Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 100 点
問題文
英大文字と英小文字からなる文字列 S が与えられます。S の英大文字のみを元の順序で連結して得られる文字列を出力してください。
制約
- S は英大文字と英小文字からなる文字列である
- S の長さは 1 以上 100 以下である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
S
出力
S の英大文字のみを元の順序で連結して得られる文字列を出力せよ。
入力例 1
AtCoderBeginnerContest
出力例 1
ACBC
S の英大文字のみを元の順序で連結して得られる文字列は ACBC です。よって、ACBC を出力します。
入力例 2
PaymentRequired
出力例 2
PR
入力例 3
program
出力例 3
S に英大文字が含まれないことがあることに注意してください。
Score : 100 points
Problem Statement
You are given a string S consisting of uppercase and lowercase English letters. Print the string obtained by concatenating only the uppercase letters of S in their original order.
Constraints
- S is a string of uppercase and lowercase English letters.
- The length of S is between 1 and 100, inclusive.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
S
Output
Print the string obtained by concatenating only the uppercase letters of S in their original order.
Sample Input 1
AtCoderBeginnerContest
Sample Output 1
ACBC
The string obtained by concatenating only the uppercase letters of S in their original order is ACBC. Hence, print ACBC.
Sample Input 2
PaymentRequired
Sample Output 2
PR
Sample Input 3
program
Sample Output 3
Note that S may contain no uppercase letters.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 200 点
問題文
高橋君はAtCoderレストランの前の待ち行列の管理をしたいです。はじめ、待ち行列に並んでいる人はいません。 また、待ち行列に並ぶ人は必ず注文する料理のメニュー番号が書かれた食券を持って並びます。
Q 個のクエリが与えられるので順に処理してください。クエリは 2 種類あり、以下のいずれかの形式で与えられます。
1 X: 待ち行列の末尾に 1 人並ぶ。このとき並ぶ人はメニュー番号が X の食券を持って並ぶ。2: 待ち行列の先頭にいる人をレストランに案内する。このとき案内される人が持っている食券のメニュー番号を出力する。
制約
- 1 \leq Q \leq 100
- 1 \leq X \leq 100
- 2 つ目の形式のクエリについて、案内する前に待ち行列に並んでいる人がいる
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
Q
\mathrm{query}_1
\mathrm{query}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{query}_Q
各クエリは以下の 2 種類のいずれかの形式で与えられる。
1 X
2
出力
問題文の指示に従ってクエリへの答えを改行区切りで出力せよ。
入力例 1
6 1 3 1 1 1 15 2 1 3 2
出力例 1
3 1
はじめ、待ち行列に並んでいる人はいません。
- 1 つ目のクエリについて、メニュー番号が 3 の食券を持った人が待ち行列の末尾に並びます。この時、待ち行列に並んでいる人が持っている食券のメニュー番号は先頭の人から順に 3 です。
- 2 つ目のクエリについて、メニュー番号が 1 の食券を持った人が待ち行列の末尾に並びます。この時、待ち行列に並んでいる人が持っている食券のメニュー番号は先頭の人から順に 3,1 です。
- 3 つ目のクエリについて、メニュー番号が 15 の食券を持った人が待ち行列の末尾に並びます。この時、待ち行列に並んでいる人が持っている食券のメニュー番号は先頭の人から順に 3,1,15 です。
- 4 つ目のクエリについて、待ち行列の先頭にいる人をレストランに案内します。案内する人はメニュー番号が 3 の食券を持っているので 3 を出力します。この時、待ち行列に並んでいる人が持っている食券のメニュー番号は先頭の人から順に 1,15 です。
- 5 つ目のクエリについて、メニュー番号が 3 の食券を持った人が待ち行列の末尾に並びます。この時、待ち行列に並んでいる人が持っている食券のメニュー番号は先頭の人から順に 1,15,3 です。
- 6 つ目のクエリについて、待ち行列の先頭にいる人をレストランに案内します。案内する人はメニュー番号が 1 の食券を持っているので 1 を出力します。この時、待ち行列に並んでいる人が持っている食券のメニュー番号は先頭の人から順に 15,3 です。
入力例 2
7 1 3 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 5 1 9 1 2
出力例 2
2 つ目の形式のクエリがないことがあることに注意してください。
Score : 200 points
Problem Statement
Takahashi wants to manage the waiting line in front of the AtCoder Restaurant. Initially, the waiting line is empty. Each person who joins the line holds a meal ticket with the menu number of the dish they will order.
Process Q queries in order. There are two types of queries, given in the following formats:
1 X: One person joins the end of the waiting line holding a ticket with menu number X.2: Takahashi guides the person at the front of the waiting line into the restaurant. Print the menu number on that person’s ticket.
Constraints
- 1 \leq Q \leq 100
- 1 \leq X \leq 100
- For each query of the second type, there is at least one person in the line before guiding.
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
Q
\mathrm{query}_1
\mathrm{query}_2
\vdots
\mathrm{query}_Q
Each query has one of the following two formats:
1 X
2
Output
For each query, print the answer as specified in the problem statement, each on its own line.
Sample Input 1
6 1 3 1 1 1 15 2 1 3 2
Sample Output 1
3 1
Initially, the waiting line is empty.
- For the first query, a person holding a ticket with menu number 3 joins the end of the line. The sequence of menu numbers held by people in line from front to back is 3.
- For the second query, a person holding a ticket with menu number 1 joins the end of the line. The sequence becomes 3,1.
- For the third query, a person holding a ticket with menu number 15 joins the end of the line. The sequence becomes 3,1,15.
- For the fourth query, guide the person at the front into the restaurant. That person holds menu number 3, so print 3. The sequence becomes 1,15.
- For the fifth query, a person holding a ticket with menu number 3 joins the end of the line. The sequence becomes 1,15,3.
- For the sixth query, guide the person at the front into the restaurant. That person holds menu number 1, so print 1. The sequence becomes 15,3.
Sample Input 2
7 1 3 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 5 1 9 1 2
Sample Output 2
Note that there may be no queries of the second type.
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 300 点
問題文
AtCoderレストランでは 1 から N までの番号がつけられている N 種類の食材を扱っています。
また、AtCoderレストランでは 1 から M までの番号がつけられている M 個の料理を提供しています。料理 i には K_i 種類の食材が使われており、食材 A_{i,1}, A_{i,2}, \ldots, A_{i,K_i} が使われています。
すぬけくんは現在 N 種類の食材がすべて苦手です。また、すぬけ君は苦手な食材が 1 種類でも使われている料理を食べることができず、苦手な食材が 1 種類も使われていない料理を食べることができます。
すぬけ君はこれから N 日間かけて苦手な食材を克服しようとしています。 すぬけ君は i 日目に食材 B_i を克服し、それ以降苦手な食材でなくなります。
i=1,2,\ldots,N について以下の値を求めてください。
- i 日目にすぬけ君が食材 B_i を克服した直後、すぬけ君が食べることができるAtCoderレストランの料理の個数
制約
- 1 \leq N \leq 3 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq M \leq 3 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq K_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq M)
- K_i の総和は 3 \times 10^{5} 以下
- 1 \leq A_{i,j} \leq N (1 \leq i \leq M, 1 \leq j \leq K_i)
- A_{i,j} \neq A_{i,k} (1 \leq i \leq M, j \neq k)
- 1 \leq B_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq N)
- B_i \neq B_j (i \neq j )
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M
K_1 A_{1,1} A_{1,2} \ldots A_{1,K_1}
K_2 A_{2,1} A_{2,2} \ldots A_{2,K_2}
\vdots
K_M A_{M,1} A_{M,2} \ldots A_{M,K_M}
B_1 B_2 \ldots B_N
出力
N 行出力せよ。k 行目には、i=k のときの値を出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 4 2 1 2 3 3 4 5 3 1 2 5 1 3 1 3 2 5 4
出力例 1
0 1 2 3 4
以下のようにすぬけ君は苦手な食材を克服します。
- 1 日目: 食材 1 を克服する。このとき、どの料理にも苦手な食材が使われているため 0 を出力する。
- 2 日目: 食材 3 を克服する。このとき、料理 4 は苦手な食材が使われなくなるため食べられるようになる。料理 4 以外の料理は苦手な食材が使われているため、 1 を出力する。
- 3 日目: 食材 2 を克服する。このとき、料理 1 は苦手な食材が使われなくなるため食べられるようになる。料理 1,4 以外の料理は苦手な食材が使われているため、 2 を出力する。
- 4 日目: 食材 5 を克服する。このとき、料理 3 は苦手な食材が使われなくなるため食べられるようになる。料理 1,3,4 以外の料理は苦手な食材が使われているため、 3 を出力する。
- 5 日目: 食材 4 を克服する。このとき、料理 2 は苦手な食材が使われなくなるため食べられるようになる。全ての料理に苦手な食材が使われていないため、 4 を出力する。
入力例 2
9 8 1 4 5 6 9 7 4 3 4 2 4 1 3 1 1 5 7 9 8 1 5 2 9 8 1 2 1 1 6 5 2 7 8 4 1 9 3
出力例 2
0 0 1 1 1 2 4 6 8
Score : 300 points
Problem Statement
The AtCoder Restaurant uses N types of ingredients numbered from 1 to N.
The restaurant offers M dishes numbered from 1 to M. Dish i uses K_i types of ingredients, namely A_{i,1}, A_{i,2}, \ldots, A_{i,K_i}.
Snuke currently dislikes all N ingredients. He cannot eat any dish that uses one or more ingredients he dislikes, and he can eat a dish that uses none of the disliked ingredients.
Over the next N days, he will overcome his dislikes one ingredient per day. On day i, he overcomes ingredient B_i, and from then on he no longer dislikes it.
For each i=1,2,\ldots,N, find:
- the number of dishes at the AtCoder Restaurant that he can eat immediately after overcoming ingredient B_i on day i.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 3 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq M \leq 3 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq K_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq M)
- The sum of K_i is at most 3 \times 10^{5}.
- 1 \leq A_{i,j} \leq N (1 \leq i \leq M, 1 \leq j \leq K_i)
- A_{i,j} \neq A_{i,k} (1 \leq i \leq M, j \neq k)
- 1 \leq B_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq N)
- B_i \neq B_j (i \neq j )
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M
K_1 A_{1,1} A_{1,2} \ldots A_{1,K_1}
K_2 A_{2,1} A_{2,2} \ldots A_{2,K_2}
\vdots
K_M A_{M,1} A_{M,2} \ldots A_{M,K_M}
B_1 B_2 \ldots B_N
Output
Print N lines. The k-th line should contain the answer for i=k.
Sample Input 1
5 4 2 1 2 3 3 4 5 3 1 2 5 1 3 1 3 2 5 4
Sample Output 1
0 1 2 3 4
Snuke overcomes his disliked ingredients as follows:
- Day 1: He overcomes ingredient 1. At this time, every dish still uses a disliked ingredient, so print 0.
- Day 2: He overcomes ingredient 3. Dish 4 no longer uses any disliked ingredient and becomes edible; all other dishes still use disliked ingredients, so print 1.
- Day 3: He overcomes ingredient 2. Dish 1 no longer uses any disliked ingredient and becomes edible; all dishes except 1 and 4 still use disliked ingredients, so print 2.
- Day 4: He overcomes ingredient 5. Dish 3 no longer uses any disliked ingredient and becomes edible; all dishes except 1, 3, and 4 still use disliked ingredients, so print 3.
- Day 5: He overcomes ingredient 4. Dish 2 no longer uses any disliked ingredient and becomes edible; now all dishes have no disliked ingredients, so print 4.
Sample Input 2
9 8 1 4 5 6 9 7 4 3 4 2 4 1 3 1 1 5 7 9 8 1 5 2 9 8 1 2 1 1 6 5 2 7 8 4 1 9 3
Sample Output 2
0 0 1 1 1 2 4 6 8
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 400 点
問題文
円周上に N 個の点が等間隔に並んでおり、時計回りに 1,2,\ldots,N と番号がつけられています。
M 本の相異なる直線があり、i 本目の直線は異なる 2 つの点、点 A_i と点 B_i を通る直線です。(1 \leq i \leq M)
以下の 2 つの条件をともに満たすような整数の組 (i,j) の個数を求めてください。
- 1 \leq i < j \leq M
- i 本目の直線と j 本目の直線は交わる
制約
- 2 \leq N \leq 10^6
- 1 \leq M \leq 3 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq A_i < B_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq M)
- (A_i,B_i) \neq (A_j,B_j) (i \neq j)
- 入力は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M A_1 B_1 A_2 B_2 \vdots A_M B_M
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
8 3 1 5 1 8 2 4
出力例 1
2
次の図のように円周上に 8 個の点と 3 本の直線があります。
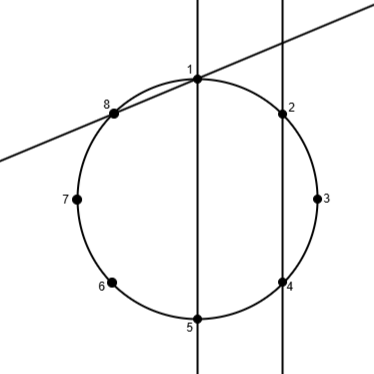
1 本目の直線と 2 本目の直線は交わります。1 本目の直線と 3 本目の直線は交わりません。2 本目の直線と 3 本目の直線は交わります。(i,j)=(1,2),(2,3) の 2 つの組が条件を満たすため、2 を出力します。
入力例 2
5 10 2 5 1 5 1 2 2 4 2 3 1 3 1 4 3 5 3 4 4 5
出力例 2
40
Score : 400 points
Problem Statement
There are N equally spaced points on a circle labeled clockwise as 1,2,\ldots,N.
There are M distinct lines, where the i-th line passes through two distinct points A_i and B_i (1 \leq i \leq M).
Find the number of pairs (i,j) satisfying:
- 1 \le i < j \le M, and
- the i-th and j-th lines intersect.
Constraints
- 2 \leq N \leq 10^6
- 1 \leq M \leq 3 \times 10^{5}
- 1 \leq A_i < B_i \leq N (1 \leq i \leq M)
- (A_i,B_i) \neq (A_j,B_j) (i \neq j)
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M A_1 B_1 A_2 B_2 \vdots A_M B_M
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
8 3 1 5 1 8 2 4
Sample Output 1
2
As shown in the diagram below, there are eight points and three lines on the circle.

The 1st and 2nd lines intersect. The 1st and 3rd lines do not intersect. The 2nd and 3rd lines intersect. Since the pairs (i,j)=(1,2),(2,3) satisfy the conditions, print 2.
Sample Input 2
5 10 2 5 1 5 1 2 2 4 2 3 1 3 1 4 3 5 3 4 4 5
Sample Output 2
40
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 450 点
問題文
時は 30XX 年、あるコンテストでは提出を行うたびにお金が必要になりました。
このコンテストには N 問の問題が出題されます。 i 問目の得点は S_i 点であり、 1 回提出を行うために C_i 円が必要です。
高橋君は i 問目に提出すると P_i % の確率でその問題に正解することができます。各提出で正解できるかどうかはそれまでの提出とは独立に決まります。
高橋君の所持金は X 円です。提出のために払った金額の総額が X 円を超えるような提出はできません。
高橋君がコンテストで正解した問題の得点の総和の期待値が最大になるように提出を行った際の総得点の期待値を求めてください。
ただし、高橋君は提出の結果を見てから次にどの問題に提出するかを決めることができるものとします。また、同じ問題に 2 回以上正解しても得点は 1 回正解した場合と変わらないとします。
制約
- 1\le N\le 8
- 1\le S_i\le 2718
- 1\le C_i\le X\le 5000
- 1\le P_i\le 100
- 入力される値は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N X S_1 C_1 P_1 S_2 C_2 P_2 \vdots S_N C_N P_N
出力
答えを出力せよ。真の値と出力との絶対誤差または相対誤差が 10^{-6} 以下のとき、正解と判定される。
入力例 1
3 2 100 1 50 200 1 20 1000 1 1
出力例 1
95
以下のような提出方法を考えます。
- まず 1 問目に提出する。
- 上の提出が正解なら 2 問目に、そうでないなら再び 1 問目に提出する。
この場合の得点の期待値は 95 点です。得点の期待値を 95 点より大きくすることはできないので、 95 を出力してください。
入力例 2
2 7 100 3 50 100 2 50
出力例 2
125
入力例 3
5 32 500 9 57 300 4 8 300 3 32 300 7 99 100 8 69
出力例 3
953.976967020096
入力例 4
7 78 100 1 100 200 2 90 300 3 80 400 4 60 450 5 50 525 6 30 650 7 1
出力例 4
1976.2441416041121021
Score : 450 points
Problem Statement
In the year 30XX, each submission to a certain contest requires a payment.
The contest has N problems. Problem i has S_i points, and each submission costs C_i yen.
When Takahashi submits to the i-th problem, he solves it with probability P_i %. Each submission’s outcome is independent of the others.
He has X yen. He cannot make any submission that would cause his total spending to exceed X yen.
Find the expected value of the total score of the problems he solves when he chooses submissions to maximize this value.
He may decide which problem to submit to next after seeing the result of the previous submission, and solving the same problem more than once awards the same score as solving it once.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 8
- 1 \leq S_i \leq 2718
- 1 \leq C_i \leq X \leq 5000
- 1 \leq P_i \leq 100
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N X S_1 C_1 P_1 S_2 C_2 P_2 \vdots S_N C_N P_N
Output
Print the answer. Your output is considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10^{-6}.
Sample Input 1
3 2 100 1 50 200 1 20 1000 1 1
Sample Output 1
95
Consider the following submission strategy:
- First, submit to the 1st problem.
- If that submission is correct, submit to the 2nd problem; otherwise, submit again to the 1st problem.
The expected total score for this strategy is 95 points. No strategy can exceed an expected score of 95, so print 95.
Sample Input 2
2 7 100 3 50 100 2 50
Sample Output 2
125
Sample Input 3
5 32 500 9 57 300 4 8 300 3 32 300 7 99 100 8 69
Sample Output 3
953.976967020096
Sample Input 4
7 78 100 1 100 200 2 90 300 3 80 400 4 60 450 5 50 525 6 30 650 7 1
Sample Output 4
1976.2441416041121021
Time Limit: 2 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 525 点
問題文
N 行 N 列のグリッドがあります。上から i 行目、左から j 列目のマスをマス (i,j) と表します。各マスには 1 から 9 までの数字が書かれており、マス (i,j) には数字 A_{i,j} が書かれています。
はじめ、コマがマス (1,1) にあります。また、 S を空文字列とし、以下の操作を 2N-1 回繰り返します:
- S の末尾に現在コマが存在するマスに書かれた数字を連結する。
- コマを現在のマスの下か右に 1 マス移動する。ただし、 2N-1 回目の操作では移動させない。
2N-1 回の操作の後、コマはマス (N,N) に存在し、 S の長さは 2N-1 となります。
最終的な文字列 S を整数としてみた値を M で割ったあまりがスコアとなります。
達成可能なスコアの最大値を求めてください。
制約
- 1\le N\le 20
- 2\le M\le 10^9
- 1\le A_{i,j}\le 9
- 入力される値は全て整数である
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
N M
A_{1,1} A_{1,2} \ldots A_{1,N}
A_{2,1} A_{2,2} \ldots A_{2,N}
\vdots
A_{N,1} A_{N,2} \ldots A_{N,N}
出力
答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
2 7 1 2 3 1
出力例 1
5
コマの動かし方は以下の 2 通りがあります:
- コマを (1,1),(1,2),(2,2) と順に動かしていく。S=
121となり、この場合のスコアは 121 を 7 で割った 2 である。 - コマを (1,1),(2,1),(2,2) と順に動かしていく。S=
131となり、この場合のスコアは 131 を 7 で割った 5 である。
スコアの最大値は 5 なので、 5 を出力してください。
入力例 2
3 100000 1 2 3 3 5 8 7 1 2
出力例 2
13712
入力例 3
5 402 8 1 3 8 9 8 2 4 1 8 4 1 8 5 9 6 2 1 6 7 6 6 7 7 6
出力例 3
384
Score : 525 points
Problem Statement
There is an N\times N grid. Let cell (i,j) denote the cell in the i-th row from the top and j-th column from the left. Each cell contains a digit from 1 to 9; cell (i,j) contains A_{i,j}.
Initially, a token is on cell (1,1). Let S be an empty string. Repeat the following operation 2N-1 times:
- Append to the end of S the digit in the current cell.
- Move the token one cell down or one cell to the right. However, do not move it in the (2N-1)-th operation.
After 2N-1 operations, the token is on cell (N,N) and the length of S is 2N-1.
Interpret S as an integer. The score is the remainder when this integer is divided by M.
Find the maximum achievable score.
Constraints
- 1 \leq N \leq 20
- 2 \leq M \leq 10^9
- 1 \leq A_{i,j} \leq 9
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
N M
A_{1,1} A_{1,2} \ldots A_{1,N}
A_{2,1} A_{2,2} \ldots A_{2,N}
\vdots
A_{N,1} A_{N,2} \ldots A_{N,N}
Output
Print the answer.
Sample Input 1
2 7 1 2 3 1
Sample Output 1
5
There are two ways to move the token:
- Move through (1,1),(1,2),(2,2). Then S=
121, and the score is the remainder when 121 is divided by 7, which is 2. - Move through (1,1),(2,1),(2,2). Then S=
131, and the score is the remainder when 131 is divided by 7, which is 5.
The maximum score is 5, so print 5.
Sample Input 2
3 100000 1 2 3 3 5 8 7 1 2
Sample Output 2
13712
Sample Input 3
5 402 8 1 3 8 9 8 2 4 1 8 4 1 8 5 9 6 2 1 6 7 6 6 7 7 6
Sample Output 3
384
Time Limit: 5 sec / Memory Limit: 1024 MiB
配点 : 650 点
問題文
整数 N,M,A,B_1,B_2 が与えられます。
\displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{N-1}\left\lbrace (Ak+B_1)\ \text{mod}\ M \right\rbrace\left\lbrace (Ak+B_2)\ \text{mod}\ M \right\rbrace を求めてください。
T 個のテストケースが与えられるので、それぞれについて答えを求めてください。
制約
- 1\le T\le 10^5
- 1\le N\le 10^6
- 1\le M\le 10^6
- 0\le A,B_1,B_2 < M
- 入力される値は全て整数
入力
入力は以下の形式で標準入力から与えられる。
T
\text{case}_1
\text{case}_2
\vdots
\text{case}_T
ただし、 \text{case}_i は i 個目のテストケースを表す。
各テストケースは以下の形式で与えられる。
N M A B_1 B_2
出力
T 行出力せよ。 i 行目には i 番目のテストケースの答えを出力せよ。
入力例 1
5 4 7 2 1 4 12 15 2 8 7 777 1 0 0 0 100 101 0 100 100 402 402 4 19 256
出力例 1
27 866 0 1000000 13728568
1 番目のテストケースについて考えます。
- k=0 のとき: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=1,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=4 です。
- k=1 のとき: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=3,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=6 です。
- k=2 のとき: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=5,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=1 です。
- k=3 のとき: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=0,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=3 です。
よって、求める値は 1\times 4+3\times 6+5\times 1+0\times 3=27 です。したがって、 1 行目には 27 を出力してください。
Score : 650 points
Problem Statement
You are given integers N,M,A,B_1,B_2.
Find \displaystyle\sum_{k=0}^{N-1}\left\lbrace (Ak+B_1)\ \text{mod}\ M \right\rbrace\left\lbrace (Ak+B_2)\ \text{mod}\ M \right\rbrace.
There are T test cases; solve each one.
Constraints
- 1\le T\le 10^5
- 1\le N\le 10^6
- 1\le M\le 10^6
- 0\le A,B_1,B_2 < M
- All input values are integers.
Input
The input is given from Standard Input in the following format:
T
\text{case}_1
\text{case}_2
\vdots
\text{case}_T
Here, \text{case}_i denotes the i-th test case.
Each test case is given in the following format:
N M A B_1 B_2
Output
Print T lines. The i-th line should contain the answer for the i-th test case.
Sample Input 1
5 4 7 2 1 4 12 15 2 8 7 777 1 0 0 0 100 101 0 100 100 402 402 4 19 256
Sample Output 1
27 866 0 1000000 13728568
Consider the first test case.
- When k=0: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=1,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=4.
- When k=1: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=3,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=6.
- When k=2: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=5,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=1.
- When k=3: \left\lbrace (2k+1)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=0,\ \left\lbrace (2k+4)\ \text{mod}\ 7 \right\rbrace=3.
Hence, the required value is 1\times 4+3\times 6+5\times 1+0\times 3=27. Thus, print 27 on the first line.