,4,4,2,2,4). There is no place where the same element appears three or more times in a row, so print No.
Sample Input 3
8 1 4 2 5 7 7 7 2
Sample Output 3
Yes
Sample Input 4
10 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Sample Output 4
No
Sample Input 5
13 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output 5
Yes
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
整数 0 の書かれたカードが 100 枚積み重なったカードの山があります。
Q 個のクエリを処理してください。それぞれのクエリは以下のいずれかです。
- タイプ 1 : 整数 x の書かれたカードを 1 枚カードの山の一番上に積み重ねる。
- タイプ 2 : カードの山の一番上のカードを取り除き、取り除いたカードに書かれている整数を出力する。ここで、本問題の制約下では必ず山にカードが存在する。
制約
- 1\le Q\le 100
- 1\le x\le 100
- タイプ 2 のクエリが 1 つ以上存在する。
- 入力される値は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
Q
\text{query}_1
\text{query}_2
\vdots
\text{query}_Q
i 番目のクエリ \text{query}_i では、まずクエリのタイプ c_i (1,2 のいずれか)が与えられる。 c_i=1 の場合はさらに整数 x が追加で与えられる。
すなわち、各クエリは以下に示す 2 つの形式のいずれかである。
1 x
2
出力
c_i=2 を満たすクエリの回数を q として、 q 行出力せよ。
j (1\le j\le q) 行目では j 番目のそのようなクエリに対する答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
6 2 1 4 1 3 2 2 2
出力例 1
0 3 4 0
各クエリを処理した後の山は順に以下のようになります:
- カードの山の一番上のカードを取り除く。取り除いたカードに書かれた整数は 0 であるため、 0 を出力する。
- カードの山は 0 の書かれたカードが 99 枚となる。
- 4 が書かれたカードを山の上に追加する。
- カードの山は上から順に 4 の書かれたカードが 1 枚、 0 の書かれたカードが 99 枚となる。
- 3 が書かれたカードを山の上に追加する。
- カードの山は上から順に 3 の書かれたカードが 1 枚、 4 の書かれたカードが 1 枚、 0 の書かれたカードが 99 枚となる。
- カードの山の一番上のカードを取り除く。取り除いたカードに書かれた整数は 3 であるため、 3 を出力する。
- カードの山は上から順に 4 の書かれたカードが 1 枚、 0 の書かれたカードが 99 枚となる。
- カードの山の一番上のカードを取り除く。取り除いたカードに書かれた整数は 4 であるため、 4 を出力する。
- カードの山は 0 の書かれたカードが 99 枚となる。
- カードの山の一番上のカードを取り除く。取り除いたカードに書かれた整数は 0 であるため、 0 を出力する。
- カードの山は 0 の書かれたカードが 98 枚となる。
入力例 2
5 2 2 2 2 2
出力例 2
0 0 0 0 0
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
There is a stack of 100 cards, each labeled with the integer 0.
Process Q queries. Each query is of one of the following:
- Type 1: Place a card labeled with an integer x on top of the stack.
- Type 2: Remove the top card of the stack and output the integer written on that removed card. Under the constraints of this problem, the stack always has at least one card.
Constraints
- 1 \le Q \le 100
- 1 \le x \le 100
- There is at least one query of type 2.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
Q
\text{query}_1
\text{query}_2
\vdots
\text{query}_Q
The i-th query \text{query}_i starts with the query type c_i (1 or 2), followed by the integer x if c_i=1.
That is, each query is in one of the following two formats:
1 x
2
Output
Let q be the number of queries with c_i=2. Print q lines.
The j-th line (1 \le j \le q) should contain the answer to the j-th such query.
Sample Input 1
6 2 1 4 1 3 2 2 2
Sample Output 1
0 3 4 0
After processing each query, the stack is as follows:
- Remove the top card of the stack. The integer on the removed card is 0, so output 0.
- The stack then has 99 cards labeled with 0.
- Add a card labeled 4 on top.
- The stack then has 1 card labeled 4, and 99 cards labeled 0, from top to bottom.
- Add a card labeled 3 on top.
- The stack then has 1 card labeled 3, 1 card labeled 4, and 99 cards labeled 0, from top to bottom.
- Remove the top card. The integer on that card is 3, so output 3.
- The stack then has 1 card labeled 4, and 99 cards labeled 0, from top to bottom.
- Remove the top card. The integer on that card is 4, so output 4.
- The stack then has 99 cards labeled 0.
- Remove the top card. The integer on that card is 0, so output 0.
- The stack then has 98 cards labeled 0.
Sample Input 2
5 2 2 2 2 2
Sample Output 2
0 0 0 0 0
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
N 個の黒色のボールと M 個の白色のボールがあります。
ボールにはそれぞれ価値がつけられており、i\ (1\leq i\leq N) 個目の黒色のボールの価値は B_i、j\ (1\leq j\leq M) 個目の白色のボールの価値は W_j です。
黒色のボールの個数が白色のボールの個数以上になるようにボールを 0 個以上選ぶとき、選んだボールの価値の総和としてありうる最大値を求めてください。
制約
- 1\leq N,M\leq 2\times 10^5
- -10^9\leq B_i,W_j\leq 10^9
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M B_1 B_2 \ldots B_N W_1 W_2 \ldots W_M
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 3 8 5 -1 3 3 -2 -4
出力例 1
19
1,2,4 個目の黒色のボールと 1 個目の白色のボールを選ぶとき、選んだボールの価値の総和は 8+5+3+3=19 となりこれが最大です。
入力例 2
4 3 5 -10 -2 -5 8 1 4
出力例 2
15
1,3 個目の黒色のボールと 1,3 個目の白色のボールを選ぶとき、選んだボールの価値の総和は 5+(-2)+8+4=15 となりこれが最大です。
入力例 3
3 5 -36 -33 -31 12 12 28 24 27
出力例 3
0
ボールを 1 つも選ばないことも可能です。
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
There are N black balls and M white balls.
Each ball has a value. The value of the i-th black ball (1 \le i \le N) is B_i, and the value of the j-th white ball (1 \le j \le M) is W_j.
Choose zero or more balls so that the number of black balls chosen is at least the number of white balls chosen. Among all such choices, find the maximum possible sum of the values of the chosen balls.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N,M \leq 2\times 10^5
- -10^9 \leq B_i, W_j \leq 10^9
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M B_1 B_2 \ldots B_N W_1 W_2 \ldots W_M
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
4 3 8 5 -1 3 3 -2 -4
Sample Output 1
19
If you choose the 1st, 2nd, and 4th black balls, and the 1st white ball, the sum of their values is 8+5+3+3=19, which is the maximum.
Sample Input 2
4 3 5 -10 -2 -5 8 1 4
Sample Output 2
15
If you choose the 1st and 3rd black balls, and the 1st and 3rd white balls, the sum of their values is 5+(-2)+8+4=15, which is the maximum.
Sample Input 3
3 5 -36 -33 -31 12 12 28 24 27
Sample Output 3
0
It is possible to choose no balls.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 400 点
問題文
頂点に 1 から N の、辺に 1 から M の番号がついた N 頂点 M 辺の単純連結無向グラフが与えられます。辺 i は頂点 u_i と頂点 v_i を結んでおり、ラベル w_i が付けられています。
頂点 1 から頂点 N への単純パス(同じ頂点を 2 度以上通らないパス)のうち、パスに含まれる辺につけられたラベルの総 XOR としてあり得る最小値を求めてください。
XOR とは
非負整数 A,B の XOR A \oplus B は、以下のように定義されます。- A \oplus B を二進表記した際の 2^k \, (k \geq 0) の位の数は、A,B を二進表記した際の 2^k の位の数のうち一方のみが 1 であれば 1、そうでなければ 0 である。
一般に k 個の整数 p_1, \dots, p_k の XOR は (\cdots ((p_1 \oplus p_2) \oplus p_3) \oplus \cdots \oplus p_k) と定義され、これは p_1, \dots, p_k の順番によらないことが証明できます。
制約
- 2\leq N\leq 10
- N-1\leq M\leq \frac{N(N-1)}{2}
- 1\leq u_i\lt v_i\leq N
- 0\leq w_i\lt 2^{60}
- 入力で与えられるグラフは単純連結無向グラフ
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M u_1 v_1 w_1 u_2 v_2 w_2 \vdots u_M v_M w_M
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
4 4 1 2 3 2 4 5 1 3 4 3 4 7
出力例 1
3
頂点 1 から頂点 4 への単純パスは以下の 2 つ存在します。
- 頂点 1 \to 頂点 2 \to 頂点 4
- 頂点 1 \to 頂点 3 \to 頂点 4
1 つ目のパスに含まれる辺につけられたラベルの総 XOR は 6、 2 つ目のパスに含まれる辺につけられたラベルの総 XOR は 3 であるため、答えは 3 です。
入力例 2
4 3 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 4 4
出力例 2
7
入力例 3
7 10 1 2 726259430069220777 1 4 988687862609183408 1 5 298079271598409137 1 6 920499328385871537 1 7 763940148194103497 2 4 382710956291350101 3 4 770341659133285654 3 5 422036395078103425 3 6 472678770470637382 5 7 938201660808593198
出力例 3
186751192333709144
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
You are given a simple connected undirected graph with N vertices numbered 1 through N and M edges numbered 1 through M. Edge i connects vertices u_i and v_i, and has a label w_i.
Among all simple paths (paths that do not pass through the same vertex more than once) from vertex 1 to vertex N, find the minimum XOR of the labels of the edges on the path.
Notes on XOR
For non-negative integers A and B, their XOR A \oplus B is defined as follows:- In the binary representation of A \oplus B, the digit in the place corresponding to 2^k \,(k \ge 0) is 1 if and only if exactly one of the digits in the same place of A and B is 1; otherwise, it is 0.
In general, the XOR of k integers p_1, \dots, p_k is defined as (\cdots ((p_1 \oplus p_2) \oplus p_3) \oplus \cdots \oplus p_k). It can be proved that it does not depend on the order of p_1, \dots, p_k.
Constraints
- 2 \leq N \leq 10
- N-1 \leq M \leq \frac{N(N-1)}{2}
- 1 \leq u_i < v_i \leq N
- 0 \leq w_i < 2^{60}
- The given graph is a simple connected undirected graph.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M u_1 v_1 w_1 u_2 v_2 w_2 \vdots u_M v_M w_M
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
4 4 1 2 3 2 4 5 1 3 4 3 4 7
Sample Output 1
3
There are two simple paths from vertex 1 to vertex 4:
- 1 \to 2 \to 4
- 1 \to 3 \to 4
The XOR of the labels on the edges of the first path is 6, and that of the second path is 3. Therefore, the answer is 3.
Sample Input 2
4 3 1 2 1 2 3 2 3 4 4
Sample Output 2
7
Sample Input 3
7 10 1 2 726259430069220777 1 4 988687862609183408 1 5 298079271598409137 1 6 920499328385871537 1 7 763940148194103497 2 4 382710956291350101 3 4 770341659133285654 3 5 422036395078103425 3 6 472678770470637382 5 7 938201660808593198
Sample Output 3
186751192333709144
Time Limit: 3 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 450 点
問題文
整数 N,M と長さ M の整数列 X=(X_1,X_2,\ldots,X_M),Y=(Y_1,Y_2,\ldots,Y_M),Z=(Z_1,Z_2,\ldots,Z_M) が与えられます。ここで、 X,Y の要素は全て 1 以上 N 以下であることが保証されます。
長さ N の非負整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) であって、以下の条件を満たす整数列を 良い整数列 と呼びます。
- 1\le i\le M を満たす全ての整数 i に対し、 A_{X_i} と A_{Y_i} の XOR が Z_i と一致する。
良い整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) が存在するか判定し、存在するならば要素の総和 \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^N A_i が最小になるような良い整数列を一つ求めてください。
XOR とは
非負整数 A,B の XOR A \oplus B は、以下のように定義されます。- A \oplus B を二進表記した際の 2^k \, (k \geq 0) の位の数は、A,B を二進表記した際の 2^k の位の数のうち一方のみが 1 であれば 1、そうでなければ 0 である。
制約
- 1\le N\le 2\times 10^5
- 0\le M\le 10^5
- 1\le X_i,Y_i\le N
- 0\le Z_i\le 10^9
- 入力される値は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M X_1 Y_1 Z_1 X_2 Y_2 Z_2 \vdots X_M Y_M Z_M
出力
良い整数列が存在しないならば -1 を出力せよ。
良い整数列が存在するならば要素の総和が最小になる良い整数列を一つ空白区切りで出力せよ。
なお、要素の総和が最小となる良い整数列が複数存在する場合は、どれを出力しても正答となる。
入力例 1
3 2 1 3 4 1 2 3
出力例 1
0 3 4
A=(0,3,4) は A_1 と A_2 の XOR が 3 、 A_1 と A_3 の XOR が 4 なので良い整数列です。
この他にも A=(1,2,5),(7,4,3) などが良い整数列ですが、良い整数列の中で総和が最小となるのは A=(0,3,4) です。
入力例 2
3 3 1 3 4 1 2 3 2 3 5
出力例 2
-1
良い整数列は存在しないので、 -1 を出力してください。
入力例 3
5 8 4 2 4 2 3 11 3 4 15 4 5 6 3 2 11 3 3 0 3 1 9 3 4 15
出力例 3
0 2 9 6 0
Score : 450 points
Problem Statement
You are given integers N, M and three integer sequences of length M: X = (X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_M), Y = (Y_1, Y_2, \ldots, Y_M), and Z = (Z_1, Z_2, \ldots, Z_M). It is guaranteed that all elements of X and Y are between 1 and N, inclusive.
We call a length-N sequence of non-negative integers A = (A_1, A_2, \ldots, A_N) a good sequence if and only if it satisfies the following condition:
- For every integer i with 1 \le i \le M, the XOR of A_{X_i} and A_{Y_i} is Z_i.
Determine whether a good sequence A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) exists, and if it exists, find one good sequence that minimizes the sum of its elements \displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^N A_i.
Notes on XOR
For non-negative integers A and B, their XOR A \oplus B is defined as follows:- In the binary representation of A \oplus B, the digit in the place corresponding to 2^k \,(k \ge 0) is 1 if and only if exactly one of the digits in the same place of A and B is 1; otherwise, it is 0.
Constraints
- 1 \le N \le 2\times 10^5
- 0 \le M \le 10^5
- 1 \le X_i, Y_i \le N
- 0 \le Z_i \le 10^9
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M X_1 Y_1 Z_1 X_2 Y_2 Z_2 \vdots X_M Y_M Z_M
Output
If no good sequence exists, print -1.
If a good sequence exists, print one good sequence that minimizes the sum of its elements, separated by spaces.
If there are multiple good sequences with the same minimum sum, printing any of them is accepted.
Sample Input 1
3 2 1 3 4 1 2 3
Sample Output 1
0 3 4
A=(0,3,4) is a good sequence because A_1 \oplus A_2 = 3 and A_1 \oplus A_3 = 4.
Other good sequences include A=(1,2,5) and A=(7,4,3), but A=(0,3,4) has the smallest sum among all good sequences.
Sample Input 2
3 3 1 3 4 1 2 3 2 3 5
Sample Output 2
-1
No good sequence exists, so print -1.
Sample Input 3
5 8 4 2 4 2 3 11 3 4 15 4 5 6 3 2 11 3 3 0 3 1 9 3 4 15
Sample Output 3
0 2 9 6 0
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 500 点
問題文
整数 N,M と長さ N の非負整数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_N) が与えられます。
k=0,1,\ldots,M-1 に対して以下の問題を解いてください。
整数列 B=(B_1,B_2,\ldots,B_N) を B_i が A_i+k を M で割ったあまりとなるように定義したときの、 B の転倒数を求めてください。
転倒数とは
数列 (A_1,A_2,\dots,A_N) の転倒数とは、 1 \le i < j \le N かつ A_i > A_j を満たす整数組 (i,j) の個数を指します。制約
- 1\le N,M\le 2\times 10^5
- 0\le A_i< M
- 入力される値は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N
出力
M 行出力せよ。
i 行目 (1\le i\le M) には、 k=i-1 の場合の答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 3 2 1 0
出力例 1
3 1 1
- k=0 のとき: B=(2 , 1 ,0) となります。このときの転倒数は 3 です。
- k=1 のとき: B=(0,2,1) となります。このときの転倒数は 1 です。
- k=2 のとき: B=(1,0,2) となります。このときの転倒数は 1 です。
入力例 2
5 6 5 3 5 0 1
出力例 2
7 3 3 1 1 5
入力例 3
7 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
出力例 3
0 6 10 12 12 10 6
Score : 500 points
Problem Statement
You are given integers N, M and a length-N sequence of non-negative integers A = (A_1, A_2, \ldots, A_N).
For k = 0, 1, \ldots, M-1, solve the following problem:
Define an integer sequence B = (B_1, B_2, \ldots, B_N) so that B_i is the remainder of A_i + k when divided by M. Find the inversion number in B.
What is the inversion number?
The inversion number of a sequence (A_1, A_2, \dots, A_N) is the number of integer pairs (i, j) satisfying 1 \le i < j \le N and A_i > A_j.Constraints
- 1 \le N,M \le 2\times 10^5
- 0 \le A_i < M
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M A_1 A_2 \ldots A_N
Output
Print M lines.
The i-th line (1 \le i \le M) should contain the answer for the case k = i-1.
Sample Input 1
3 3 2 1 0
Sample Output 1
3 1 1
- For k=0: B=(2, 1, 0). The inversion number is 3.
- For k=1: B=(0, 2, 1). The inversion number is 1.
- For k=2: B=(1, 0, 2). The inversion number is 1.
Sample Input 2
5 6 5 3 5 0 1
Sample Output 2
7 3 3 1 1 5
Sample Input 3
7 7 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
Sample Output 3
0 6 10 12 12 10 6
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 600 点
問題文
H 行 W 列のグリッドがあり、それぞれのマスには 0 または 1 が書かれています。上から i 行目、左から j 行目のマスには整数 A_{i,j} が書かれています。
このグリッドに対して、2 種類の操作を好きな順番で何度でも行うことができます。
- 操作 X: 整数 x\ (1\leq x\leq H) を選ぶ。各整数 1\leq y\leq W に対して A_{x,y} を 1-A_{x,y} で置き換える。
- 操作 Y: 整数 y\ (1\leq y\leq W) を選ぶ。各整数 1\leq x\leq H に対して A_{x,y} を 1-A_{x,y} で置き換える。
操作が終了した後の \displaystyle \sum_{x=1}^H\sum_{y=1}^W A_{x,y} としてあり得る最小値を求めてください。
制約
- 1\leq H\leq 2\times 10^5
- 1\leq W\leq 18
- H,W は整数
- A_{i,1}A_{i,2}\ldots A_{i,W} は
0および1からなる長さ W の文字列
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
H W
A_{1,1}A_{1,2}\ldots A_{1,W}
A_{2,1}A_{2,2}\ldots A_{2,W}
\vdots
A_{H,1}A_{H,2}\ldots A_{H,W}
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 3 100 010 110
出力例 1
2
以下のように操作すると、グリッドの状態は下図のように変化し \displaystyle \sum_{x=1}^H\sum_{y=1}^W A_{x,y}=2 にすることができます。
- 操作 Y で y=1 を選ぶ
- 操作 X で x=2 を選ぶ
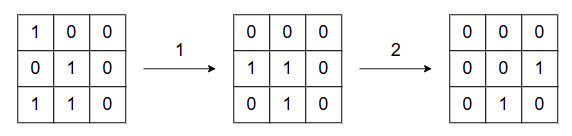
\displaystyle \sum_{x=1}^H\sum_{y=1}^W A_{x,y}\leq 1 にすることはできないので答えは 2 です。
入力例 2
3 4 1111 1111 1111
出力例 2
0
入力例 3
10 5 10000 00111 11000 01000 10110 01110 10101 00100 00100 10001
出力例 3
13
Score : 600 points
Problem Statement
There is a H \times W grid, and each cell contains 0 or 1. The cell at the i-th row from the top and the j-th column from the left contains an integer A_{i,j}.
You can perform the following two operations any number of times in any order:
- Operation X: Choose an integer x (1 \leq x \leq H). For every integer 1 \leq y \leq W, replace A_{x,y} with 1 - A_{x,y}.
- Operation Y: Choose an integer y (1 \leq y \leq W). For every integer 1 \leq x \leq H, replace A_{x,y} with 1 - A_{x,y}.
Find the minimum possible value of \displaystyle \sum_{x=1}^H\sum_{y=1}^W A_{x,y} after the process.
Constraints
- 1 \leq H \leq 2\times 10^5
- 1 \leq W \leq 18
- H and W are integers.
- A_{i,1}A_{i,2}\ldots A_{i,W} is a length-W string consisting of
0and1.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
H W
A_{1,1}A_{1,2}\ldots A_{1,W}
A_{2,1}A_{2,2}\ldots A_{2,W}
\vdots
A_{H,1}A_{H,2}\ldots A_{H,W}
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
3 3 100 010 110
Sample Output 1
2
By performing the following operations, the grid changes as shown below, and you get \displaystyle \sum_{x=1}^H\sum_{y=1}^W A_{x,y} = 2.
- Operation Y with y=1
- Operation X with x=2

It is impossible to make \displaystyle \sum_{x=1}^H\sum_{y=1}^W A_{x,y} \leq 1, so the answer is 2.
Sample Input 2
3 4 1111 1111 1111
Sample Output 2
0
Sample Input 3
10 5 10000 00111 11000 01000 10110 01110 10101 00100 00100 10001
Sample Output 3
13