Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
正整数 A,B が与えられます。
A+B の二乗を出力してください。
制約
- 1\leq A,B \leq 2025
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
A B
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
20 25
出力例 1
2025
(20+25)^2=2025 です。
入力例 2
30 25
出力例 2
3025
入力例 3
45 11
出力例 3
3136
入力例 4
2025 1111
出力例 4
9834496
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
You are given two positive integers A and B.
Output the square of A + B.
Constraints
- 1 \leq A,B \leq 2025
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
A B
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
20 25
Sample Output 1
2025
(20+25)^2=2025.
Sample Input 2
30 25
Sample Output 2
3025
Sample Input 3
45 11
Sample Output 3
3136
Sample Input 4
2025 1111
Sample Output 4
9834496
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 150 点
問題文
九九の表に現れる 81 個の整数のうち、X でないものの総和を求めてください。
縦 9 マス、横 9 マスのグリッドがあります。
グリッドの各マスには整数が書きこまれていて、グリッドの上から i 行目、左から j 列目のマスには i \times j が書きこまれています。
整数 X が与えられます。グリッドに書きこまれた 81 個の整数のうち X でないものの総和を求めてください。値の等しい整数が異なるマスに書きこまれている場合は別々に加算する点に注意してください。
制約
- X は 1 以上 81 以下の整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
X
出力
グリッドに書きこまれた 81 個の整数のうち X でないものの総和を出力せよ。
入力例 1
1
出力例 1
2024
グリッドに 1 が書きこまれたマスは上から 1 行目、左から 1 列目のマスのみです。1 でない整数を全て足し合わせると総和は 2024 になります。
入力例 2
11
出力例 2
2025
グリッドに 11 が書きこまれたマスは存在しません。よって 81 個の整数全てを足し合わせた総和である 2025 が答えとなります。
入力例 3
24
出力例 3
1929
Score : 150 points
Problem Statement
Among the 81 integers that appear in the 9-by-9 multiplication table, find the sum of those that are not X.
There is a grid of size 9 by 9.
Each cell of the grid contains an integer: the cell at the i-th row from the top and the j-th column from the left contains i \times j.
You are given an integer X. Among the 81 integers written in this grid, find the sum of those that are not X. If the same value appears in multiple cells, add it for each cell.
Constraints
- X is an integer between 1 and 81, inclusive.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
X
Output
Print the sum of the integers that are not X among the 81 integers written in the grid.
Sample Input 1
1
Sample Output 1
2024
The only cell with 1 in the grid is the cell at the 1st row from the top and 1st column from the left. Summing all integers that are not 1 yields 2024.
Sample Input 2
11
Sample Output 2
2025
There is no cell containing 11 in the grid. Thus, the answer is 2025, the sum of all 81 integers.
Sample Input 3
24
Sample Output 3
1929
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 350 点
問題文
10 以上の正整数のうち、十進数表記したときに先頭の桁(最も大きい位)の数字がそれ以外のどの桁の数字よりも真に大きくなるようなものを ヘビ数 とよびます。 例えば、31 や 201 はヘビ数ですが、35 や 202 はヘビ数ではありません。
L 以上 R 以下のヘビ数が何個あるか求めてください。
制約
- 10\leq L \leq R \leq 10^{18}
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
L R
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
97 210
出力例 1
6
97 以上 210 以下のヘビ数は、97,98,100,200,201,210 の 6 個です。
入力例 2
1000 9999
出力例 2
2025
入力例 3
252509054433933519 760713016476190692
出力例 3
221852052834757
Score : 350 points
Problem Statement
A positive integer not less than 10 whose top digit (the most significant digit) in decimal representation is strictly larger than every other digit in that number is called a Snake number. For example, 31 and 201 are Snake numbers, but 35 and 202 are not.
Find how many Snake numbers exist between L and R, inclusive.
Constraints
- 10 \leq L \leq R \leq 10^{18}
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
L R
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
97 210
Sample Output 1
6
The Snake numbers between 97 and 210, inclusive, are 97, 98, 100, 200, 201, and 210: there are six.
Sample Input 2
1000 9999
Sample Output 2
2025
Sample Input 3
252509054433933519 760713016476190692
Sample Output 3
221852052834757
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 400 点
問題文
H 行 W 列のグリッドがあります。 上から i 行目、左から j 列目のマスを (i,j) と表記します。
各マスはスタートマス・ゴールマス・空きマス・障害物マスのいずれかであり、その情報は H 個の長さ W の文字列 S_1,S_2,\dots,S_H によって表されます。
具体的には、マス (i,j) は S_i の j 文字目が S であるときスタートマス、G であるときゴールマス、. であるとき空きマス、# であるとき障害物マスです。
ここで、スタートマスとゴールマスはちょうど 1 つずつ存在することが保証されます。
あなたは今スタートマスにいます。 あなたの目標は、今いるマスと辺で隣接するマスに移動することを繰り返してゴールマスへ行くことです。 ただし、障害物マスやグリッドの外に移動することはできず、また縦移動と横移動を 1 回ずつ交互に行わなければなりません。(最初の移動の向きは任意です。)
ゴールマスへ行くことが可能であるか判定し、可能ならば移動回数の最小値を求めてください。
より形式的には、以下の条件をすべて満たすマスの列 (i_1,j_1),(i_2,j_2),\dots,(i_k,j_k) が存在するか判定し、存在するならば k-1 の最小値を求めてください。
- すべての 1\leq l\leq k について、1\leq i_l\leq H かつ 1\leq j_l\leq W であり、(i_l,j_l) は障害物マスでない
- (i_1,j_1) はスタートマス
- (i_k,j_k) はゴールマス
- すべての 1\leq l\leq k-1 について、|i_l-i_{l+1}|+|j_l-j_{l+1}|=1
- すべての 1\leq l\leq k-2 について、i_l\neq i_{l+1} ならば i_{l+1}=i_{l+2}
- すべての 1\leq l\leq k-2 について、j_l\neq j_{l+1} ならば j_{l+1}=j_{l+2}
制約
- 1\leq H,W \leq 1000
- H,W は整数
- S_i は
S,G,.,#からなる長さ W の文字列 - スタートマスとゴールマスはちょうど 1 つずつ存在する
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
H W S_1 S_2 \vdots S_H
出力
ゴールマスへ行くことが可能ならば移動回数の最小値を、不可能ならば -1 を出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 5 .S#.G ..... .#...
出力例 1
7
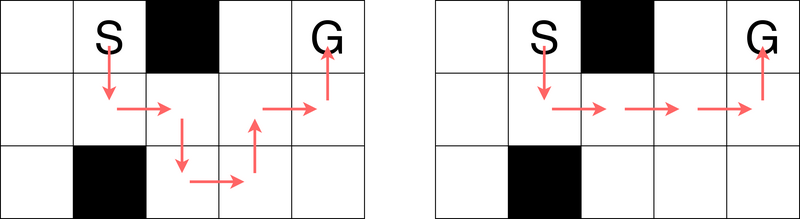
左図のように (1,2)\rightarrow(2,2)\rightarrow(2,3)\rightarrow(3,3)\rightarrow(3,4)\rightarrow(2,4)\rightarrow(2,5)\rightarrow(1,5) と移動することで、7 回の移動でゴールマスへ行くことができます。 6 回以下の移動でゴールマスへ行くことはできないので、答えは 7 です。
右図のように横移動を連続で行う経路(あるいは縦移動を連続で行う経路)はとれないことに注意してください。
入力例 2
3 5 ..#.G ..... S#...
出力例 2
-1
ゴールマスへ行くことはできません。
入力例 3
8 63 ............................................................... ..S...#............................#####..#####..#####..####G.. ..#...#................................#..#...#......#..#...... ..#####..####...####..####..#..#...#####..#...#..#####..#####.. ..#...#..#..#...#..#..#..#..#..#...#......#...#..#..........#.. ..#...#..#####..####..####..####...#####..#####..#####..#####.. ................#.....#........#............................... ................#.....#........#...............................
出力例 3
148
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
You are given a grid with H rows and W columns. Let (i,j) denote the cell at the i-th row from the top and the j-th column from the left.
Each cell is one of the following: a start cell, a goal cell, an empty cell, or an obstacle cell. This information is described by H strings S_1,S_2,\dots,S_H, each of length W. Specifically, the cell (i,j) is a start cell if the j-th character of S_i is S, a goal cell if it is G, an empty cell if it is ., and an obstacle cell if it is #. It is guaranteed that there is exactly one start cell and exactly one goal cell.
You are currently on the start cell. Your objective is to reach the goal cell by repeatedly moving to a cell adjacent by an edge to the one you are in. However, you cannot move onto an obstacle cell or move outside the grid, and you must alternate between moving vertically and moving horizontally each time. (The direction of the first move can be chosen arbitrarily.)
Determine if it is possible to reach the goal cell. If it is, find the minimum number of moves required.
More formally, check if there exists a sequence of cells (i_1,j_1),(i_2,j_2),\dots,(i_k,j_k) satisfying all of the following conditions. If such a sequence exists, find the minimum value of k-1.
- For every 1 \leq l \leq k, it holds that 1 \leq i_l \leq H and 1 \leq j_l \leq W, and (i_l,j_l) is not an obstacle cell.
- (i_1,j_1) is the start cell.
- (i_k,j_k) is the goal cell.
- For every 1 \leq l \leq k-1, |i_l - i_{l+1}| + |j_l - j_{l+1}| = 1.
- For every 1 \leq l \leq k-2, if i_l \neq i_{l+1}, then i_{l+1} = i_{l+2}.
- For every 1 \leq l \leq k-2, if j_l \neq j_{l+1}, then j_{l+1} = j_{l+2}.
Constraints
- 1 \leq H,W \leq 1000
- H and W are integers.
- Each S_i is a string of length W consisting of
S,G,.,#. - There is exactly one start cell and exactly one goal cell.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
H W S_1 S_2 \vdots S_H
Output
If it is possible to reach the goal cell, print the minimum number of moves. Otherwise, print -1.
Sample Input 1
3 5 .S#.G ..... .#...
Sample Output 1
7

As shown in the left figure, you can move as (1,2)\rightarrow(2,2)\rightarrow(2,3)\rightarrow(3,3)\rightarrow(3,4)\rightarrow(2,4)\rightarrow(2,5)\rightarrow(1,5), reaching the goal cell in 7 moves. It is impossible in 6 moves or fewer, so the answer is 7.
Note that you cannot take a path that moves horizontally (or vertically) consecutively without alternating as shown in the right figure.
Sample Input 2
3 5 ..#.G ..... S#...
Sample Output 2
-1
It is not possible to reach the goal cell.
Sample Input 3
8 63 ............................................................... ..S...#............................#####..#####..#####..####G.. ..#...#................................#..#...#......#..#...... ..#####..####...####..####..#..#...#####..#...#..#####..#####.. ..#...#..#..#...#..#..#..#..#..#...#......#...#..#..........#.. ..#...#..#####..####..####..####...#####..#####..#####..#####.. ................#.....#........#............................... ................#.....#........#...............................
Sample Output 3
148
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 500 点
問題文
正整数 n の桁和を、n を 10 進法で表したときの各桁の和と定義します。例えば 2025 の桁和は 2 + 0 + 2 + 5 = 9 です。
正整数 n が n の桁和で割り切れる時、n を 良い整数 と呼びます。例えば 2025 はその桁和である 9 で割り切れるので良い整数です。
正整数の組 (a, a+1) であって a と a+1 が共に良い整数であるものを 双子の良い整数 と呼びます。例えば (2024, 2025) は双子の良い整数です。
正整数 N が与えられます。N \leq a かつ a + 1 \leq 2N であるような双子の良い整数 (a, a + 1) を発見してください。そのような (a, a + 1) が存在しない場合はそのことを報告してください。
制約
- N は 1 以上 10^{100000} 未満の整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N
出力
問題文の条件を満たす (a, a+1) が存在する場合は a を、存在しない場合は -1 を出力せよ。a は leading-zeros を省略した表現で出力する必要がある点に注意せよ。
条件を満たす (a, a+1) が複数存在する場合はどれを出力してもよい。
入力例 1
5
出力例 1
8
(8, 9) は問題文の条件を満たす双子の良い整数です。他にも (5, 6), (6, 7), (7, 8), (9, 10) が条件を満たします。
入力例 2
21
出力例 2
-1
問題文の条件を満たす双子の良い整数は存在しません。
入力例 3
1234
出力例 3
2024
(2024, 2025) は問題文の条件を満たす双子の良い整数です。
入力例 4
1234567890123456789012345678901234567890
出力例 4
1548651852734633803438094164372911259190
Score : 500 points
Problem Statement
The digit sum of a positive integer n is defined as the sum of its digits when n is written in decimal. For example, the digit sum of 2025 is 2 + 0 + 2 + 5 = 9.
A positive integer n is called a good integer if it is divisible by its digit sum. For example, 2025 is a good integer because it is divisible by its digit sum of 9.
A pair of positive integers (a, a+1) is called twin good integers if both a and a+1 are good integers. For example, (2024, 2025) is twin good integers.
You are given a positive integer N. Find a pair of twin good integers (a, a + 1) such that N \leq a and a + 1 \leq 2N. If no such pair exists, report that fact.
Constraints
- N is an integer at least 1 and less than 10^{100000}.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
Output
If there exists such a pair (a, a+1), output a. Otherwise, output -1. Do not print leading zeros.
If there are multiple such pairs, you may print any.
Sample Input 1
5
Sample Output 1
8
(8, 9) is a valid pair of twin good integers satisfying the conditions. Other examples include (5, 6), (6, 7), (7, 8), (9, 10).
Sample Input 2
21
Sample Output 2
-1
No pair of twin good integers satisfies the conditions.
Sample Input 3
1234
Sample Output 3
2024
(2024, 2025) is a valid pair of twin good integers.
Sample Input 4
1234567890123456789012345678901234567890
Sample Output 4
1548651852734633803438094164372911259190
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 550 点
問題文
正整数 N,M および、各要素が 1 以上 N 以下の整数である長さ N の数列 A=(A_1,A_2,\dots,A_N) が与えられます。
各要素が 1 以上 M 以下の整数である長さ N の数列 x=(x_1,x_2,\dots,x_N) のうち、以下の条件を満たすものの数を 998244353 で割った余りを求めてください。
- 全ての i\ (1\leq i\leq N) について、x_i \leq x_{A_i}
制約
- 1\leq N,M \leq 2025
- 1\leq A_i\leq N
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3 3 2 1 1
出力例 1
6
x=(1,1,1),(2,2,1),(2,2,2),(3,3,1),(3,3,2),(3,3,3) が条件を満たします。
入力例 2
4 9 1 1 1 1
出力例 2
2025
入力例 3
10 5 9 4 5 5 4 2 1 5 7 2
出力例 3
10010
Score : 550 points
Problem Statement
You are given positive integers N, M, and a sequence A = (A_1, A_2, \dots, A_N) of length N, each element being an integer between 1 and N, inclusive.
Find the number, modulo 998244353, of sequences x = (x_1, x_2, \dots, x_N) of length N, each element being an integer between 1 and M, inclusive, that satisfy the following condition:
- x_i \leq x_{A_i} for every i (1 \leq i \leq N).
Constraints
- 1 \leq N, M \leq 2025
- 1 \leq A_i \leq N
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M A_1 A_2 \dots A_N
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
3 3 2 1 1
Sample Output 1
6
The sequences x=(1,1,1),(2,2,1),(2,2,2),(3,3,1),(3,3,2),(3,3,3) satisfy the condition.
Sample Input 2
4 9 1 1 1 1
Sample Output 2
2025
Sample Input 3
10 5 9 4 5 5 4 2 1 5 7 2
Sample Output 3
10010
Time Limit: 12 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 675 点
問題文
頂点に 1 から N までの番号がついた N 頂点の単純無向連結グラフ G のうち次の条件を満たすものの個数を 998244353 で割った余りを求めてください。
- G に含まれる任意の回路の辺数が素数である。
ここで回路とは、同じ頂点を 2 回以上通ってもよい閉路を意味する。(同じ辺を 2 回以上通ってはならない)
制約
- N は 1 以上 2.5 \times 10^5 以下の整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N
出力
問題文の条件を満たす単純無向連結グラフ G の個数を 998244353 で割った余りを出力せよ。
入力例 1
3
出力例 1
4
条件を満たすグラフ G は以下の 4 個です。
- (1, 2), (1, 3) を辺集合に持つグラフ
- (1, 2), (2, 3) を辺集合に持つグラフ
- (1, 3), (2, 3) を辺集合に持つグラフ
- (1, 2), (1, 3), (2, 3) を辺集合に持つグラフ
入力例 2
2025
出力例 2
879839321
入力例 3
61261
出力例 3
202537766
Score : 675 points
Problem Statement
Find the number, modulo 998244353, of simple undirected connected graphs G with N vertices labeled from 1 to N that satisfy the following condition:
- For every circuit in G, the number of edges in that circuit is a prime number.
Here, a circuit is a closed trail that may pass through the same vertex more than once (but must not use the same edge more than once).
Constraints
- N is an integer between 1 and 2.5 \times 10^5, inclusive.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N
Output
Print the number, modulo 998244353, of simple undirected connected graphs G satisfying the condition.
Sample Input 1
3
Sample Output 1
4
There are four such graphs G:
- The graph with edges (1, 2) and (1, 3)
- The graph with edges (1, 2) and (2, 3)
- The graph with edges (1, 3) and (2, 3)
- The graph with edges (1, 2), (1, 3), and (2, 3)
Sample Input 2
2025
Sample Output 2
879839321
Sample Input 3
61261
Sample Output 3
202537766